目录
一,remote sync,远程同步
是一个开源的快速备份工具,可以在不同主机之间镜像同步整个目录树,支持增量备份,并保持链接和权限,且采用优化的同步算法,传输前执行压缩,因此非常适用于异地备份、镜像服务器等应用。
在远程同步任务中,负责发起rsync同步操作的客户机称为发起端,而负责响应来自客户机的rsync同步操作的服务器称为同步源。在同步过程中,同步源负责提供文件的原始位置,发起端应对该位置具有读取权限。
?
配置rsync远程同步
环境准备:
rsync同步源:192.168.18.91
rsync客户机:192.168.18.109
关闭防火墙和selinux(两台都需要此操作)
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
源服务器配置:
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -q rsync ##查看是否安装软件
rsync-3.0.9-18.el7.x86_64
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/rsyncd.conf ##配置配置文件
uid = nobody
gid = nobody
use chroot = yes
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid
dont compress = *.gz *.tgz *.zip *.z *.Z *.rpm *.deb *.bz2
address = 192.168.18.91
port = 873
log file = /var/log/rsycd.log
hosts allow = 192.168.18.0/24
[ftp]
path = /var/www/html
comment = web service
read only = yes
auth users = backuper
secrets file = /etc/rsyncd_users.db
各字段含义:
uid = nobody
gid = nobody
use chroot = yes? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?#禁锢在源目录
address = 192.168.18.91? ? ? ? ? ?#监听地址
port 873? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? #监听端口号 tcp/udp 873
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log? ? ? ?#日志地址
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid? ? ? #存放进程ID的文件位置
hosts allow = 192.168.18.0/24? #允许访问的客户机地址[ftp]? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? #共享模块名称
path = /home/ftp? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? #原目录实际路径
comment = ftp export area? ?#备注
read only = yes? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? #是否只读
dont comperss = *.gz *.bz2 *.tgz *.zip *.rar *.z? ? #同步时不再压缩的文件类型
auth users = backuper? ? #授权账户,多个账号以空格分隔
secrets file = /etc/rsyncd_users.db? ? #存放账户信息的数据文件如果采用匿名的方式,只要将其中的“auth users” 和“secrets file” 配置项去掉即可
为备份账户创建数据文件
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/rsyncd_users.db
backuper:123123
##账户:密码 格式用分号隔开
[root@localhost ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd_users.db ##权限一定要600给需同步的的目录权限。并开启服务
[root@localhost ~]# chmod -R 777 /var/www/html/
[root@localhost ~]# rsync --daemon
[root@localhost ~]# ss -natp|grep rsync
tcp 0 0 192.168.18.91:873 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 24382/rsync 服务端创建文件
[root@localhost ~]# cd /var/www/html/
[root@localhost html]# touch {1..10}.txt
[root@localhost html]# ls
10.txt 2.txt 4.txt 6.txt 8.txt
1.txt 3.txt 5.txt 7.txt 9.txt客户端(发起端)命令
客户端: rsync [选项] 原始位置 目标位置
常用选项###
-r:递归模式,包含目录及子目录中的所有文件。
-l:对于符号链接文件仍然复制为符号链接文件。
-V:显示同步过程的详细(verbose)信息。
-z:在传输文件时进行压缩(compress)
-a:归档模式,递归并保留对象属性,等同于 -rlptgoD
-p:保留文件的权限标记。
-t:保留文件的时间标记
-g:保留文件的属组标记(仅超级用户使用)。
-o:保留文件的属主标记(仅超级用户使用)
-H:保留硬连接文件
-A:保留ACL属性信息
-D:保留设备文件及其他特殊文件。
--delete:删除目标位置有而原始位置没有的文件
--checksum:根据对象的校验和来决定是否跳过文件
客户端使用命令同步
[root@localhost opt]# rsync -avz backuper@192.168.18.91::ftp /opt/
Password: ##输入设置的密码 backuper是设置的用户
receiving incremental file list
./
1.txt
10.txt
2.txt
3.txt
4.txt
5.txt
6.txt
7.txt
8.txt
9.txt
sent 250 bytes received 562 bytes 95.53 bytes/sec
total size is 0 speedup is 0.00
[root@localhost opt]# ls
10.txt 2.txt 4.txt 6.txt 8.txt
1.txt 3.txt 5.txt 7.txt 9.txt
服务端再次创建数据
[root@localhost html]# touch file{1..10}
[root@localhost html]# ls
10.txt 3.txt 6.txt 9.txt file2 file5 file8
1.txt 4.txt 7.txt file1 file3 file6 file9
2.txt 5.txt 8.txt file10 file4 file7
客户端同步
[root@localhost opt]# rsync -avz rsync://backuper@192.168.18.91/ftp /opt/
Password: ##与上面的命令相同的效果
receiving incremental file list
./
file1
file10
file2
file3
file4
file5
file6
file7
file8
file9
sent 250 bytes received 644 bytes 255.43 bytes/sec
total size is 0 speedup is 0.00
[root@localhost opt]# ls
10.txt 3.txt 6.txt 9.txt file2 file5 file8
1.txt 4.txt 7.txt file1 file3 file6 file9
2.txt 5.txt 8.txt file10 file4 file7
可以在客户端设置免交互模式同步
[root@localhost opt]# echo "123123">/etc/server.pass ##在服务端定义了位置
[root@localhost opt]# chmod 600 /etc/server.pass ##密码文件必须是600权限服务无端创建数据
[root@localhost html]# touch zzzzz.exe
[root@localhost html]# ls
10.txt 3.txt 6.txt 9.txt file2 file5 file8
1.txt 4.txt 7.txt file1 file3 file6 file9
2.txt 5.txt 8.txt file10 file4 file7 zzzzz.exe
客户端
[root@localhost opt]# rsync -avz --password-file=/etc/server.pass
backuper@192.168.18.91::ftp /opt/ ###可以实现免交互同步
receiving incremental file list
./
zzzzz.exe
sent 79 bytes received 338 bytes 75.82 bytes/sec
total size is 0 speedup is 0.00
[root@localhost opt]# ls
10.txt 3.txt 6.txt 9.txt file2 file5 file8
1.txt 4.txt 7.txt file1 file3 file6 file9
2.txt 5.txt 8.txt file10 file4 file7 zzzzz.exe
也可以做一个定时任务
[root@localhost mnt]#crontab -e
30 23 * * * /usr/bin/rsync -az --password-file=/etc/server.pass
backuper@192.168.18.91::ftp /mnt/二,rsync实时同步
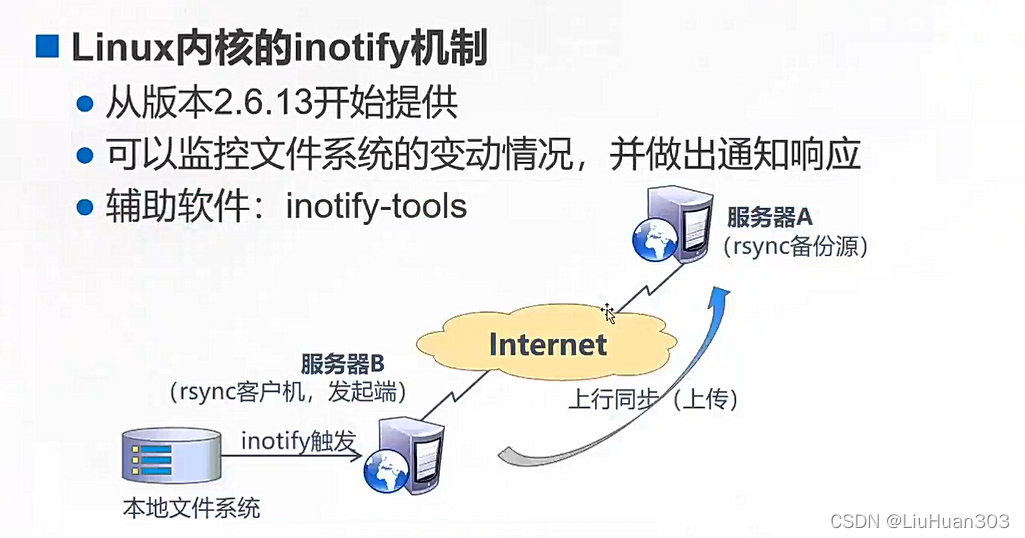
使用inotify通知接口,可以用来监控文件系统的各种变化情况,如文件存取、删除、移动、修改等。利用这一机制,可以非常方便地实现文件异动告警、增量备份,并针对目录或文件的变化及时作出响应。
将inotify机制与rsync相结合,可以实现触发式备份(实时同步),即只要原始位置的文档发生变化,则立即启动增量备份操作;否则处于静默等待状态。这样,就避免了按固定周期备份时存在的延迟性、周期过密等问题。
因为inotify通知机制由 Linux内核提供,因此主要做本机监控,在触发式备份中,应用时更适合上行同步
配置实时同步
服务端修改配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/rsyncd.conf
[ftp]
path = /var/www/html
comment = web service
read only = no ##修改只读模式为no
auth users = backuper
secrets file = /etc/rsyncd_users.db
"/etc/rsyncd.conf" 37L, 812C 37,1 底端
调整inotify内核参数
[root@localhost html]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
# sysctl settings are defined through files in
# /usr/lib/sysctl.d/, /run/sysctl.d/, and /etc/sysctl.d/.
#
# Vendors settings live in /usr/lib/sysctl.d/.
# To override a whole file, create a new file with the same in
# /etc/sysctl.d/ and put new settings there. To override
# only specific settings, add a file with a lexically later
# name in /etc/sysctl.d/ and put new settings there.
#
# For more information, see sysctl.conf(5) and sysctl.d(5).
fs.inotify.max_queued_events = 32768
fs.inotify.max_user_instances = 1024
fs.inotify.max_user_watches = 1048576
:wq
[root@localhost html]# sysctl -p ###使其生效
fs.inotify.max_queued_events = 32768
fs.inotify.max_user_instances = 1024
fs.inotify.max_user_watches = 1048576
重启服务
[root@localhost html]# ss -natp |grep rsync
LISTEN 0 5 192.168.18.91:873 *:*
users:(("rsync",pid=24382,fd=4))
[root@localhost html]# kill 24382
[root@localhost html]# ss -natp |grep rsync
[root@localhost html]# rsync --daemon ##重新加载
[root@localhost html]# ss -natp |grep rsync
LISTEN 0 5 192.168.18.91:873 *:*
users:(("rsync",pid=24518,fd=4))客户端配置
安装inotify-tools辅助工具
inotifywait:用于持续监控,实时输出结果(增删改属性修改)
inotifywatch:用于短期监控,任务完成后再出汇总结果
[root@localhost opt]# rm -rf *
[root@localhost opt]# rz -E
rz waiting to receive.
[root@localhost opt]# tar xf inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz
[root@localhost opt]# cd inotify-tools-3.14/
[root@localhost inotify-tools-3.14]# ./configure
checking for a BSD-compatible install... /usr/bin/install -c
checking whether build environment is sane... yes
checking for a thread-safe mkdir -p... /usr/bin/mkdir -p
checking for gawk... gawk
checking whether make sets $(MAKE)... yes
[root@localhost inotify-tools-3.14]# make && make install
make all-recursive
make[1]: 进入目录“/opt/inotify-tools-3.14”
Making all in libinotifytools
make[2]: 进入目录“/opt/inotify-tools-3.14/libinotifytools”
make[3]: 进入目录“/opt/inotify-tools-3.14”
make[3]: 离开目录“/opt/inotify-tools-3.14”
........
make[2]: 对“install-exec-am”无需做任何事。
make[2]: 对“install-data-am”无需做任何事。
make[2]: 离开目录“/opt/inotify-tools-3.14”
make[1]: 离开目录“/opt/inotify-tools-3.14”
编写启动脚本
[root@localhost inotify-tools-3.14]# vim /opt/inotify.sh
#!/bin/bash
INOTIFY_CMD="inotifywait -mrq -e create,delete,move,modify,attrib
/var/www/html"
RSYNC_CMD="rsync -azH --delete --password-file=/etc/server.pass
/var/www/html/ backuper@192.168.18.91::ftp"
$INOTIFY_CMD | while read DIRECTORY EVENT FILE
do
if [ $(pgrep rsync | wc -l) -le 0 ] ; then
$RSYNC_CMD
# echo "${FILE} was rsynced" >>/opt/inotify_rsync.log
fi
done
[root@localhost inotify-tools-3.14]# chmod +x /opt/inotify.sh
###给脚本执行权限创建同步目录
[root@localhost inotify-tools-3.14]# mkdir /var/www/html -p
[root@localhost inotify-tools-3.14]# chmod -R 777 /var/www/html/
###赋予权限
[root@localhost opt]# ./inotify.sh & ##后台运行脚本
[1] 96690
现将服务端的数据删除
[root@localhost html]# rm -rf *
[root@localhost html]# ls
在开启两个客户端连接
##可以先执行“inotifywait”命令,然后另外再开启一个新的终端向 /var/www/html 目录下添加文件、移动文件,在原来的终端中跟踪屏幕输出结果。
[root@localhost ~]# inotifywait -mrq -e modify,create,move,delete ?/var/www/html
-e 用来指定要监控哪些事情
-m 表示持续监控
-r 表示递归整个目录
-q 简化输出信息
一个开启实时监控
[root@localhost ~]# inotifywait -mrq -e modify,create,move,delete
/var/www/html
一台进入目录创建数据
[root@localhost /]# cd /var/www/html/
[root@localhost html]# ls
[root@localhost html]# touch {1..10}.txt
[root@localhost html]# ls
10.txt 2.txt 4.txt 6.txt 8.txt
1.txt 3.txt 5.txt 7.txt 9.txt
客户端实时监控
[root@localhost ~]# inotifywait -mrq -e modify,create,move,var/www/html
/var/www/html/ CREATE 1.txt
/var/www/html/ CREATE 2.txt
/var/www/html/ CREATE 3.txt
/var/www/html/ CREATE 4.txt
/var/www/html/ CREATE 5.txt
/var/www/html/ CREATE 6.txt
/var/www/html/ CREATE 7.txt
/var/www/html/ CREATE 8.txt
/var/www/html/ CREATE 9.txt
/var/www/html/ CREATE 10.txt
服务端
[root@localhost html]# ls
10.txt 2.txt 4.txt 6.txt 8.txt
1.txt 3.txt 5.txt 7.txt 9.txt
客户端删除数据
[root@localhost html]# rm -rf 10.txt
[root@localhost html]# rm -rf 9.txt
客户端实时监控
/var/www/html/ DELETE 10.txt
/var/www/html/ DELETE 9.txt服务端数据同步被删除
[root@localhost html]# ls
1.txt 2.txt 3.txt 4.txt 5.txt 6.txt 7.txt 8.txt
补充:rsync可以快速删除大量文件
在主节点上创建文件
[root@localhost data]# cd /opt
[root@localhost opt]# touch {1..1000}.txt
[root@localhost opt]# ls
1000.txt 326.txt 552.txt 779.txt
100.txt 327.txt 553.txt 77.txt
101.txt 328.txt 554.txt 780.txt
102.txt 329.txt 555.txt 781.txt
103.txt 32.txt 556.txt 782.txt
.......
319.txt 545.txt 771.txt 998.txt
31.txt 546.txt 772.txt 999.txt
320.txt 547.txt 773.txt 99.txt
321.txt 548.txt 774.txt 9.txt
322.txt 549.txt 775.txt mysql-5.7.20
323.txt 54.txt 776.txt mysql-boost-5.7.20.tar.gz
324.txt 550.txt 777.txt rh
325.txt 551.txt 778.txt
[root@localhost /]# mkdir /data ###创建一个空的目录
[root@localhost /]# ls
bin data etc lib media opt root sbin sys usr
boot dev home lib64 mnt proc run srv tmp var
[root@localhost /]# cd /data
[root@localhost data]# ls
[root@localhost data]# [root@localhost opt]# rsync --delete-before -aHv --progress -stats /data/ /opt
....... ###将后面的文件对照前面的文件删除
deleting 101.txt ###前面的文件是空文件就是把后面文件全部删除
deleting 1000.txt
deleting 100.txt
deleting 10.txt
deleting 1.txt
./
sent 29 bytes received 15 bytes 29.33 bytes/sec
total size is 0 speedup is 0.00
[root@localhost opt]# ls ##文件已经删除
[root@localhost opt]#