文章目录
一、PV和PVC的引入
Volume 提供了非常好的数据持久化方案,不过在可管理性上还有不足。
拿前面 AWS EBS 的例子来说,要使用 Volume,Pod 必须事先知道如下信息:
- 当前 Volume 来自 AWS EBS。
- EBS Volume 已经提前创建,并且知道确切的 volume-id。
Pod 通常是由应用的开发人员维护,而 Volume 则通常是由存储系统的管理员维护。开发人员要获得上面的信息:
- 要么询问管理员。
- 要么自己就是管理员。
这样就带来一个管理上的问题:应用开发人员和系统管理员的职责耦合在一起了。如果系统规模较小或者对于开发环境这样的情况还可以接受。但当集群规模变大,特别是对于生成环境,考虑到效率和安全性,这就成了必须要解决的问题。
Kubernetes 给出的解决方案是 PersistentVolume (PV)和 PersistentVolumeClaim(PVC)。
PersistentVolume (PV) 是外部存储系统中的一块存储空间,由管理员创建和维护。与 Volume 一样,PV 具有持久性,生命周期独立于 Pod。
PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC) 是对 PV 的申请 (Claim)。PVC 通常由普通用户创建和维护。需要为 Pod 分配存储资源时,用户可以创建一个 PVC,指明存储资源的容量大小和访问模式(比如只读)等信息,Kubernetes 会查找并提供满足条件的 PV。
有了 PersistentVolumeClaim,用户只需要告诉 Kubernetes 需要什么样的存储资源,而不必关心真正的空间从哪里分配,如何访问等底层细节信息。这些 Storage Provider 的底层信息交给管理员来处理,只有管理员才应该关心创建 PersistentVolume 的细节信息。
二、通过NFS实现持久化存储
1、配置nfs
需要安装
k8s-master:nfs-server
k8s-node1:nfs-client
k8s-node2:nfs-client
所有节点安装nfs
yum install -y nfs-common nfs-utils
在master节点创建共享目录
[root@k8s-master k8s]# mkdir /nfsdata
授权共享目录
[root@k8s-master k8s]# chmod 666 /nfsdata
编辑exports文件
[root@k8s-master k8s]# cat /etc/exports
/nfsdata *(rw,no_root_squash,no_all_squash,sync)
配置生效
启动rpc和nfs(注意顺序)
[root@k8s-master k8s]# systemctl start rpcbind
[root@k8s-master k8s]# systemctl start nfs
作为准备工作,我们已经在 k8s-master 节点上搭建了一个 NFS 服务器,目录为 /nfsdata:
2、创建PV
下面创建一个 PV mypv1,配置文件 nfs-pv1.yml 如下:
[root@k8s-master ~]# vim nfs-pv1.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: mypv1
spec:
capacity:
storage: 1Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Recycle
storageClassName: nfs
nfs:
path: /nfsdata
server: 192.168.153.148 #指定nfs目录所在的机器的地址
① capacity 指定 PV 的容量为 1G。
② accessModes 指定访问模式为 ReadWriteOnce,支持的访问模式有:
- ReadWriteOnce:PV 能以 read-write 模式 mount 到单个节点。
- ReadOnlyMany:PV 能以 read-only 模式 mount 到多个节点。
- ReadWriteMany :PV 能以 read-write 模式 mount 到多个节点。
③ persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy 指定当 PV 的回收策略为 Recycle,支持的策略有:
- Retain: 需要管理员手工回收。
- Recycle:清除 PV 中的数据,效果相当于执行
rm -rf /thevolume/*。 - Delete: 删除 Storage Provider 上的对应存储资源,例如 AWS EBS、GCE PD、Azure Disk、- OpenStack Cinder Volume 等。
④ storageClassName 指定 PV 的 class 为 nfs。相当于为 PV 设置了一个分类,PVC 可以指定 class 申请相应 class 的 PV。
⑤ 指定 PV 在 NFS 服务器上对应的目录。
创建 mypv1:
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f nfs-pv1.yml

STATUS为Available,表示mypv1就绪,可以被 PVC 申请。
3、创建PVC
接下来创建 PVC mypvc1,配置文件 nfs-pvc1.yml 如下:
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat nfs-pvc1.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: mypvc1
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: nfs
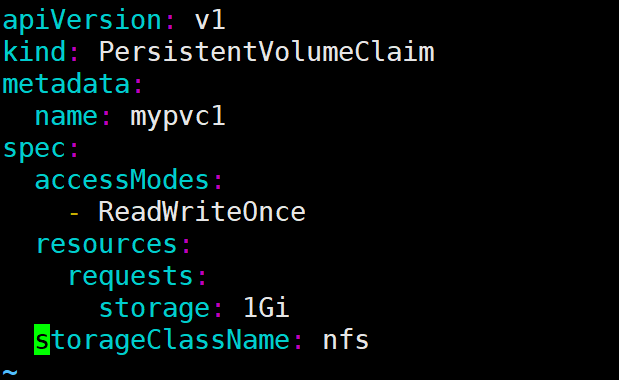
PVC 就很简单了,只需要指定 PV 的容量,访问模式和 class。
执行命令创建 mypvc1:
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f nfs-pvc1.yml
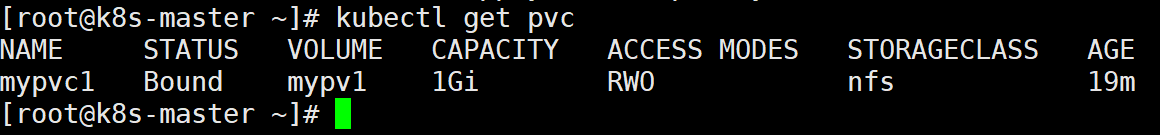
从 kubectl get pvc 和 kubectl get pv 的输出可以看到 mypvc1 已经 Bound 到 mypv1,申请成功。
4、创建pod
上面已经创建好了pv和pvc,pod中直接使用这个pvc即可
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat pod1.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mypod1
spec:
containers:
- name: mypod1
image: busybox
args:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- sleep 30000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/mydata"
name: mydata
volumes:
- name: mydata
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mypvc1
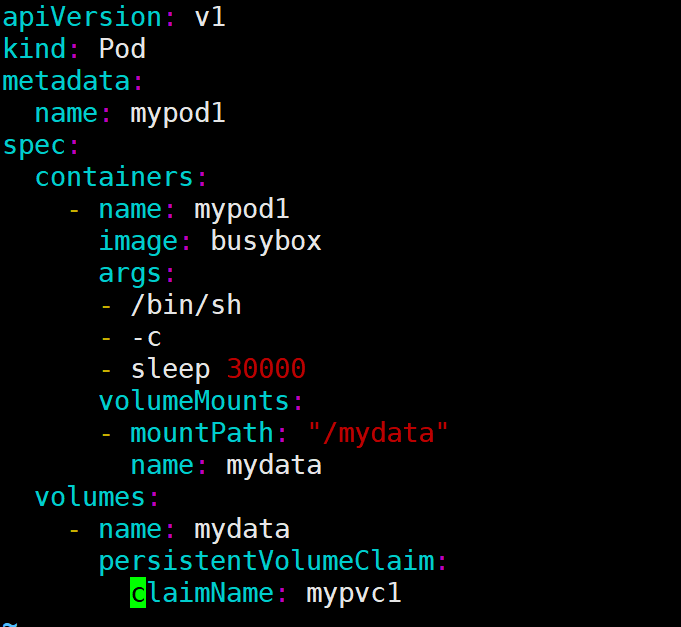
与使用普通 Volume 的格式类似,在 volumes 中通过 persistentVolumeClaim 指定使用 mypvc1 申请的 Volume。
通过命令创建mypod1:
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f pod1.yml
5、验证
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl exec -it mypod1 /bin/sh
/ # ls mydata/
/ # echo "youngfit" > mydata/hello.txt
/ # ls mydata/
hello.txt
/ # exit
[root@k8s-master ~]# ls /nfsdata/ #也可在nfs的共享目录中查看到,说明卷共享成功
hello.txt
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat /nfsdata/hello.txt
youngfit
可见,在 Pod 中创建的文件 /mydata/hello.txt 确实已经保存到了 NFS 服务器目录 /nfsdata中。
如果不再需要使用 PV,可用删除 PVC 回收 PV。
在这里,可以尝试在任何一方删除文件,文件在两端都会消失;
三、PV的回收
当 PV 不再需要时,可通过删除 PVC 回收。未删除pvc之前 pv的状态是Bound

删除pod
[root@k8s-master pvc]# kubectl delete pod mypod1
删除pvc
[root@k8s-master pvc]# kubectl delete pvc mypvc1
再次查看pv的状态
[root@k8s-master pvc]# kubectl get pv
删除pvc之后pv的状态变为Available,,此时解除绑定后则可以被新的 PVC 申请。
/nfsdata文件中的文件被删除了

因为 PV 的回收策略设置为 Recycle,所以数据会被清除,

但这可能不是我们想要的结果。如果我们希望保留数据,可以将策略设置为 Retain
[root@k8s-master pvc]# vim nfs-pv1.yml
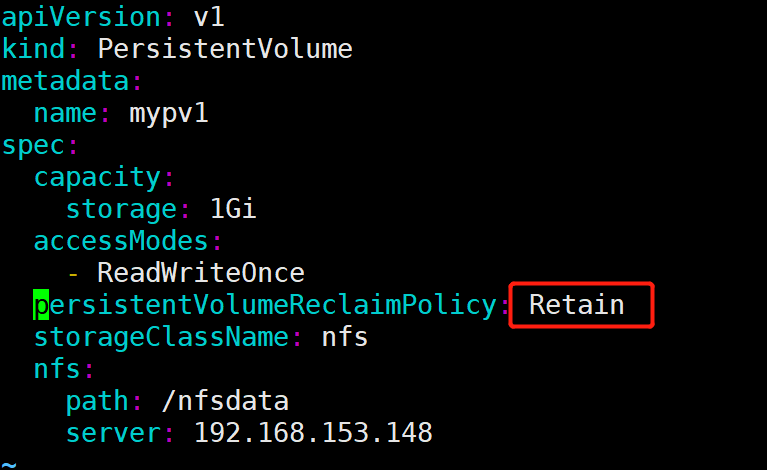
[root@k8s-master pvc]# kubectl apply -f nfs-pv1.yml

回收策略已经变为 Retain,通过下面步骤验证其效果:
重新创建mypvc1
[root@k8s-master pvc]# kubectl apply -f nfs-pvc1.yml
重新创建pod,引用mypvc1
[root@k8s-master pvc]# kubectl apply -f pod1.yml
进入pod中,创建文件
[root@k8s-master pvc]# kubectl exec -it mypod1 /bin/sh
/ # echo 'youngfit' > mydata/hello.txt
/ # ls mydata/
hello.txt
/ # exit
在nfs目录下检验
[root@k8s-master pvc]# ls /nfsdata/
hello.txt
[root@k8s-master pvc]# cat /nfsdata/hello.txt
youngfit
删除pod
[root@k8s-master pvc]# kubectl delete -f pod1.yml
pod "mypod1" deleted
[root@k8s-master pvc]# ls /nfsdata/
hello.txt
删除pvc(mypvc1)
[root@k8s-master pvc]# kubectl delete pvc mypvc1
persistentvolumeclaim "mypvc1" deleted
[root@k8s-master pvc]# ls /nfsdata/
hello.txt
[root@k8s-master pvc]# cat /nfsdata/hello.txt
youngfit
发现数据仍然保留
虽然 mypv1 中的数据得到了保留,但其 PV 状态会一直处于 Released,不能被其他 PVC 申请。为了重新使用存储资源,可以删除并重新创建 mypv1。删除操作只是删除了 PV 对象,存储空间中的数据并不会被删除。
[root@k8s-master pvc]# ls /nfsdata/
hello.txt
[root@k8s-master pvc]# kubectl delete pv mypv1
persistentvolume "mypv1" deleted
[root@k8s-master pvc]# ls /nfsdata/
hello.txt
[root@k8s-master pvc]# kubectl apply -f nfs-pv1.yml
persistentvolume/mypv1 created
[root@k8s-master pvc]# kubectl get pod
No resources found in default namespace.
[root@k8s-master pvc]# kubectl get pv

新建的 mypv1 状态为 Available,已经可以被 PVC 申请。
PV 还支持 Delete 的回收策略,会删除 PV 在 Storage Provider 上对应存储空间。NFS 的 PV 不支持 Delete,支持 Delete 的 Provider 有 AWS EBS、GCE PD、Azure Disk、OpenStack Cinder Volume 等。
四、PV/PVC的静态供给
所有节点下载nfs
yum install -y nfs-common nfs-utils
master节点作为nfs服务端
[root@k8s-master k8s]# cat /etc/exports
/data/opv *(rw,no_root_squash,no_all_squash,sync)
[root@k8s-master k8s]#chmod 777 -R /data/opv
[root@k8s-master k8s]#systemctl restart nfs
master节点操作
#1.定义pv
[root@k8s-master pvc2]# cat pv-pod.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: my-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 5Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
nfs:
path: /data/opv #nfs服务端共享的目录
server: 192.168.153.148 #nfs服务器的地址
[root@k8s-master pvc2]# kubectl apply -f pv-pod.yaml
#2.定义pvc和deployment
[root@k8s-master pvc2]# cat pvc-pod.yaml
[root@k8s-master pvc2]# kubectl apply -f pvc-pod.yaml
#3,暴露一下端口
[root@k8s-master pvc2]# cat pv-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: pv-svc
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 8080
nodePort: 30001
targetPort: 80
selector: #选择器
app: nginx
#4.nfs服务器操作
[root@k8s-master pvc2]# echo youngfit >> /data/opv/index.html
#5.访问,看效果

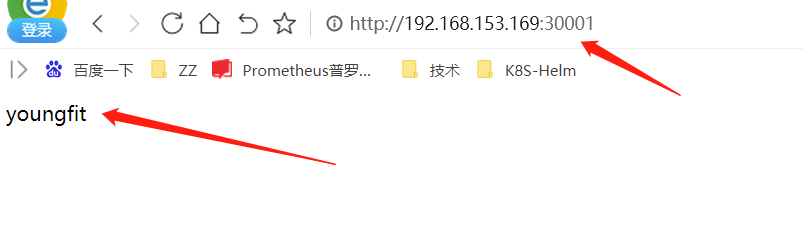
五、PV的动态供给
前面的例子中,我们提前创建了 PV,然后通过 PVC 申请 PV 并在 Pod 中使用,这种方式叫做静态供给(Static Provision)。
与之对应的是动态供给(Dynamical Provision),即如果没有满足 PVC 条件的 PV,会动态创建 PV。相比静态供给,动态供给有明显的优势:不需要提前创建 PV,减少了管理员的工作量,效率高。
动态供给是通过 StorageClass 实现的,StorageClass 定义了如何创建 PV,下面是两个例子。
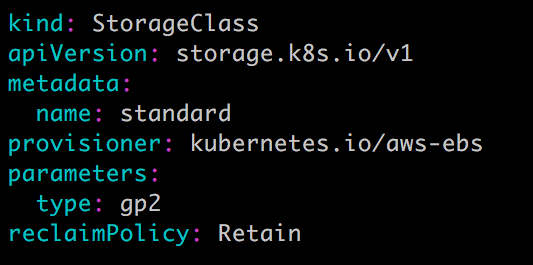
StorageClass standard
StorageClass slow:
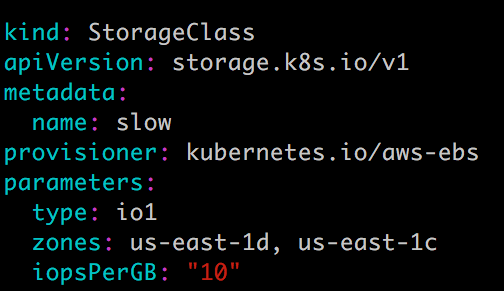
这两个 StorageClass 都会动态创建 AWS EBS,不同在于 standard 创建的是 gp2 类型的 EBS,而 slow 创建的是 io1 类型的 EBS。不同类型的 EBS 支持的参数可参考 AWS 官方文档。
StorageClass 支持 Delete 和 Retain 两种 reclaimPolicy,默认是 Delete。
与之前一样,PVC 在申请 PV 时,只需要指定 StorageClass 和容量以及访问模式,比如:
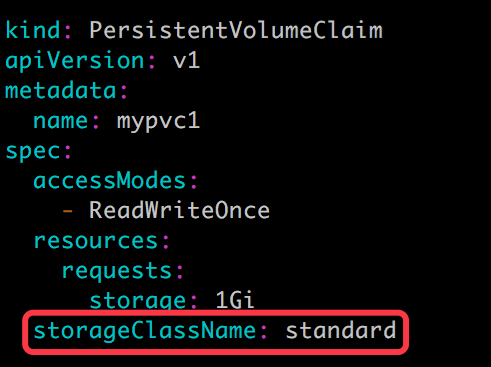
除了 AWS EBS,Kubernetes 支持其他多种动态供给 PV 的 Provisioner,完整列表请参考 https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/storage-classes/#provisioner
六、PV&&PVC在应用中的持久化存储
[root@k8s-master pv]# kubectl delete -f pod1.yml
[root@k8s-master pv]# cat pod1.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mydep
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: busy
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: busy
spec:
containers:
- name: mypod1
image: busybox
args:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- sleep 30000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/mydata"
name: mydata
volumes:
- name: mydata
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mypvc1
[root@k8s-master pv]# kubectl apply -f pod1.yml
[root@k8s-master pv]# kubectl exec -it mydep-6b4f9c68b9-mqtcl /bin/sh
/ # echo youngfit > mydata/qf.txt
/ # exit
查看pod运行在了哪个节点,将节点关闭。发现另外一个节点,会接手,而且数据仍然存在
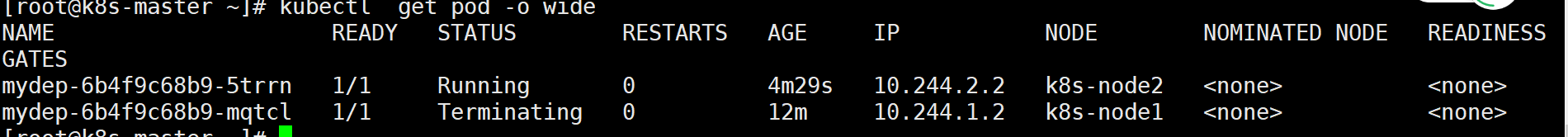

七、PV&&PVC在应用在mysql的持久化存储实战项目
下面演示如何为 MySQL 数据库提供持久化存储,步骤为:
- 创建 PV 和 PVC。
- 部署 MySQL。
- 向 MySQL 添加数据。
- 模拟节点宕机故障,Kubernetes 将 MySQL 自动迁移到其他节点。
- 验证数据一致性。
首先创建 PV 和 PVC,配置如下:
mysql-pv.yml
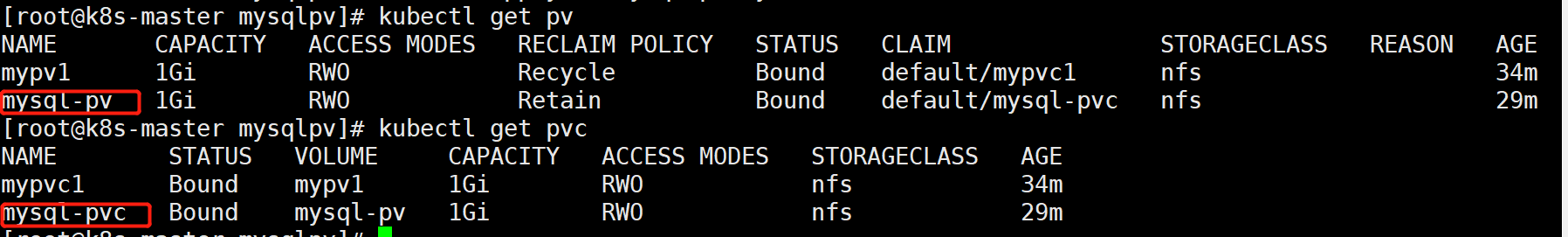
[root@k8s-master mysqlpv]# cat mysql-pv.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: mysql-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 1Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
storageClassName: nfs
nfs:
path: /nfsdata/mysql-pv
server: 192.168.153.148
[root@k8s-master mysqlpv]# kubectl apply -f mysqlpod.yml
mysql-pvc.yml
[root@k8s-master mysqlpv]# cat mysql-pvc.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: mysql-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: nfs
[root@k8s-master mysqlpv]# kubectl apply -f mysql-pvc.yml
接下来部署 MySQL,配置文件如下:
[root@k8s-master mysqlpv]# cat mysqlpod.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mysql
spec:
ports:
- port: 3306
selector:
app: mysql
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mysql
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mysql
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mysql
spec:
containers:
- image: daocloud.io/library/mysql:5.7.5-m15 #这里的镜像一定要选对,能确保拉取到,而且能使用变量
name: mysql
env:
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: password
ports:
- containerPort: 3306
name: mysql
volumeMounts:
- name: mysql-persistent-storage
mountPath: /var/lib/mysql
volumes:
- name: mysql-persistent-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mysql-pvc
[root@k8s-master mysqlpv]# kubectl apply -f mysqlpod.yml
PVC mysql-pvc Bound 的 PV mysql-pv 将被 mount 到 MySQL 的数据目录 var/lib/mysql。
MySQL 被部署到 k8s-node1
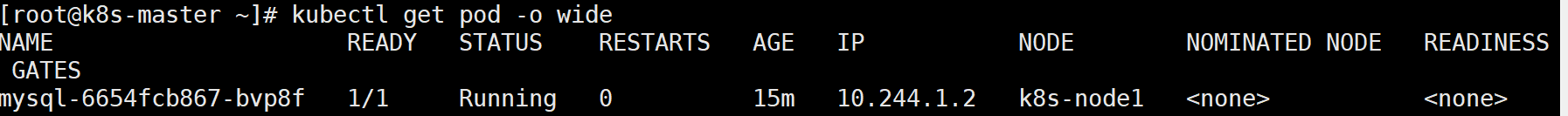
① 切换到数据库 mysql。
② 创建数据库表 my_id。
③ 插入一条数据。
④ 确认数据已经写入。
关闭 k8s-node1,模拟节点宕机故障。
[root@k8s-master mysqlpv]# kubectl exec -it mysql-6654fcb867-mqtcl /bin/bash
root@mysql-6654fcb867-mqtcl:/# mysql -uroot -p'password'
mysql> create database feige;
mysql> create table feige.t1(id int);
mysql> insert into feige.t1(2);
[root@k8s-node1 ~]# poweroff
验证数据的一致性:
由于node1节点已经宕机,node2节点接管了这个任务,pod转移,需要等待一段时间,我这里等待了5分钟左右。。
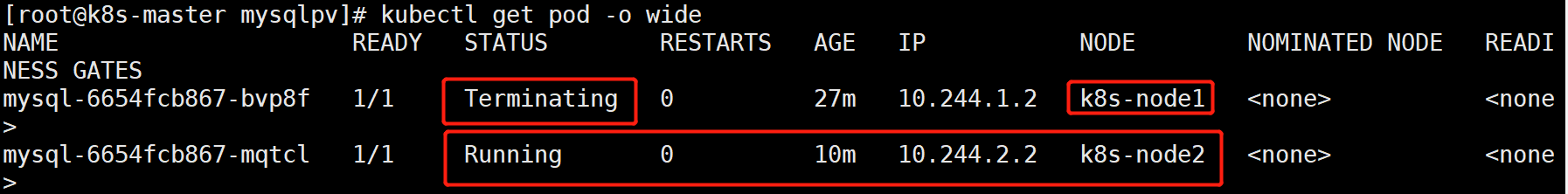
进入新的pod中,数据仍然存在,持久化成功。很安全
[root@k8s-master mysqlpv]# kubectl exec -it mysql-6654fcb867-mqtcl /bin/bash
root@mysql-6654fcb867-mqtcl:/# mysql -uroot -p'password'
mysql> select * from feige.t1;
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 1 |
| 2 |
+------+
2 rows in set (0.01 sec)
MySQL 服务恢复,数据也完好无损。
八、PV/PVC动态供给项目实战
提前说明:由于本地动态实战,我在v1.22.2版本中,尝试多次未成功,采用了v1.19.0版本的k8s集群;

Dynamic Provisioning机制工作的核心在于StorageClass的API对象。
StorageClass声明存储插件,用于自动创建PV
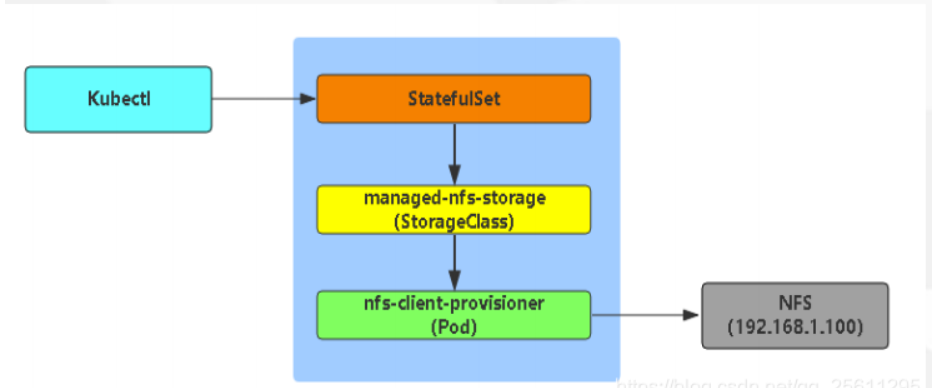
当我们k8s业务上来的时候,大量的pvc,此时我们人工创建匹配的话,工作量就会非常大了,需要动态的自动挂载相应的存储,‘我们需要使用到StorageClass,来对接存储,靠他来自动关联pvc,并创建pv。
Kubernetes支持动态供给的存储插件:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/storage-classes/
因为NFS不支持动态存储,所以我们需要借用这个存储插件。
nfs动态相关部署可以参考:
https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/external-storage/tree/master/nfs-client/deploy
部署步骤:
1、部署nfs
3个节点都下载:
# yum -y install nfs-utils rpcbind
主节点配置nfs服务端
[root@master pvc-test]# mkdir /opt/container_data
[root@master pvc-test]# chmod 777 -R /opt/container_data
[root@master pvc-test]# cat /etc/exports
/opt/container_data *(rw,no_root_squash,no_all_squash,sync)
[root@master pvc-test]# systemctl start rpcbind
[root@master pvc-test]# systemctl start nfs
2、定义一个storage
[root@master pvc-test]# cat storageclass-nfs.yaml
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: managed-nfs-storage
provisioner: fuseim.pri/ifs
3、部署授权
因为storage自动创建pv需要经过kube-apiserver,所以要进行授权
-
创建1个sa
-
创建1个clusterrole,并赋予应该具有的权限,比如对于一些基本api资源的增删改查;
-
创建1个clusterrolebinding,将sa和clusterrole绑定到一起;这样sa就有权限了;
-
然后pod中再使用这个sa,那么pod再创建的时候,会用到sa,sa具有创建pv的权限,便可以自动创建pv;
[root@master pvc-test]# cat rbac.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumeclaims"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["storageclasses"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: run-nfs-client-provisioner
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
4、部署一个自动创建pv的服务
这里自动创建pv的服务由nfs-client-provisioner 完成
[root@master pvc-test]# cat deployment-nfs.yaml
kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
# imagePullSecrets:
# - name: registry-pull-secret
serviceAccount: nfs-client-provisioner
containers:
- name: nfs-client-provisioner
#image: quay.io/external_storage/nfs-client-provisioner:latest
image: lizhenliang/nfs-client-provisioner:v2.0.0
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-client-root
mountPath: /persistentvolumes
env:
- name: PROVISIONER_NAME
#这个值是定义storage里面的那个值
value: fuseim.pri/ifs
- name: NFS_SERVER
value: 172.17.0.21
- name: NFS_PATH
value: /opt/container_data
volumes:
- name: nfs-client-root
nfs:
server: 172.17.0.21
path: /opt/container_data
创建:
[root@master pvc-test]# kubectl apply -f storageclass-nfs.yaml
[root@master pvc-test]# kubectl apply -f rbac.yaml
[root@master pvc-test]# kubectl apply -f deployment-nfs.yaml
查看创建好的storage:
[root@master storage]# kubectl get sc
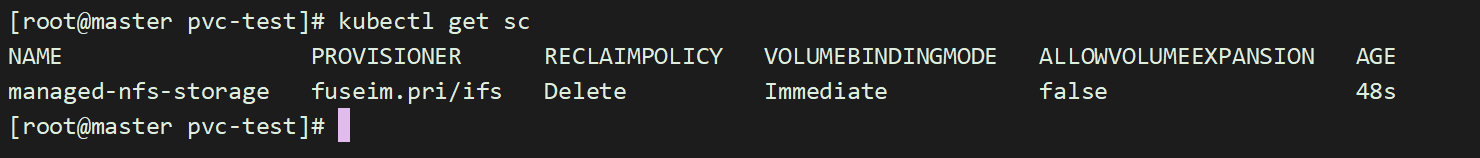
nfs-client-provisioner 会以pod运行在k8s中,
[root@master storage]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nfs-client-provisioner-855887f688-hrdwj 1/1 Running 0 77s
5、部署有状态服务,测试自动创建pv
部署yaml文件参考:https://kubernetes.io/docs/tutorials/stateful-application/basic-stateful-set/
我们部署一个nginx服务,让其html下面自动挂载数据卷,
[root@master pvc-test]# cat nginx.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
name: web
clusterIP: None
selector:
app: nginx
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: web
spec:
serviceName: "nginx"
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: web
volumeMounts:
- name: www
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: www
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
storageClassName: "managed-nfs-storage"
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
[root@master pvc-test]# kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml
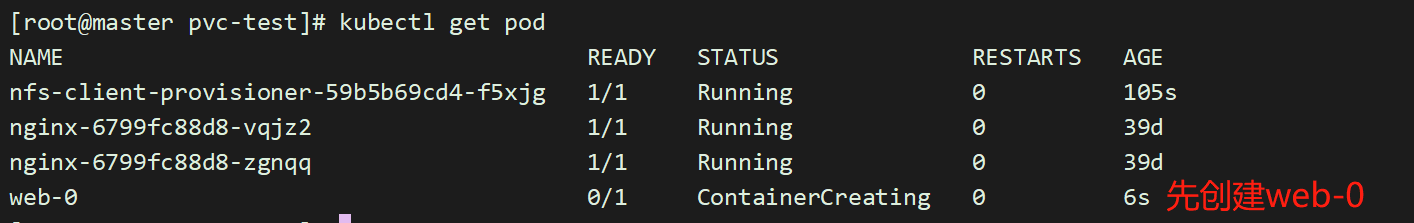
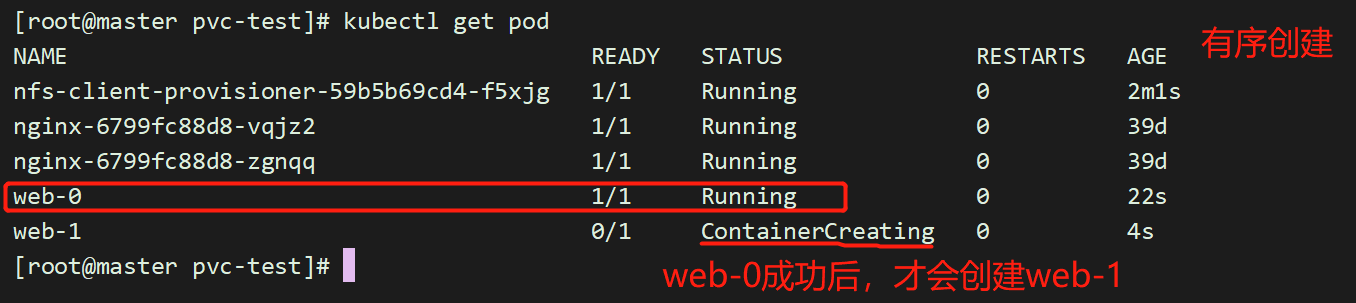
进入其中一个容器,创建一个文件:
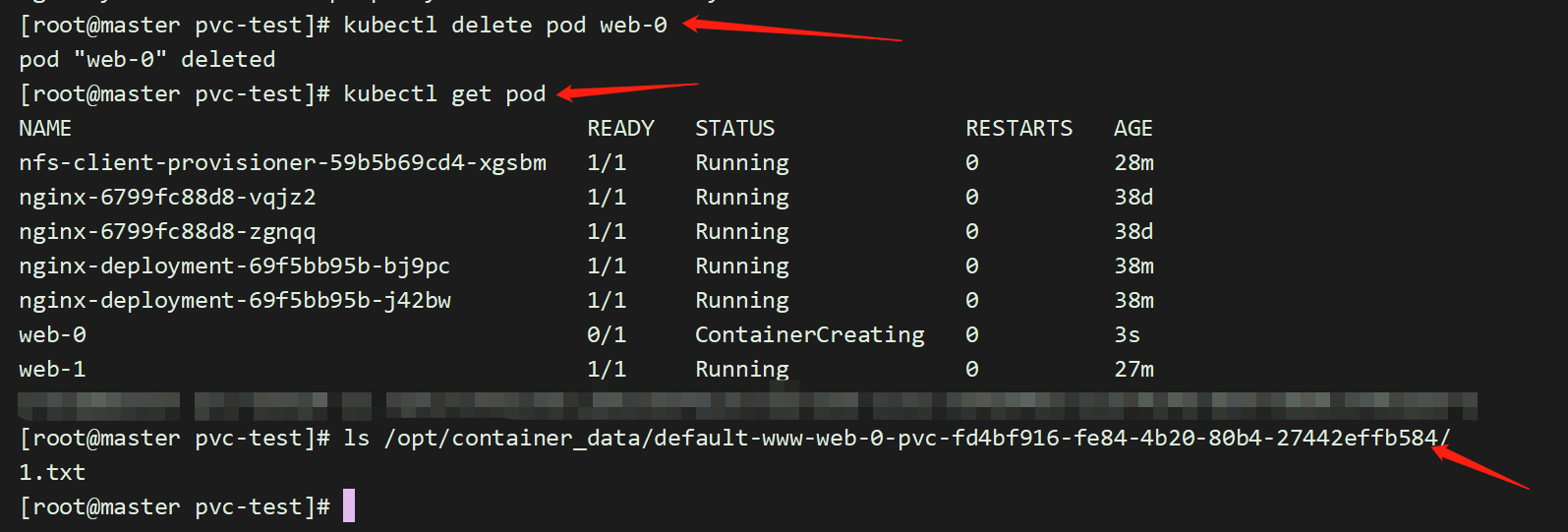
[root@master pvc-test]# kubectl exec -it web-0 /bin/sh
# cd /usr/share/nginx/html
# touch 1.txt
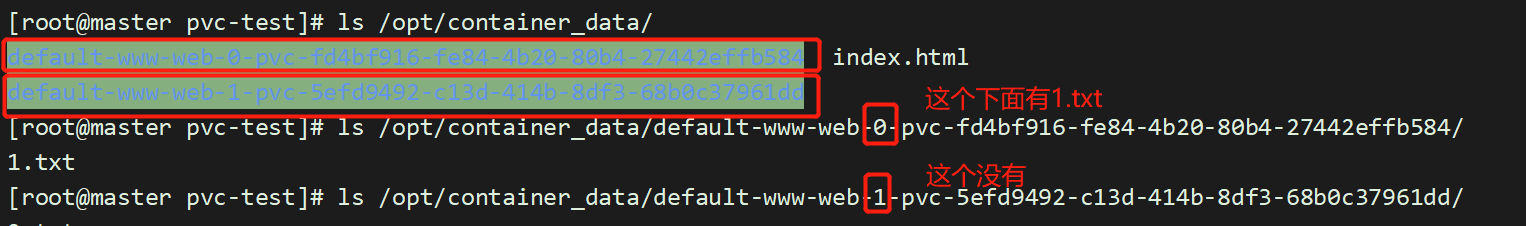
直接在web-1的目录下,创建一个文件:
[root@master pvc-test]# touch /opt/container_data/default-www-web-1-pvc-5efd9492-c13d-414b-8df3-68b0c37961dd/2.txt
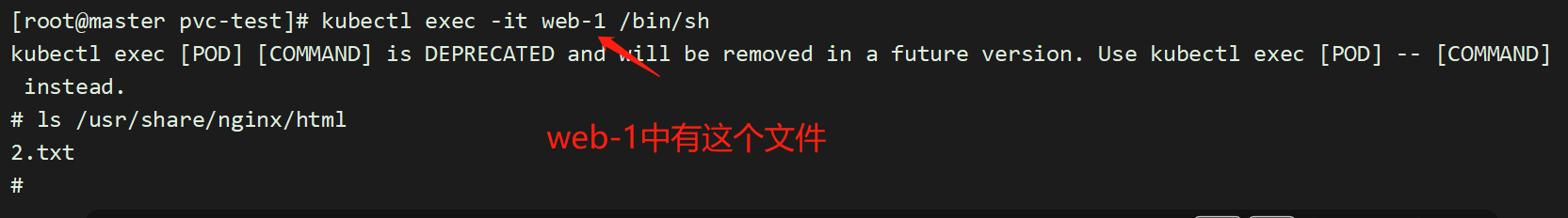
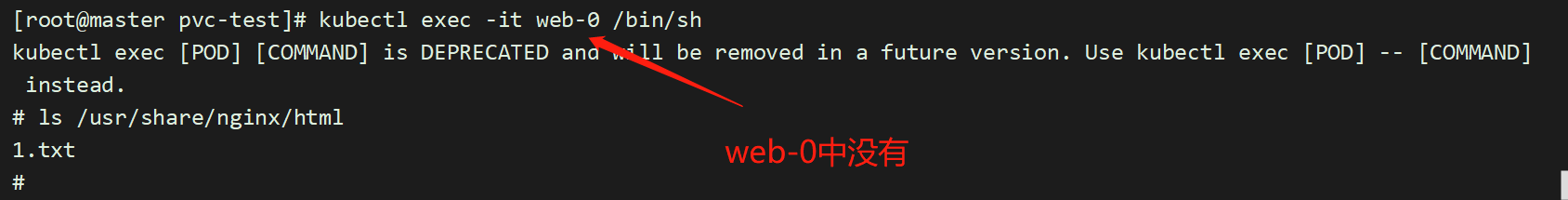
而且,删除一个pod web-0,数据仍然存在,不会丢失。保证了数据持久化;