主要第一次学, 代码的话也就边抄边学
先把代码放上来
#coding:utf-8
from socket import *
# 创建socket,绑定到端口,开始监听
tcpSerPort = 8899
tcpSerSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
# Prepare a server socket
tcpSerSock.bind(('', tcpSerPort))
tcpSerSock.listen(5)
while True:
# 开始从客户端接收请求
print('Ready to serve...')
tcpCliSock, addr = tcpSerSock.accept()
print('Received a connection from: ', addr)
message = tcpCliSock.recv(4096).decode()
# 从请求中解析出filename
filename = message.split()[1].partition("//")[2].replace('/', '_')
fileExist = "false"
try:
# 检查缓存中是否存在该文件
f = open(filename, "r")
outputdata = f.readlines()
fileExist = "true"
print('File Exists!')
# 缓存中存在该文件,把它向客户端发送
for i in range(0, len(outputdata)):
tcpCliSock.send(outputdata[i].encode())
print('Read from cache')
# 缓存中不存在该文件,异常处理
except IOError:
print('File Exist: ', fileExist)
if fileExist == "false":
# 在代理服务器上创建一个tcp socket
print('Creating socket on proxyserver')
c = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
hostn = message.split()[1].partition("//")[2].partition("/")[0]
print('Host Name: ', hostn)
try:
# 连接到远程服务器80端口
c.connect((hostn, 80))
print('Socket connected to port 80 of the host')
c.sendall(message.encode())
# Read the response into buffer
buff = c.recv(4096)
tcpCliSock.sendall(buff)
# Create a new file in the cache for the requested file.
# Also send the response in the buffer to client socket
# and the corresponding file in the cache
tmpFile = open("./" + filename, "w")
tmpFile.writelines(buff.decode().replace('\r\n', '\n'))
tmpFile.close()
except:
print("Illegal request")
else:
# HTTP response message for file not found
# Do stuff here
print('File Not Found...Stupid Andy')
# Close the client and the server sockets
tcpCliSock.close()
tcpSerSock.close()
Problem1 python socket.send和sendall()区别
socket.send is a low-level method and basically just the C/syscall
method send(3) / send(2). It can send less bytes than you requested,
but returns the number of bytes sent.socket.sendall is a high-level Python-only method that sends the
entire buffer you pass or throws an exception. It does that by calling
socket.send until everything has been sent or an error occurs.If you’re using TCP with blocking sockets and don’t want to be
bothered by internals (this is the case for most simple network
applications), use sendall.
简单来说send一般确定大小, 少于你填的参数比如1024, 4096
sendall将整个缓存给你传过去了
如果不想被中断之类的干扰传输过程, 就用sendll
Problem2 string.split()[].patition()
这个主要是对数据报的切分处理
split()
默认以空格作为切割
[0] 会返回第一个空格/分割符前面的字符串
[1] 返回后面的字符串
patition("//") 将字符串分割成三分
[0] //之前
[1] //
[2] //后面
Problem3 file.readlines() writelines()
作为列表返回文件中的所有行,其中每一行都是列表对象中的一项, 通常因为message是分行的在文本文件中
writelines() 将接收到的一行一行写回去
Problem4 HTTP代理服务器的过程
首先定义自身代理服务器的端口8899, 绑定并监听
创建客户端套接字线程去接收服务端的socket, 并获取其地址
打开IE浏览器 设置本地代理8899 当输入http://gaia.cs.umass.edu/wireshark-labs/INTRO-wireshark-file1.html 时向8899 发送请求message 请求HTML文件 其中进行了三次握手
我在这里将客户端接收的请求报文暂存一下来获取目的文件的主机和文件名 ** 为什么请求从客户端套接字获取???因为两个报文都需要手打, 确定前面的是请求报文**
对于服务端来说, 检查该文件 有就直接发送没有的话继续
服务端创建一条线程向源主机gaia.cs.umass.edu建立TCP连接 并将之前客户端接收到的报文message发过去 并将文件给存下来
再次请求时就可以返回该文件了
problem5 缓存问题
因为以前打开过, 再想打开报文时 发现
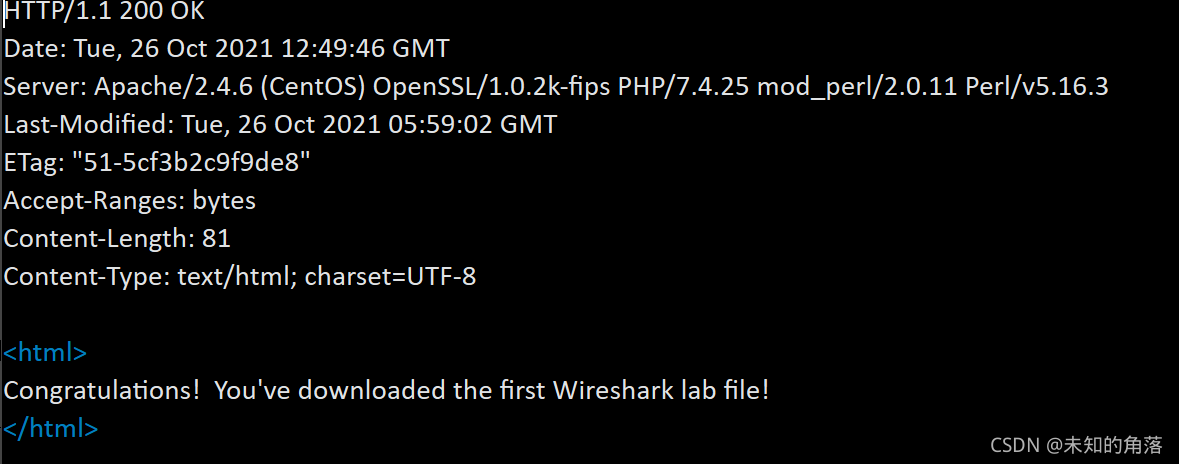
此时无法获取目的主机以及文件, 会出现字符串分割错误