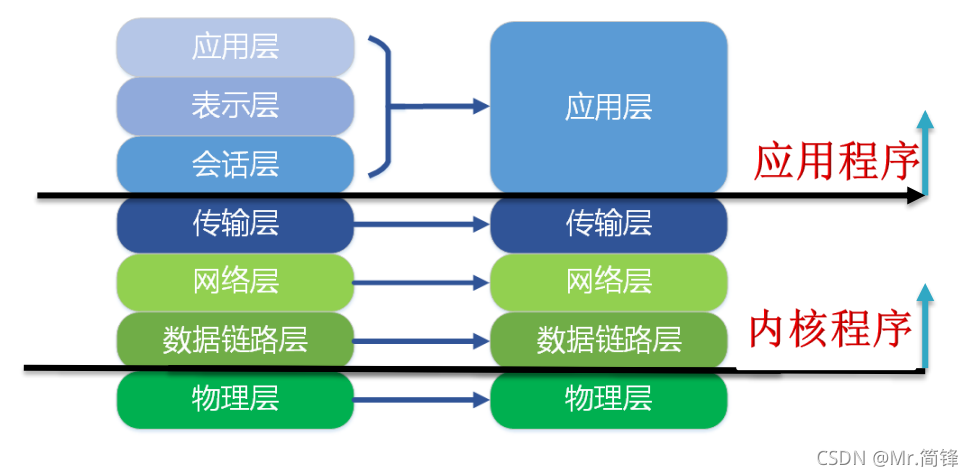
?在物理层上,双绞线传的是电信号,光纤传的是光信号。网卡的作用就是将物理层的光电信号转换为数字信号。在send的过程其实就是把数字信号转换为模拟信号(光电信号)。网卡即不在物理层,也不在数据链路层,而是在这两层之间做转换。然后把这个数据(通过sk_buff) 迁移到协议栈。 然后协议栈解析完数据之后将数据放入recv?buffer ,然后应用程序通过系统调用就能得到这个数据。? ?
这个过程有两次拷贝,? ? ?后来出现一种方式(DMA),将网卡映射到内存中去(mmap)。 应用程序是可以在内存中间直接读取这块映射过来的数据的。(DMA的方式不需要通过CPU去执行指令,直接将数据放入内存)这就叫零拷贝。
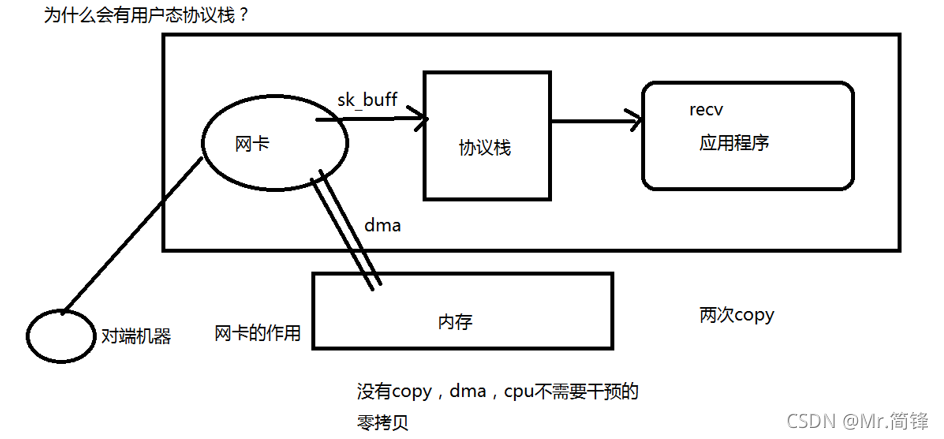
?MMAP的底层实现是有DMA这种方式的支持的。需要一条总线。? ? ?当DMA传输完数据之后会给CPU引发一个中断。
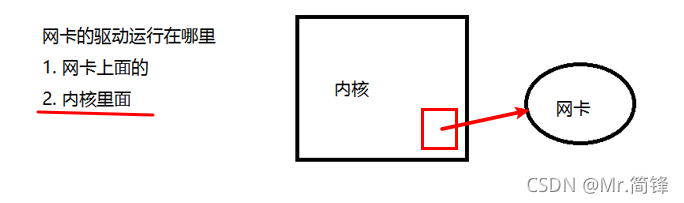
?网卡驱动是运行在内核里面的,它使得网卡能够正常工作,能够正常收发数据。
有了用户态协议栈,我们对网卡的想象空间会更大
如何取到一帧完整的数据:
1:使用原生的socket? ? (RAW SOCKET)
2:利用一些开源框架? ?----? ?netmap
3:利用一些成熟的商业的框架? ?----? dpdk
柔性数组
5 #define ETH_LEN 6
6
7
8 struct ethhdr{
9 unsigned char dst[ETH_LEN]; // 目的地址
10 unsigned char src[ETH_LEN]; // 源地址
11 unsigned short proto; // 类型
12 };
13
14 struct iphead{
15 unsigned char version:4, // 版本
16 headlen:4; // 首部长度
17 unsigned char tos; // 服务类型
18 unsigned short totlen; // 总长度
19 unsigned short id; // 16位标识
20 unsigned short flag:3, // 3位标志位
21 offset:13, // 13位片偏移
22 unsigned char ttl; // 8位生存时间
23 unsigned char proto; // 8位协议,用来形容传输层用的是什么协议
24 unsigned short check; // 校验和
25
26 unsigned int sip; // 源地址
27 unsigned int dip; // 目的地址
28 };
29
30
31 struct updhdr{
32 unsigned short sport; // 源端口号
33 unsigned short dport; // 目的端口号
34 unsigned short length; // UDP长度
35 unsigned short check; // UDP校验
36 };
37
38 // UDP包
39 struct udppkt{
40 struct ethhdr eth; // 以太网头
41 struct iphdr ip; // IP头
42 struct udphdr udp;// UDP头
43
44 unsigned char payload[0]; // 柔性数组(0长数组)
45
46 };
长度为0的数组的主要用途是为了满足需要变长度的结构体
用法 : 在一个结构体的最后, 申明一个长度为0的数组, 就可以使得这个结构体是可变长的. 对于编译器来说, 此时长度为0的数组并不占用空间, 因为数组名本身不占空间, 它只是一个偏移量, 数组名这个符号本身代表了一个不可修改的地址常量
对于编译器而言, 数组名仅仅是一个符号, 它不会占用任何空间, 它在结构体中, 只是代表了一个偏移量, 代表一个不可修改的地址常量!
两个情况下是可以使用柔性数组的:
1:内存是已经分配好的。
2:这个柔性数组的长度我们是可以通过其他方法计算出来的。
eth0:物理网卡? ? ens33:虚拟网卡? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
sudo vim /etc/default/grub? ? ? ? ?-------------->? ? GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=??net.ifnames=0 biosdevname=0? (将ens33改成eth0)?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/poll.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#define NETMAP_WITH_LIBS
#include <net/netmap_user.h>
#pragma pack(1)
#define ETH_ALEN 6
#define PROTO_IP 0x0800
#define PROTO_ARP 0x0806
#define PROTO_UDP 17
#define PROTO_ICMP 1
#define PROTO_IGMP 2
struct ethhdr {
unsigned char h_dest[ETH_ALEN];
unsigned char h_source[ETH_ALEN];
unsigned short h_proto;
};
struct iphdr {
unsigned char version;
unsigned char tos;
unsigned short tot_len;
unsigned short id;
unsigned short flag_off;
unsigned char ttl;
unsigned char protocol;
unsigned short check;
unsigned int saddr;
unsigned int daddr;
};
struct udphdr {
unsigned short source;
unsigned short dest;
unsigned short len;
unsigned short check;
};
struct udppkt {
struct ethhdr eh;
struct iphdr ip;
struct udphdr udp;
unsigned char body[128];
};
struct arphdr {
unsigned short h_type;
unsigned short h_proto;
unsigned char h_addrlen;
unsigned char protolen;
unsigned short oper;
unsigned char smac[ETH_ALEN];
unsigned int sip;
unsigned char dmac[ETH_ALEN];
unsigned int dip;
};
struct arppkt {
struct ethhdr eh;
struct arphdr arp;
};
struct icmphdr {
unsigned char type;
unsigned char code;
unsigned short check;
unsigned short identifier;
unsigned short seq;
unsigned char data[32];
};
struct icmppkt {
struct ethhdr eh;
struct iphdr ip;
struct icmphdr icmp;
};
void print_mac(unsigned char *mac) {
int i = 0;
for (i = 0;i < ETH_ALEN-1;i ++) {
printf("%02x:", mac[i]);
}
printf("%02x", mac[i]);
}
void print_ip(unsigned char *ip) {
int i = 0;
for (i = 0;i < 3;i ++) {
printf("%d.", ip[i]);
}
printf("%d", ip[i]);
}
void print_arp(struct arppkt *arp) {
print_mac(arp->eh.h_dest);
printf(" ");
print_mac(arp->eh.h_source);
printf(" ");
printf("0x%04x ", ntohs(arp->eh.h_proto));
printf(" ");
}
int str2mac(char *mac, char *str) {
char *p = str;
unsigned char value = 0x0;
int i = 0;
while (p != '\0') {
if (*p == ':') {
mac[i++] = value;
value = 0x0;
} else {
unsigned char temp = *p;
if (temp <= '9' && temp >= '0') {
temp -= '0';
} else if (temp <= 'f' && temp >= 'a') {
temp -= 'a';
temp += 10;
} else if (temp <= 'F' && temp >= 'A') {
temp -= 'A';
temp += 10;
} else {
break;
}
value <<= 4;
value |= temp;
}
p ++;
}
mac[i] = value;
return 0;
}
void echo_arp_pkt(struct arppkt *arp, struct arppkt *arp_rt, char *hmac) {
memcpy(arp_rt, arp, sizeof(struct arppkt));
memcpy(arp_rt->eh.h_dest, arp->eh.h_source, ETH_ALEN);
str2mac(arp_rt->eh.h_source, hmac);
arp_rt->eh.h_proto = arp->eh.h_proto;
arp_rt->arp.h_addrlen = 6;
arp_rt->arp.protolen = 4;
arp_rt->arp.oper = htons(2);
str2mac(arp_rt->arp.smac, hmac);
arp_rt->arp.sip = arp->arp.dip;
memcpy(arp_rt->arp.dmac, arp->arp.smac, ETH_ALEN);
arp_rt->arp.dip = arp->arp.sip;
}
void echo_udp_pkt(struct udppkt *udp, struct udppkt *udp_rt) {
memcpy(udp_rt, udp, sizeof(struct udppkt));
memcpy(udp_rt->eh.h_dest, udp->eh.h_source, ETH_ALEN);
memcpy(udp_rt->eh.h_source, udp->eh.h_dest, ETH_ALEN);
udp_rt->ip.saddr = udp->ip.daddr;
udp_rt->ip.daddr = udp->ip.saddr;
udp_rt->udp.source = udp->udp.dest;
udp_rt->udp.dest = udp->udp.source;
}
unsigned short in_cksum(unsigned short *addr, int len)
{
register int nleft = len;
register unsigned short *w = addr;
register int sum = 0;
unsigned short answer = 0;
while (nleft > 1) {
sum += *w++;
nleft -= 2;
}
if (nleft == 1) {
*(u_char *)(&answer) = *(u_char *)w ;
sum += answer;
}
sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff);
sum += (sum >> 16);
answer = ~sum;
return (answer);
}
void echo_icmp_pkt(struct icmppkt *icmp, struct icmppkt *icmp_rt) {
memcpy(icmp_rt, icmp, sizeof(struct icmppkt));
icmp_rt->icmp.type = 0x0; //
icmp_rt->icmp.code = 0x0; //
icmp_rt->icmp.check = 0x0;
icmp_rt->ip.saddr = icmp->ip.daddr;
icmp_rt->ip.daddr = icmp->ip.saddr;
memcpy(icmp_rt->eh.h_dest, icmp->eh.h_source, ETH_ALEN);
memcpy(icmp_rt->eh.h_source, icmp->eh.h_dest, ETH_ALEN);
icmp_rt->icmp.check = in_cksum((unsigned short*)&icmp_rt->icmp, sizeof(struct icmphdr));
}
int main() {
struct ethhdr *eh;
struct pollfd pfd = {0};
struct nm_pkthdr h;
unsigned char *stream = NULL;
struct nm_desc *nmr = nm_open("netmap:eth0", NULL, 0, NULL);
if (nmr == NULL) {
return -1;
}
pfd.fd = nmr->fd;
pfd.events = POLLIN;
while (1) {
int ret = poll(&pfd, 1, -1);
if (ret < 0) continue;
if (pfd.revents & POLLIN) {
stream = nm_nextpkt(nmr, &h);
eh = (struct ethhdr*)stream;
if (ntohs(eh->h_proto) == PROTO_IP) {
struct udppkt *udp = (struct udppkt*)stream;
if (udp->ip.protocol == PROTO_UDP) {
struct in_addr addr;
addr.s_addr = udp->ip.saddr;
int udp_length = ntohs(udp->udp.len);
printf("%s:%d:length:%d, ip_len:%d --> ", inet_ntoa(addr), udp->udp.source,
udp_length, ntohs(udp->ip.tot_len));
udp->body[udp_length-8] = '\0';
printf("udp --> %s\n", udp->body);
#if 1
struct udppkt udp_rt;
echo_udp_pkt(udp, &udp_rt);
nm_inject(nmr, &udp_rt, sizeof(struct udppkt));
#endif
#if 0
} else if (udp->ip.protocol == PROTO_ICMP) {
struct icmppkt *icmp = (struct icmppkt*)stream;
printf("icmp ---------- --> %d, %x\n", icmp->icmp.type, icmp->icmp.check);
if (icmp->icmp.type == 0x08) {
struct icmppkt icmp_rt = {0};
echo_icmp_pkt(icmp, &icmp_rt);
//printf("icmp check %x\n", icmp_rt.icmp.check);
nm_inject(nmr, &icmp_rt, sizeof(struct icmppkt));
}
#endif
} else if (udp->ip.protocol == PROTO_IGMP) {
} else {
printf("other ip packet");
}
#if 0
} else if (ntohs(eh->h_proto) == PROTO_ARP) {
struct arppkt *arp = (struct arppkt *)stream;
struct arppkt arp_rt;
if (arp->arp.dip == inet_addr("192.168.2.217")) {
echo_arp_pkt(arp, &arp_rt, "00:50:56:33:1c:ca");
nm_inject(nmr, &arp_rt, sizeof(struct arppkt));
}
#endif
}
}
}
}