1 概述
见名知意,此类主要用于数据传输,是一个守护线程,在创建DFSOutputStream的过程中被启动,启动之后再run方法之中使用一个while死循环(直到流或者客户端关闭)才停止运行,里面主要的逻辑是通过维护一个dataQueue队列,等待主线程往其中添加packet数据,等到添加了packet数据之后,会触发数据的发送,将数据发送到对应pipeline对应的dn之中,从而完成数据的传输。
2 源码分析
2.1 DataStreamer的前提调用
根据前文,在DFSOutputStream#newStreamForCreate中会创建对应的DFSOutputStream:
final DFSOutputStream out;
// 判断是否配置了ErasureCodingPolicy从而创建不同的DFSOutputStream对象
// 过程中会使用通过rpc远程创建INodeFile返回的HDFSFileStatus对象
if(stat.getErasureCodingPolicy() != null) {
out = new DFSStripedOutputStream(dfsClient, src, stat,
flag, progress, checksum, favoredNodes);
} else {
out = new DFSOutputStream(dfsClient, src, stat,
flag, progress, checksum, favoredNodes, true);
}
// 启动往dn pipeline发送packet数据的的DataStreamer
out.start();这里主要看非ErasureCoding一节,即创建DFSOutputStreamer
/** Construct a new output stream for creating a file. */
protected DFSOutputStream(DFSClient dfsClient, String src,
HdfsFileStatus stat, EnumSet<CreateFlag> flag, Progressable progress,
DataChecksum checksum, String[] favoredNodes, boolean createStreamer) {
// 这里主要进行一些初始化的操作
this(dfsClient, src, flag, progress, stat, checksum);
this.shouldSyncBlock = flag.contains(CreateFlag.SYNC_BLOCK);
// 参见下文关于此方法的解释,因为涉及到一张图,哈哈
computePacketChunkSize(dfsClient.getConf().getWritePacketSize(),
bytesPerChecksum);
// 在这里直接创建DataStreamer
if (createStreamer) {
streamer = new DataStreamer(stat, null, dfsClient, src, progress,
checksum, cachingStrategy, byteArrayManager, favoredNodes,
addBlockFlags);
}
}
private DFSOutputStream(DFSClient dfsClient, String src,
EnumSet<CreateFlag> flag,
Progressable progress, HdfsFileStatus stat, DataChecksum checksum) {
super(getChecksum4Compute(checksum, stat));
this.dfsClient = dfsClient;
this.src = src;
this.fileId = stat.getFileId();
this.blockSize = stat.getBlockSize();
this.blockReplication = stat.getReplication();
this.fileEncryptionInfo = stat.getFileEncryptionInfo();
this.cachingStrategy = new AtomicReference<>(
dfsClient.getDefaultWriteCachingStrategy());
this.addBlockFlags = EnumSet.noneOf(AddBlockFlag.class);
if (flag.contains(CreateFlag.NO_LOCAL_WRITE)) {
this.addBlockFlags.add(AddBlockFlag.NO_LOCAL_WRITE);
}
if (flag.contains(CreateFlag.NO_LOCAL_RACK)) {
this.addBlockFlags.add(AddBlockFlag.NO_LOCAL_RACK);
}
if (flag.contains(CreateFlag.IGNORE_CLIENT_LOCALITY)) {
this.addBlockFlags.add(AddBlockFlag.IGNORE_CLIENT_LOCALITY);
}
if (progress != null) {
DFSClient.LOG.debug("Set non-null progress callback on DFSOutputStream "
+"{}", src);
}
initWritePacketSize();
this.bytesPerChecksum = checksum.getBytesPerChecksum();
if (bytesPerChecksum <= 0) {
throw new HadoopIllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid value: bytesPerChecksum = " + bytesPerChecksum + " <= 0");
}
if (blockSize % bytesPerChecksum != 0) {
throw new HadoopIllegalArgumentException("Invalid values: "
+ HdfsClientConfigKeys.DFS_BYTES_PER_CHECKSUM_KEY
+ " (=" + bytesPerChecksum + ") must divide block size (=" +
blockSize + ").");
}
this.byteArrayManager = dfsClient.getClientContext().getByteArrayManager();
}下面解释下computePacketChunkSize
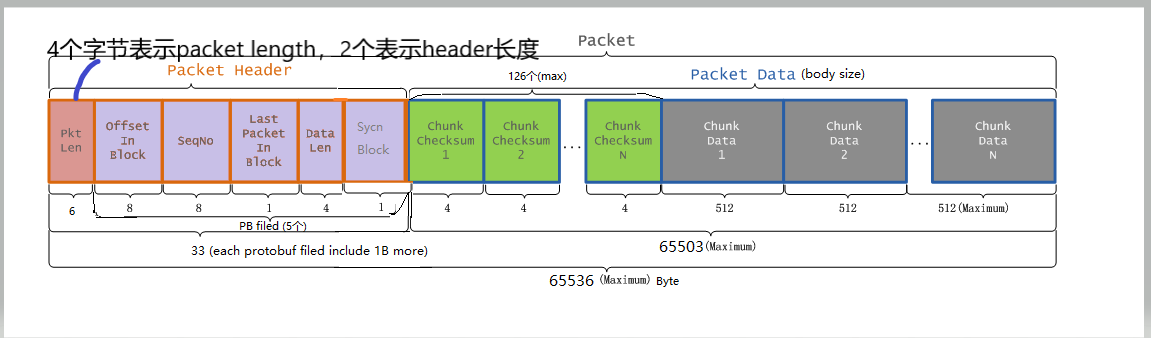
protected void computePacketChunkSize(int psize, int csize) {
// 64Kb - packetHeader长度(33b,如下图)
final int bodySize = psize - PacketHeader.PKT_MAX_HEADER_LEN;
// getChecksumSize默认是使用crc32,即4b,csize默认是512b,因此chunkSize=516b
final int chunkSize = csize + getChecksumSize();
chunksPerPacket = Math.max(bodySize/chunkSize, 1);
// packet的真实大小
packetSize = chunkSize*chunksPerPacket;
DFSClient.LOG.debug("computePacketChunkSize: src={}, chunkSize={}, "
+ "chunksPerPacket={}, packetSize={}",
src, chunkSize, chunksPerPacket, packetSize);
}
2.2 DataStreamer构造函数
没啥太多可介绍的,就是参数初始化
/**
* construction with tracing info
*/
DataStreamer(HdfsFileStatus stat, ExtendedBlock block, DFSClient dfsClient,
String src, Progressable progress, DataChecksum checksum,
AtomicReference<CachingStrategy> cachingStrategy,
ByteArrayManager byteArrayManage, String[] favoredNodes,
EnumSet<AddBlockFlag> flags) {
this(stat, block, dfsClient, src, progress, checksum, cachingStrategy,
byteArrayManage, false, favoredNodes, flags);
stage = BlockConstructionStage.PIPELINE_SETUP_CREATE;
}
private DataStreamer(HdfsFileStatus stat, ExtendedBlock block,
DFSClient dfsClient, String src,
Progressable progress, DataChecksum checksum,
AtomicReference<CachingStrategy> cachingStrategy,
ByteArrayManager byteArrayManage,
boolean isAppend, String[] favoredNodes,
EnumSet<AddBlockFlag> flags) {
this.block = new BlockToWrite(block);
this.dfsClient = dfsClient;
this.src = src;
this.progress = progress;
this.stat = stat;
this.checksum4WriteBlock = checksum;
this.cachingStrategy = cachingStrategy;
this.byteArrayManager = byteArrayManage;
this.isLazyPersistFile = isLazyPersist(stat);
this.isAppend = isAppend;
this.favoredNodes = favoredNodes;
final DfsClientConf conf = dfsClient.getConf();
this.dfsclientSlowLogThresholdMs = conf.getSlowIoWarningThresholdMs();
this.excludedNodes = initExcludedNodes(conf.getExcludedNodesCacheExpiry());
this.errorState = new ErrorState(conf.getDatanodeRestartTimeout());
this.addBlockFlags = flags;
}2.3 run方法
由于这个对象实际上是一个线程,因此在DFSOutputStream#newStreamForCreate方法中最后启动start()方法时,就是调用线程的run方法执行操作(实在有点长。。。。)。
/*
* streamer thread is the only thread that opens streams to datanode,
* and closes them. Any error recovery is also done by this thread.
*/
@Override
public void run() {
long lastPacket = Time.monotonicNow();
TraceScope scope = null;
// 死循环知道客户端或者流关闭
while (!streamerClosed && dfsClient.clientRunning) {
// if the Responder encountered an error, shutdown Responder
if (errorState.hasError()) {
closeResponder();
}
DFSPacket one;
try {
// process datanode IO errors if any
boolean doSleep = processDatanodeOrExternalError();
final int halfSocketTimeout = dfsClient.getConf().getSocketTimeout()/2;
synchronized (dataQueue) {
// wait for a packet to be sent.
long now = Time.monotonicNow();
/**
* shouldRun:是否应该停止,根据流是否关闭、是否发生异常、是否客户端停止运行决定
* dataQueue:最重要的一个变量,== 0表示还未开始写数据
* stage:block的阶段
* 现在距离上一个packet是否过去了指定客户端socket(60s)的一半
* doSleep:数据流突然出现故障
* 如果这些条件满足了,则让dataQueue休眠等待数据写入
*/
while ((!shouldStop() && dataQueue.size() == 0 &&
(stage != BlockConstructionStage.DATA_STREAMING ||
now - lastPacket < halfSocketTimeout)) || doSleep) {
long timeout = halfSocketTimeout - (now-lastPacket);
timeout = timeout <= 0 ? 1000 : timeout;
timeout = (stage == BlockConstructionStage.DATA_STREAMING)?
timeout : 1000;
try {
dataQueue.wait(timeout);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.debug("Thread interrupted", e);
}
doSleep = false;
now = Time.monotonicNow();
}
if (shouldStop()) {
continue;
}
// get packet to be sent.
// 获取需要发送的packet
// 如果数据队列为空,那么先创建一个心跳packet(此心跳用于告知dn客户端仍存活),否则获取正常的数据packet
if (dataQueue.isEmpty()) {
one = createHeartbeatPacket();
} else {
try {
// 写入管道拥挤(客户端请求过于频繁)时,会进行一定的休眠
backOffIfNecessary();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.debug("Thread interrupted", e);
}
one = dataQueue.getFirst(); // regular data packet
SpanId[] parents = one.getTraceParents();
if (parents.length > 0) {
scope = dfsClient.getTracer().
newScope("dataStreamer", parents[0]);
scope.getSpan().setParents(parents);
}
}
}
// get new block from namenode.
LOG.debug("stage={}, {}", stage, this);
if (stage == BlockConstructionStage.PIPELINE_SETUP_CREATE) {
// 此逻辑用于创建新文件
LOG.debug("Allocating new block: {}", this);
//nextBlockOutputStream()方法用来向Namenode 申请块信息,返回LocatedBlock 对象,
// 其包含了 数据流pipeline 数据流节点信息 DatanodeInfo
setPipeline(nextBlockOutputStream());
// 初始化数据流,在其中会启动一个ResponseProcessor线程,此线程用来处理来自dn的响应
// 所谓响应即ack,每当我们发出一个数据Packet,DataNode都需要发送ACK回复我们表示他收到了
// 因此这样可以看出是每一个block对应一个响应线程,当此block写完关闭时,则会关闭此线程
initDataStreaming();
} else if (stage == BlockConstructionStage.PIPELINE_SETUP_APPEND) {
// 此逻辑用于往文件添加数据
LOG.debug("Append to block {}", block);
// 这里也是创建一个dataStreamer
setupPipelineForAppendOrRecovery();
if (streamerClosed) {
continue;
}
// 初始化dataStream,在其中会启动一个ResponseProcessor线程,此线程用来处理来自dn的响应
// 所谓响应即ack,每当我们发出一个数据Packet,DataNode都需要发送ACK回复我们表示他收到了
initDataStreaming();
}
// 获取packet数据在block中的最后偏移量
long lastByteOffsetInBlock = one.getLastByteOffsetBlock();
if (lastByteOffsetInBlock > stat.getBlockSize()) {
throw new IOException("BlockSize " + stat.getBlockSize() +
" < lastByteOffsetInBlock, " + this + ", " + one);
}
// 判断是否是最后一个packet
// 里面会等待所有lastPacket之前的Packet被确认。然后把流水线状态设置为关闭,
// 但是此时还没有把lastPacket写到流水线上。
if (one.isLastPacketInBlock()) {
// wait for all data packets have been successfully acked
synchronized (dataQueue) {
while (!shouldStop() && ackQueue.size() != 0) {
try {
// wait for acks to arrive from datanodes
// 等待从dn返回的ack
dataQueue.wait(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.debug("Thread interrupted", e);
}
}
}
if (shouldStop()) {
continue;
}
// 指示pipeline关闭
stage = BlockConstructionStage.PIPELINE_CLOSE;
}
// send the packet
SpanId spanId = SpanId.INVALID;
synchronized (dataQueue) {
// move packet from dataQueue to ackQueue
if (!one.isHeartbeatPacket()) {
if (scope != null) {
spanId = scope.getSpanId();
scope.detach();
one.setTraceScope(scope);
}
scope = null;
// 将此处理的packet移到ack队列中,指示这些packet处于等待被确认的过程中
dataQueue.removeFirst();
ackQueue.addLast(one);
packetSendTime.put(one.getSeqno(), Time.monotonicNow());
dataQueue.notifyAll();
}
}
LOG.debug("{} sending {}", this, one);
// write out data to remote datanode
try (TraceScope ignored = dfsClient.getTracer().
newScope("DataStreamer#writeTo", spanId)) {
// 将packet写入流水线中
one.writeTo(blockStream);
blockStream.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
// HDFS-3398 treat primary DN is down since client is unable to
// write to primary DN. If a failed or restarting node has already
// been recorded by the responder, the following call will have no
// effect. Pipeline recovery can handle only one node error at a
// time. If the primary node fails again during the recovery, it
// will be taken out then.
// 用于标识当没有明显异常收到时,标记第一个dn为挂起而停止传输
errorState.markFirstNodeIfNotMarked();
throw e;
}
lastPacket = Time.monotonicNow();
// update bytesSent
long tmpBytesSent = one.getLastByteOffsetBlock();
if (bytesSent < tmpBytesSent) {
bytesSent = tmpBytesSent;
}
if (shouldStop()) {
continue;
}
// Is this block full?
// 通知当前block已经写完,从而等待acks
if (one.isLastPacketInBlock()) {
// wait for the close packet has been acked
synchronized (dataQueue) {
while (!shouldStop() && ackQueue.size() != 0) {
dataQueue.wait(1000);// wait for acks to arrive from datanodes
}
}
if (shouldStop()) {
continue;
}
// 当一个块写完之后,需要添加新的块,会在上一个块end掉的时候(调用endBlock),
// 把stage设置成PIPELINE_SETUP_CREATE,这样一来下次流水线也是被建立来创建新的块,达到添加块的目的。
endBlock();
}
if (progress != null) { progress.progress(); }
// This is used by unit test to trigger race conditions.
if (artificialSlowdown != 0 && dfsClient.clientRunning) {
Thread.sleep(artificialSlowdown);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
// Log warning if there was a real error.
if (!errorState.isRestartingNode()) {
// Since their messages are descriptive enough, do not always
// log a verbose stack-trace WARN for quota exceptions.
if (e instanceof QuotaExceededException) {
LOG.debug("DataStreamer Quota Exception", e);
} else {
LOG.warn("DataStreamer Exception", e);
}
}
lastException.set(e);
assert !(e instanceof NullPointerException);
errorState.setInternalError();
if (!errorState.isNodeMarked()) {
// Not a datanode issue
streamerClosed = true;
}
} finally {
if (scope != null) {
scope.close();
scope = null;
}
}
}
closeInternal();
}2.4 nextBlockOutputStream
此方法再创建一个新块时被调用:
if (stage == BlockConstructionStage.PIPELINE_SETUP_CREATE) {
// 此逻辑用于创建新文件
LOG.debug("Allocating new block: {}", this);
//nextBlockOutputStream()方法用来向Namenode 申请块信息,返回LocatedBlock 对象,
// 其包含了 数据流pipeline 数据流节点信息 DatanodeInfo
setPipeline(nextBlockOutputStream());
// 初始化数据流,在其中会启动一个nextBlockOutputStream线程,此线程用来处理来自dn的响应
// 所谓响应即ack,每当我们发出一个数据Packet,DataNode都需要发送ACK回复我们表示他收到了
// 因此这样可以看出是每一个block对应一个响应线程,当此block写完关闭时,则会关闭此线程
initDataStreaming();
} 这个方法返回的是一个LocatedBlock,包含了一个块的信息。包括Block的备份存储位置,块的大小,块的BGS和BlockId。
/**
* Open a DataStreamer to a DataNode so that it can be written to.
* This happens when a file is created and each time a new block is allocated.
* Must get block ID and the IDs of the destinations from the namenode.
* Returns the list of target datanodes.
*/
protected LocatedBlock nextBlockOutputStream() throws IOException {
LocatedBlock lb;
DatanodeInfo[] nodes;
StorageType[] nextStorageTypes;
String[] nextStorageIDs;
int count = dfsClient.getConf().getNumBlockWriteRetry();
boolean success;
final ExtendedBlock oldBlock = block.getCurrentBlock();
// 循环创建一个新块,知道成功或者到达block写入的重试次数
do {
// 由于是创建新块,老块的异常就直接清除了
errorState.resetInternalError();
lastException.clear();
// 不想将块副本保存到那些dn节点
DatanodeInfo[] excluded = getExcludedNodes();
// 创建一个新块,rpc调用namenode的addBlock操作
lb = locateFollowingBlock(
excluded.length > 0 ? excluded : null, oldBlock);
// 设置一些基础信息,如当前块、传输数据量、密钥等
block.setCurrentBlock(lb.getBlock());
block.setNumBytes(0);
bytesSent = 0;
accessToken = lb.getBlockToken();
nodes = lb.getLocations();
nextStorageTypes = lb.getStorageTypes();
nextStorageIDs = lb.getStorageIDs();
// Connect to first DataNode in the list.
// 建立和流水线上的第一个dn的连接
// 这里会先建立一个pipeline的socket连接
// 而后调用Sender#writeBlock方法通知那些包含在pipeline中的dn
// 最后接受来自dn的回复,做后续的判断
success = createBlockOutputStream(nodes, nextStorageTypes, nextStorageIDs,
0L, false);
if (!success) {
LOG.warn("Abandoning " + block);
dfsClient.namenode.abandonBlock(block.getCurrentBlock(),
stat.getFileId(), src, dfsClient.clientName);
block.setCurrentBlock(null);
final DatanodeInfo badNode = nodes[errorState.getBadNodeIndex()];
LOG.warn("Excluding datanode " + badNode);
excludedNodes.put(badNode, badNode);
}
} while (!success && --count >= 0);
if (!success) {
throw new IOException("Unable to create new block.");
}
return lb;
}2.5 ResponseProcessor线程
这是一个守护线程,用来处理来自dn的ack。DataNode接收到Packet后需要向客户端回复ACK,表示自己已经收到Packet了,而接收处理ACK的线程类就是ResponseProcessor。
对每一个块的传输都需要新建一个ResponseProcessor,当块传输完,客户端会通过endBlock方法间接地把当前ResponseProcessor销毁掉。下次传输新的Block的时候通过初始化传输环境方法initDataStreaming来间接地创建ResponseProcessor。
启动之后同样主要看run()方法呀:
@Override
public void run() {
setName("ResponseProcessor for block " + block);
// 创建一个代表ack的对象
PipelineAck ack = new PipelineAck();
TraceScope scope = null;
// 循环接受ack,除非线程关闭、客户端停止运行、最后一个packet
while (!responderClosed && dfsClient.clientRunning && !isLastPacketInBlock) {
// process responses from datanodes.
try {
// read an ack from the pipeline
// 从管道中读取ack
ack.readFields(blockReplyStream);
if (ack.getSeqno() != DFSPacket.HEART_BEAT_SEQNO) {
Long begin = packetSendTime.get(ack.getSeqno());
if (begin != null) {
long duration = Time.monotonicNow() - begin;
if (duration > dfsclientSlowLogThresholdMs) {
LOG.info("Slow ReadProcessor read fields for block " + block
+ " took " + duration + "ms (threshold="
+ dfsclientSlowLogThresholdMs + "ms); ack: " + ack
+ ", targets: " + Arrays.asList(targets));
}
}
}
LOG.debug("DFSClient {}", ack);
// 获取packet序号,在客户端和DataNode的通信中,数据是以Packet为单位进行传输的,每个packet的序号独一无二
// 根据这个序号可以获知此ack对应那个packet
// 序号是从0开始计数的,序号为-1的Packet是心跳包,客户端用他来告诉DataNode客户端还活着。
// 序号为-2的包为未知包,收到这个包需要抛出异常
long seqno = ack.getSeqno();
// processes response status from datanodes.
ArrayList<DatanodeInfo> congestedNodesFromAck = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = ack.getNumOfReplies()-1; i >=0 && dfsClient.clientRunning; i--) {
// 从ack的header信息中获取对应的dn的状态
final Status reply = PipelineAck.getStatusFromHeader(ack
.getHeaderFlag(i));
// 根据状态查看dn是否处于繁忙
if (PipelineAck.getECNFromHeader(ack.getHeaderFlag(i)) ==
PipelineAck.ECN.CONGESTED) {
congestedNodesFromAck.add(targets[i]);
}
// Restart will not be treated differently unless it is
// the local node or the only one in the pipeline.
// 根据状态判断是否有dn处于重启过程中
if (PipelineAck.isRestartOOBStatus(reply)) {
final String message = "Datanode " + i + " is restarting: "
+ targets[i];
// 根据是否等待,如果等待将会把将当前传进来的节点标记为正在重启的节点
// 并且为他设置重启时限,把BadNode记录清除掉(这时的BadNode一般是流水线上第一个DataNode,
// BadNode指的是工作过程发生错误或者无法联系上的DataNode)
errorState.initRestartingNode(i, message,
shouldWaitForRestart(i));
throw new IOException(message);
}
// node error
// 检查ACK的回应是否是SUCCESS,如果不是,表示对应的DataNode没有
// 正常接收Packet,那么将把该DataNode标记为BadNode。
if (reply != SUCCESS) {
errorState.setBadNodeIndex(i); // mark bad datanode
throw new IOException("Bad response " + reply +
" for " + block + " from datanode " + targets[i]);
}
}
// 将上面得到的繁忙节点加入到DataStreamer的成员变量congestedNodes中,
// 这个变量用来标记所有繁忙节点,以便输出日志(DataStreamer的backIfNecessary)的时候观察哪些节点繁忙。
if (!congestedNodesFromAck.isEmpty()) {
synchronized (congestedNodes) {
congestedNodes.clear();
congestedNodes.addAll(congestedNodesFromAck);
}
} else {
synchronized (congestedNodes) {
congestedNodes.clear();
lastCongestionBackoffTime = 0;
}
}
assert seqno != PipelineAck.UNKOWN_SEQNO :
"Ack for unknown seqno should be a failed ack: " + ack;
if (seqno == DFSPacket.HEART_BEAT_SEQNO) { // a heartbeat ack
continue;
}
// a success ack for a data packet
DFSPacket one;
// ackQueue中存储的都是待确认的packet,如果数据包发出去之后流水线失败,
// 得不到确认。数据包可以从ackQueue恢复,不至于以前的Packet丢失。
synchronized (dataQueue) {
one = ackQueue.getFirst();
}
// 收到的ACK的序号和ackQueue队头元素的序号一不一样,如果不一样,说明可能收发乱序了
if (one.getSeqno() != seqno) {
throw new IOException("ResponseProcessor: Expecting seqno " +
one.getSeqno() + " for block " + block +
" but received " + seqno);
}
isLastPacketInBlock = one.isLastPacketInBlock();
// Fail the packet write for testing in order to force a
// pipeline recovery.
if (DFSClientFaultInjector.get().failPacket() &&
isLastPacketInBlock) {
failPacket = true;
throw new IOException(
"Failing the last packet for testing.");
}
// update bytesAcked
// getLastByteOffsetBlock其实就是最后一个包的结尾相对Block起始位置的偏移量。也就是现在写了的数据量。
// offsetInBlock + dataPos - dataStart
block.setNumBytes(one.getLastByteOffsetBlock());
synchronized (dataQueue) {
scope = one.getTraceScope();
if (scope != null) {
scope.reattach();
one.setTraceScope(null);
}
lastAckedSeqno = seqno;
pipelineRecoveryCount = 0;
// 移除已经被确认的packet
ackQueue.removeFirst();
packetSendTime.remove(seqno);
dataQueue.notifyAll();
one.releaseBuffer(byteArrayManager);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
if (!responderClosed) {
lastException.set(e);
errorState.setInternalError();
// 标记第一个dn为badNode,因为第一个建立连接,嫌疑最大
errorState.markFirstNodeIfNotMarked();
synchronized (dataQueue) {
dataQueue.notifyAll();
}
if (!errorState.isRestartingNode()) {
LOG.warn("Exception for " + block, e);
}
responderClosed = true;
}
} finally {
if (scope != null) {
scope.close();
}
scope = null;
}
}
}?