RH358配置Web服务器–使用Nginx配置Web服务器
介绍Nginx的基础应用与配置。做为基础理解与运用。
RH358专栏地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41765918/category_11532281.html
1. 安装 Nginx
Nginx是Apache HTTP服务器的替代品,也是互联网上使用最广泛的web服务器之一。它的设计目标之一是提供比Apache更好的性能,并处理更多的并发请求。它还经常用作反向缓存代理和负载均衡。但是,它在配置上不如Apache灵活,并且在某些情况下更难使用新特性进行扩展。
RHEL 8 提供 Nginx 作为 application streams。有两个版本可用
-
Nginx 1.14的应用程序流是随着RHEL 8.0发布的,将在2021年5月退休,并被设置为默认值。
-
Nqinx 1.16的应用程序流随着RHEL 8.1发布,将在11月退休2021。
[root@host ~]# yum module install nginx:1.16
可以使用下面的命令来验证Nginx的安装和版本:
[root@host ~]# nginx -v
nginx version: nginx/1.16.1
2. 配置 Nginx
Nginx的默认配置根目录是/etc/nginx。其主配置文件为/etc/nginx/nginx.conf。该文件包含web服务器的全局设置,包括主网站的默认服务器块。它还从/etc/nginx/conf.d加载额外的配置文件。
Nginx 的配置文件中包含指令。指令由指令名称、空格分隔的参数列表以及结束指令的分号组成。
块指令与简单指令相似,但不是以分号结束,而以括在大括号中的?组额外指令结束。
在配置的顶层,有四个特殊的块指令称为上下文,它们将指令分组在一起,以管理不同类型的流量:
-
events:用于常规连接处理
-
http:用于 HTTP 流量
-
mail:用于电子邮件流量
-
stream:用于 TCP 和 UDP 流量
没有包含在这些上下文中的顶层指令称为在主上下文中。
在本课程中,最重要的上下文是http上下文。/etc/nginx/conf.d中的.conf文件被加载到该上下文中。
配置虚拟服务器
在http上下文中,server block指令定义了Nginx提供的http虚拟服务器。创建一个新的虚拟服务器最简单的方法是在/etc/nginx/conf.d中放置一个包含一个或多个服务器块的 .conf文件
下面的示例指定了一个基本的虚拟服务器,它与端口80/TCP和主机名example.com或www.example.com相匹配。location指令将其文档根目录设置为/srv/www/www.example.com。
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
location / {
root /srv/www/www.example.com;
}
}
服务器名可以是精确的名称,可以包含一个通配符来替换名称的第一部分或最后一部分,或者可以使用正则表达式:
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.example.com *.lab.example.com ~^server.?\.example.\com$;
location / {
root /srv/www/www.example.com;
}
}
当搜索一个匹配基于名称的虚拟主机的虚拟服务器时,Nginx尝试找到第一个匹配的名称,如下所示:
-
使用与之匹配的确切名称。
-
如果没有找到匹配,Nginx尝试匹配以星号开头的最长通配符名。
-
如果没有找到匹配,Nginx尝试匹配以星号结尾的最长通配符名。
-
最后,按照配置文件顺序匹配的第一个正则表达式。
access_log指令和error_log指令设置日志文件的路径、格式和配置。主要参数是要使用的日志格式。(/etc/nginx/nginx.conf配置文件中http上下文中的log_format指令定义了main.)
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
access_log /var/log/nginx/example.com_access.log main;
error_log /var/log/nginx/example.com_error.log main;
location / {
root /srv/www/example.com;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
文档根目录的内容必须是运行nginx进程的nginx用户可读的。Nginx使用与Apache HTTP Server相同的SELinux上下文。
配置TLS虚拟服务器
配置支持HTTPS协议的虚拟服务器:
-
将 listen 设置为 443 ssl
-
将 ssl_certificate 设置为包含 TLS 服务器证书的文件
-
将 ssl_certificate_key 设置为包含 TLS 服务器证书私钥的文件
产生的server块可能如下所示:
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/pki/tls/certs/example.com.rsa.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/pki/tls/private/example.com.rsa.key;
location / {
root /sites/$domain;
}
}
如果希望在端口80/TCP上使用HTTP连接到您的站点的用户被自动重定向到安全站点,可以添加另一个服务器块来监听端口80/TCP,该服务器块使用返回指令发送一个HTTP 301 Redirect来实现此目的。完整的配置如下所示:
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/pki/tls/certs/example.com.rsa.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/pki/tls/private/example.com.rsa.key;
location / {
root /sites/$domain;
}
}
检查配置文件是否有错误
有两个命令对于验证配置文件是否有错误非常有用。
-
nginx -t将检查你的配置文件的语法问题,并尝试打开配置文件引用的任何文件。它在退出时提供一个简短的报告
-
nginx -T将做同样的事情,但它也将转储配置文件到标准输出时,退出
当对配置文件进行更改时,需要重新加载nginx服务才能使更改生效。
3. 运行Nginx
启动Nginx,使用Nginx服务单元:
[root@host ~]# systemctl enable --now nginx
这将以nginx用户启动nginx进程。
还需要确保http和https防火墙服务是打开的,以便客户端可以与服务器通信。
4. 课本练习
[student@workstation ~]$ lab web-nginx start
1. 找出Nginx默认安装的版本。
[root@servera ~]# yum module list *nginx*
Last metadata expiration check: 0:02:55 ago on Tue 29 Jun 2021 10:44:45 AM CST.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.1 AppStream (dvd)
Name Stream Profiles Summary
nginx 1.14 [d] common [d] nginx webserver
nginx 1.16 common [d] nginx webserver
Hint: [d]efault, [e]nabled, [x]disabled, [i]nstalled
[root@servera ~]# yum module reset nginx
Last metadata expiration check: 0:03:02 ago on Tue 29 Jun 2021 10:44:45 AM CST.
Dependencies resolved.
Nothing to do.
Complete!
[root@servera ~]# yum module -y install nginx:1.16
2. 使用标识内容和适当的SELinux上下文创建两个内容目录。
[root@servera ~]# mkdir -p /srv/nginx/{www-a,servera}/www
3. 在两个内容目录中创建带有不同web内容的index.html文件。
[root@servera ~]# echo 'This is the www-a page' > /srv/nginx/www-a/www/index.html
[root@servera ~]# echo 'This is the servera page' > /srv/nginx/servera/www/index.html
4. 将目录/srv/nginx重新标记为httpd_sys_content_t从而添加到SELinux策略中。
[root@servera ~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t '/srv/nginx(/.*)?'
[root@servera ~]# restorecon -vvFR /srv/nginx
Relabeled /srv/nginx from unconfined_u:object_r:var_t:s0 to system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /srv/nginx/www-a from unconfined_u:object_r:var_t:s0 to system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /srv/nginx/www-a/www from unconfined_u:object_r:var_t:s0 to system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /srv/nginx/www-a/www/index.html from unconfined_u:object_r:var_t:s0 to system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /srv/nginx/servera from unconfined_u:object_r:var_t:s0 to system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /srv/nginx/servera/www from unconfined_u:object_r:var_t:s0 to system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /srv/nginx/servera/www/index.html from unconfined_u:object_r:var_t:s0 to system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
5. 按要求创建TLS虚拟服务器
[root@servera ~]# scp workstation:/home/student/*.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/ #环境已经弄好
root@workstation's password: redhat
[root@servera ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/www-a.lab.example.com.conf
server {
listen 80 ;
server_name www-a.lab.example.com;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www-a.lab.example.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/pki/tls/certs/www-a.lab.example.com.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/pki/tls/private/www-a.lab.example.com.key;
location / {
root /srv/nginx/www-a/www;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
[root@servera ~]# cp /etc/nginx/conf.d/www-a.lab.example.com.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/servera.lab.example.com.conf
[root@servera ~]# sed -i 's/www-a/servera/g' /etc/nginx/conf.d/servera.lab.example.com.conf
6. 将证书和密钥文件拷贝到服务器的/etc/pki/tls/certs和/etc/pki/tls/private目录下。
[root@servera ~]# cd /etc/pki/tls/certs
[root@servera certs]# scp workstation:/home/student/*.crt ./
root@workstation's password: redhat
cacert.crt 100% 1395 683.7KB/s 00:00
servera.lab.example.com.crt 100% 4583 1.6MB/s 00:00
www-a.lab.example.com.crt 100% 4577 1.7MB/s 00:00
[root@servera certs]# cd /etc/pki/tls/private
[root@servera private]# scp workstation:/home/student/*.key ./
root@workstation's password: redhat
servera.lab.example.com.key 100% 1708 460.3KB/s 00:00
www-a.lab.example.com.key 100% 1704 561.5KB/s 00:00
7. 启动并启用Nginx服务并打开相应的防火墙端口。
[root@servera private]# systemctl enable --now nginx
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nginx.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service.
[root@servera private]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http --add-service=https
success
[root@servera private]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
8. 测试访问。
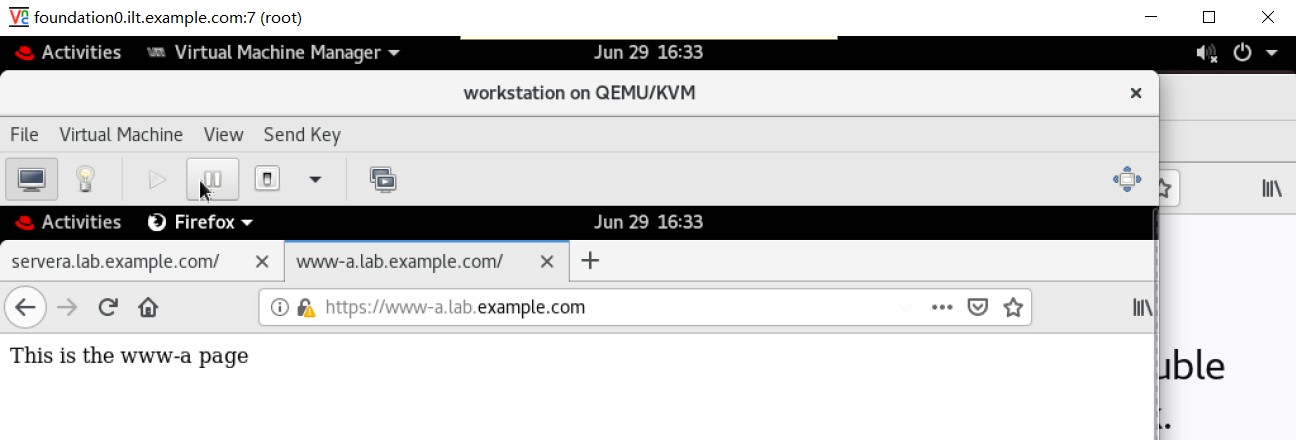
完成实验。
[student@workstation ~]$ lab web-nginx finish
总结
- 安装和配置Nginx。
- 配置与演示web服务。
- 若喜欢金鱼哥的文章,顺手点个赞。也可点个关注,因为后续会不断上干货。
