一、什么是自定义容器
自定义容器本质上也是一个组件,常见的 LinearLayout、FrameLayout、GridLayout、ScrollView和 RelativeLayout 等等组件都是容器,容器除了有自己的外观,还能用来容纳各种组件,以一种特定的规则规定组件应该在什么位置、显示多大。
一般情况下,我们更关注自定义组件的外观及功能,但自定义容器则更关注其内的组件怎么排列和摆放,比如线性布局 LinearLayout 中的组件只能水平排列或垂直排列,帧布局FrameLayout中的组件可以重叠,相对布局 RelativeLayout 中的组件可以以某一个组件为参照定位自身的位 置……容器还关注组件与容器四个边框之间的距离(padding),或者容器内组件与组件之间的距离(margin)
事实上,容器是可以嵌套的,一个容器中,既可以是普通的子组件,也可以是另一个子容器。
容器类一般要继承 ViewGroup 类,ViewGroup 类同时也是 View 的子类,ViewGroup 又是一个抽象类,定义了 onLayout()等抽象方法。当然,根据需要,我们也可以让容器类继承自 FrameLayout 等 ViewGroup 的子类,比如 ListView 继承自 ViewGroup,而 ScrollView
水平滚动容器类则从 FrameLayout 派生。
1.1 ViewGroup类
ViewGroup作为容器类的父类,自然有他自己鲜明的特征,开发自定义容器必须先要了解ViewGroup。在ViewGroup 中,定义了一个 View[]类型的数组mChildren,该数组保存了容器中所有的子组件,负责维护组件的添加、移除、管理组件顺序等功能,另一个成员变量mChildrenCount 则保存了容器中子组件的数量。在布局文件(layout)中,容器中的子元素会根据顺序自动添加到mChildren数组中。
ViewGroup 具备了容器类的基本特征和运作流程,也定义了相关的方法用于访问容器内的组件,获取子View数量和子View的方法:
/**
* 获取容器内的子组件的个数
*
* @return
*/
public int getChildCount();
/**
* 容器内的所有子组件都存储在名为 mChildren的View[]数组中,该方法通过索引index找到指定位置的子组件
*
* @param index
* @return
*/
public View getChildAt(int index);
添加View有如下方法:
public void addView(View child, int index, LayoutParams params);
public void addView(View child, LayoutParams params);
public void addView(View child, int index);
public void addView(View child);
向容器中添加新的子组件时,子组件不能有父容器,否则会抛出“The specified child already has a parent(该组件已有父容器)”的异常。
删除View有如下方法:
public void removeViewAt(int index);
public void removeView(View view);
public void removeViews(int start, int count);
测量View有如下方法:
// 测量给定的子组件的尺寸
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int parentHeightMeasureSpec);
// 测量所有子组件的尺寸
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec);
// 该方法从View类中继承,用于测量组件或容器自己的尺寸,参数widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec为0时表示按实际大小进行测量,将0传入方法常常会有奇效。
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec);
ViewGroup 运行的基本流程大致为:
1)测量容器尺寸
重写 onMeasure()方法测量容器大小,和自定义View有所区别的是,在测量容器大小之前,必须先调用measureChildren()方法测量所有包含的子View的大小,不然结果永远为 0。
2)确定每个子组件的位置
重写 onLayout()方法确定每个子组件的位置(这个其实挺麻烦,也是定义容器的难点部分),在onLayout()方法中,调用View的layout()方法确定子组件的位置。
3)绘制容器
重写 onDraw()方法,其实ViewGroup类并没有重写onDraw()方法,除非有特别的要求,自定义容器也很少去重写。比如LinearLayout 重写了该方法用于绘制水平或垂直分割条,而FrameLayout则是重写了draw()方法,作用其实是一样的。
1.2 ViewGroup的工作原理
1.2.1 ViewGroup的onMeasure分析
ViewGroup作为View的子类,流程基本是相同的,但另一方面ViewGroup作为容器的父类,又有些差异,我们通过阅读源码来了解ViewGroup的工作原理,前面说到,重写ViewGroup的onMeasure()方法时,必须先调用measureChildren()方法测量子组件的尺寸,该方法源码如下:
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int size = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {
// 测量指定子View
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
measureChildren()方法中,循环遍历每一个子组件,如果当前子组件的可见性不为GONE也,就是没有隐藏则继续调用measureChild(child,widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec)方法测量当前子组件child的大小,我们继续进入measureChild()方法。
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
// 计算子View测量模式
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
// 调用子View的measure方法
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
measureChild()方法结合父容器的 MeasureSpec、父容器的Padding和子组件LayoutParams 三个因素利用getChildMeasureSpec() 计算出子组件的尺寸模式和尺寸大小(可以跟踪到getChildMeasureSpec()方法中查看,前面基础篇也有介绍),并调用子组件的measure()方法进行尺寸测量measure()方法的实现如下:
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
// 最终触发子View的onMeasure方法
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
...
}
真相慢慢露出水面,View的measure()方法调用了 onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec)方法,该方法正是我们重写子View的用来测量组件尺寸的方法,至此,测量组件尺寸的工作已掌握到开发人员手中。
当measureChildren流程走完之后,该自定义容器内的所有子View就可以通过getMeasureWidth()和getMeasureHeight获取测量后的宽高了,然后容器自身就可以计算出最大宽度和高度来定义自身的宽高了。模板代码如下:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 1.先测量所有的子View
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 然后测量自身宽高
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
// 假设每一行只能放一个子控件,具体按照需求而定
int maxWidth = 0;
int totalHeight = 0;
int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 记录每一行的最大宽度
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, child.getMeasuredWidth());
totalHeight += child.getMeasuredHeight();
}
if (widthMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
width = Math.min(width, maxWidth);
}
if (heightMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
height = Math.min(height, totalHeight);
}
// 2.设置父容器的宽高
setMeasuredDimension(width,height);
}
1.2.2 ViewGroup的onLayout分析
分析完ViewGroup的onMeasure原理后,再来分析onLayout的原理,在 onLayout()方法中, 我们将调用子组件的 layout()方法,这里要一分为二,如果子组件是一个 View,定位流程到此结束,如果子组件又是一个容器呢?我们进入 layout()方法进行跟踪。
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
...
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
// 如果子View也是容器类,那么也会调用onLayout进行分发
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
...
}
}
如果子组件是一个容器,又会继续调用该容器的 onLayout()方法对孙组件进行定位,所以,onLayout()方法也是一个递归的过程。
举个例子,重写自定义容器的onLayout方法如下:
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
int top = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 布局子View
child.layout(l, top, l + child.getMeasuredWidth(), top + child.getMeasuredHeight());
// 假设一行只能放一个子View ,那么放完上一个后,需要下一个的top
top += child.getMeasuredHeight();
}
}
1.2.3 ViewGroup的onDraw分析
onMeasure()方法和onLayout()方法调用完成后,该轮到onDraw()方法了,ViewGroup类并没有重写该方法,通常情况下重写onDraw是不会回调的,除非该自定义容器设置背景色或者背图,从第一章中我们都知道每一个组件在绘制时是会调用View的draw()方法的,我们进入draw()方法进行跟踪。
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
...
/*
* Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
* in the appropriate order:
*
* 1. Draw the background
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
* 7. If necessary, draw the default focus highlight
*/
// Step 1, draw the background, if needed
int saveCount;
drawBackground(canvas);
// skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case)
final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0;
boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0;
if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) {
// Step 3, draw the content
onDraw(canvas);
// Step 4, draw the children
dispatchDraw(canvas);
drawAutofilledHighlight(canvas);
// Overlay is part of the content and draws beneath Foreground
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
}
// Step 6, draw decorations (foreground, scrollbars)
onDrawForeground(canvas);
// Step 7, draw the default focus highlight
drawDefaultFocusHighlight(canvas);
if (isShowingLayoutBounds()) {
debugDrawFocus(canvas);
}
// we're done...
return;
}
...
}
draw()方法中执行了语句dispatchDraw(canvas),但是,当我们跟踪到View类的dispatchDraw()方法时发现该方法是空的。
但对于ViewGroup来说,该方法的作用非同小可,因为ViewGroup重写了dispatchDraw()方法。并且该方法是一定会回调的,重写此方法后记得需要调用super.dispatchDraw,因为子View的绘制分发是在ViewGroup的dispatchDraw方法内的,如果不调用super.dispatchDraw,那么子View将不会绘制。
// ViewGroup.java
@Override
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
...
final int childrenCount = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
int flags = mGroupFlags;
...
for (int i = 0; i < childrenCount; i++) {
while (transientIndex >= 0 && mTransientIndices.get(transientIndex) == i) {
final View transientChild = mTransientViews.get(transientIndex);
if ((transientChild.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE ||
transientChild.getAnimation() != null) {
// 调用drawChild来触发子组件的绘制
more |= drawChild(canvas, transientChild, drawingTime);
}
...
}
...
}
...
}
dispatchDraw()方法的作用是将绘制请求纷发到给子组件,并调用drawChild()方法来完成子组件的绘制,drawChild()方法的源码如下:
protected boolean drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime) {
// 非常精简,就一行代码
return child.draw(canvas, this, drawingTime);
}
继续看View的draw方法,注意是3个参数的draw方法
boolean draw(Canvas canvas, ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime) {
...
if (!drawingWithDrawingCache) {
if (drawingWithRenderNode) {
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK;
((RecordingCanvas) canvas).drawRenderNode(renderNode);
} else {
// Fast path for layouts with no backgrounds
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW) == PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW) {
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK;
dispatchDraw(canvas);
} else {
// 关键代码,调用View的一个参数的draw方法,最终会触发onDraw方法
draw(canvas);
}
}
}
...
return more;
}
可以看到ViewGroup经过dispathDraw方法最终会回调子View的draw方法,而View的draw方法前面我们已经分析过了,最终会触发子View的onDraw方法。
二、综合案例
2.1 CornerLayout布局
CornerLayout 布局是一个自定义容器,用于将子组件分别显示在容器的4个角落,不接受超过4个子组件的情形,默认情况下,子组件按照从左往右、从上往下的顺序放置,但可以为子组件指定位置(左上角 left_top、右上角 right_top、左下角 left_bottom、右下角right_bottom)。CornerLayout并不具备实用价值,因为FrameLayout布局能轻易实现CornerLayout 的功能,但是,对于理解布局容器的开发却能提供一种非常清晰的方法和思路(这个才是最重要的,不是么?)。
2.1.1 分析容器的宽高
先画一个草图来帮助我们分析

上图中,蓝色框表示CornerLayout布局的区域A、B、C、D 是CornerLayout内的4个子组件,对于CornerLayout来说,首先要测量的是他的尺寸大小,当其layout_width为wrap_content时,它的宽度计算应该满足下面要求:
容器的最小宽度 = 容器的paddingLeft + 容器的paddingRight +
A或者C的最大leftMargin+rightMargin +
A或者C的最大宽度 +
B或者D的最大宽度 +
B或者D的最大leftMargin+rightMargin
当容器的layout_height为wrap_content时,它的高度计算应该满足下面要求:
容器的最小高度 = 容器的paddingTop + 容器的paddingBottom +
A或者B的最大topMargin+bottomMargin +
A或者B的最大高度 +
C或者D的最大高度 +
C或者D的最大topMargin+bottomMargin
这样才不至于子组件出现重叠,当然,如果layout_width 和 layout_height指定了具体值或者屏幕不够大的情况下设置为match_parent,子组件仍有可能会出现重叠现象。
2.1.2 分析容器的内边距
上面分析padding,View类已经提供了对应的方法获取上下左右的内边距了,如下所示:
public int getPaddingLeft();
public int getPaddingTop();
public int getPaddingRight();
public int getPaddingBottom();
2.1.3 分析子View的外边距
而对于子View外边距,我们只能通过MarginLayoutParams来获取,MarginLayoutParams是ViewGroup.LayoutParams的子类,它暴露了公共的属性可以获取View的四个方向的外边距
public static class MarginLayoutParams extends ViewGroup.LayoutParams {
public int leftMargin;
public int topMargin;
public int rightMargin;
public int bottomMargin;
}
然而ViewGroup在添加子View的时候,使用的LayoutParams并不是MarginLayoutParams,这个可以查看其addView方法源码:
public void addView(View child, LayoutParams params) {
addView(child, -1, params);
}
public void addView(View child, int index, LayoutParams params) {
...
requestLayout();
invalidate(true);
addViewInner(child, index, params, false);
}
你可能会说这也看不出什么名堂啊, 我们来想一下我们定义在布局中的子View是如何被加载到父容器的,了解过Activity的setContentView源码的人就会知道布局的解析其实是通过LayoutInflate来完成,我们看看LayoutInflate的inflate方法
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
...
final String name = parser.getName();
if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
...
} else {
// Temp is the root view that was found in the xml 注意这句话Temp就是布局的根View
final View temp = createViewFromTag(root, name, inflaterContext, attrs);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null;
if (root != null) {
// 创建布局根View的布局参数
params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
if (!attachToRoot) {
temp.setLayoutParams(params);
}
}
...
// Inflate all children under temp against its context. 注意这句话,就是解析temp根容器下的所有子view
rInflateChildren(parser, temp, attrs, true);
...
return result;
}
final void rInflateChildren(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, AttributeSet attrs, boolean finishInflate) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
// 一句话,看rInflate
rInflate(parser, parent, parent.getContext(), attrs, finishInflate);
}
void rInflate(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, Context context,AttributeSet attrs, boolean finishInflate) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
...
while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG ||
parser.getDepth() > depth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
continue;
}
final String name = parser.getName();
if (TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS.equals(name)) {
...// 前面都是合法性检测
} else {
// 创建子View
final View view = createViewFromTag(parent, name, context, attrs);
// 此parent就是父容器
final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent;
// 1.关键代码生成子View的布局属性
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
// 如果子View也是容器类,则调用下面方法继续递归
rInflateChildren(parser, view, attrs, true);
// 2.关键代码,终于看到了ViewGroup的addView方法调用了,并且传入的params是通过generateLayoutParams生成的.
viewGroup.addView(view, params);
}
}
}
现在我们来看看ViewGroup的generateLayoutParams方法
// 在解析xml的时候会调用
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
// 注意看返回的是LayoutParams,而不是MarginLayoutParams
return new LayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
// 这里直接返回参数
return p;
}
// 在代码中调用addView的时候,如果子View没有传布局参数,那么就会调用此方法生成默认的布局参数
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
// 注意看返回的是LayoutParams,而不是MarginLayoutParams
return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
观察上面3个生成布局参数的方法可以发现ViewGroup默认生成的其实是LayoutParams而不是MarginLayoutParams,因此我们这个CornerLayout容器需要重写这3个方法,使其返回的是MarginLayoutParams,这样我们在获取子View的布局参数的时候就可以得到MarginLayoutParams了,进而就可以获取到子View的外边距了,重写如下:
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(p);
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new MarginLayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
2.1.4 重写CornerLayout的onMeasure方法确定容器的宽高
在确定容器的宽高前,我们需要先调用measureChildren方法测量子View,否则获取子View的宽高都是0,具体代码如下:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 1.先测量所有的子View
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 2.计算容器自身的宽高
int width = calcSelfWidth(widthMeasureSpec);
int height = calcSelfHeight(heightMeasureSpec);
// 3.设置容器的最终宽高
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
// 计算容器的宽度
private int calcSelfWidth(int widthMeasureSpec) {
int mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
if (mode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
// 针对wrap_content处理
int count = getChildCount();
// 分别表示左上角、左下角、右上角、右下角的View的宽度
int ltWidth = 0;
int lbWidth = 0;
int rtWidth = 0;
int rbWidth = 0;
// 分别表示表示左上角、左下角、右上角、右下角的View的左右外边距
int ltMarginH = 0;
int lbMarginH = 0;
int rtMarginH = 0;
int rbMarginH = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
if (i == 0) {
// 左上角
ltWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
ltMarginH = params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin;
} else if (i == 1) {
// 右上角
rtWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
rtMarginH = params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin;
} else if (i == 2) {
// 左下角
lbWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
lbMarginH = params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin;
} else if (i == 3) {
// 右下角
rbWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
rbMarginH = params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin;
}
}
// 容器的最小宽度 = 容器的paddingLeft + 容器的paddingRight + A或者C的最大leftMargin+rightMargin + A或者C的最大宽度 + B或者D的最大宽度 + B或者D的最大leftMargin+rightMargin
width = getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight() +
Math.max(ltMarginH, lbMarginH) +
Math.max(ltWidth, lbWidth) +
Math.max(rtWidth, rbWidth) +
Math.max(rtMarginH, rbMarginH);
}
return width;
}
// 计算容器高度
private int calcSelfHeight(int heightMeasureSpec) {
int mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if (mode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
// 针对wrap_content处理
int count = getChildCount();
// 分别表示左上角、左下角、右上角、右下角的View的高度
int ltHeight = 0;
int lbHeight = 0;
int rtHeight = 0;
int rbHeight = 0;
// 分别表示表示左上角、左下角、右上角、右下角的View的上下外边距
int ltMarginV = 0;
int lbMarginV = 0;
int rtMarginV = 0;
int rbMarginV = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
if (i == 0) {
// 左上角
ltHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
ltMarginV = params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin;
} else if (i == 1) {
// 右上角
rtHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
rtMarginV =params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin;
} else if (i == 2) {
// 左下角
lbHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
lbMarginV = params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin;
} else if (i == 3) {
// 右下角
rbHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
rbMarginV = params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin;
}
}
//容器的最小高度 = 容器的paddingTop + 容器的paddingBottom + A或者B的最大topMargin+bottomMargin + A或者B的最大高度 + C或者D的最大高度 + C或者D的最大topMargin+bottomMargin
height = getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom() +
Math.max(ltMarginV, rtMarginV) +
Math.max(ltHeight, rtHeight) +
Math.max(lbHeight, rbHeight) +
Math.max(lbMarginV, rbMarginV);
}
return height;
}
2.1.5 重写CornerLayout的onLayout方法确定子View的位置
现在需要对子View在容器的4个角落进行位置摆放了.具体代码如下:
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int count = getChildCount();
// 内边距
int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();
int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 外边距
int leftMargin = params.leftMargin;
int rightMargin = params.rightMargin;
int topMargin = params.topMargin;
int bottomMargin = params.bottomMargin;
// 子View宽高
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
if (i == 0) {
// 左上角
int left = paddingLeft + leftMargin;
int top = paddingTop + topMargin;
child.layout(left, top, left + childWidth, top + childHeight);
} else if (i == 1) {
// 右上角
int left = getMeasuredWidth() - paddingRight - rightMargin - childWidth;
int top = paddingTop + topMargin;
child.layout(left, top, left + childWidth, top + childHeight);
} else if (i == 2) {
// 左下角
int left = paddingLeft + leftMargin;
int top = getMeasuredHeight() - paddingBottom - bottomMargin - childHeight;
child.layout(left, top, left + childWidth, top + childHeight);
} else if (i == 3) {
// 右下角
int left = getMeasuredWidth() - paddingRight - rightMargin - childWidth;
int top = getMeasuredHeight() - paddingBottom - bottomMargin - childHeight;
child.layout(left, top, left + childWidth, top + childHeight);
}
}
}
2.1.6 效果展示
1)父容器match_parent的效果

2) 父容器wrap_content的效果

3) 父容器wrap_content+padding效果

黑色背景是我故意加的,为了能看出内边距
4) 父容器wrap_content+padding+子View外边距效果
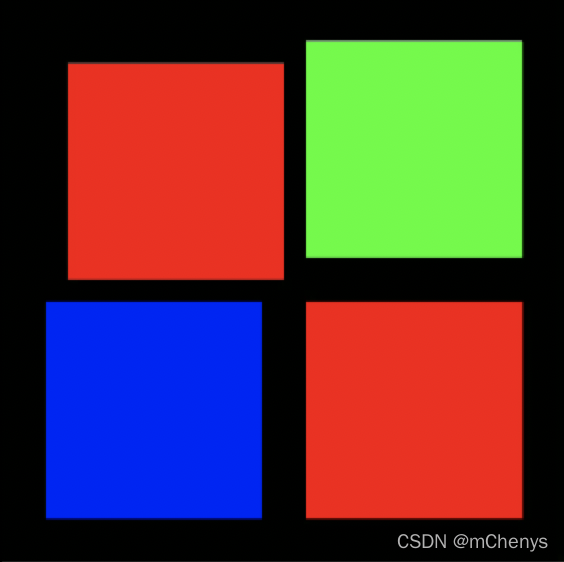
上图值设置了左上角的4个方向的margin,然后父容器的宽度和高度都撑大了。
2.1.7 自定义LayoutParams
我们前面接触过 LayoutParams 和 MarginLayoutParams 等布局参数类,这两个类都是ViewGroup 的静态内部类。这也为我们自定义 LayoutParams提供了参考依据,各位可以去阅读这两个类的源码以便有更多的了解。
到目前为止,CornerLayout 还不支持显示方位,这也是唯一尚未实现的需求。本节我们将一起来实现这个功能。
方位包含 4 个方向:左上角、右上角、左下角、右下角,在 attrs.xml 文件中,定义一个名为layout_position 的属性,类型为 enum,枚举出这 4 个值。
<declare-styleable name="CornerLayout">
<attr name="layout_position" format="enum">
<enum name="left_top" value="0" />
<enum name="right_top" value="1" />
<enum name="left_bottom" value="2" />
<enum name="right_bottom" value="3" />
</attr>
</declare-styleable>
然后新建PositionLayoutParams继承自MarginLayoutParams, PositionLayoutParams作为CornerLayout的静态内部类
public class CornerLayout extends ViewGroup {
....
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) {
// 返回自定义的LayoutParams
return new PositionLayoutParams(p);
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
// 返回自定义的LayoutParams,关键代码将布局的属性集合传递给了自定义布局参数PositionLayoutParams
return new PositionLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
// 返回自定义的LayoutParams
return new PositionLayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
// 自定义布局参数
public static class PositionLayoutParams extends ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams {
// 4个方位
public static final int LEFT_TOP = 0;
public static final int RIGHT_TOP = 1;
public static final int LEFT_BOTTOM = 2;
public static final int RIGHT_BOTTOM = 3;
public static final int NONE = -1;
public int position;
public PositionLayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
//读取 layout_position 属性
TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CornerLayout);
position = a.getInt(R.styleable.CornerLayout_layout_position, NONE);
a.recycle();
}
public PositionLayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
}
public PositionLayoutParams(ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
public PositionLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
}
}
上述代码中,根据父类的要求定义了4 个构造方法,其中构造方法,其中带AttributeSet参数的构造方法中我们对layout_position属性进行了读取.如果未读取到该属性,则默认值为 NONE。其次定义了4个常量与layout_position属性的4个枚举值相对应。然后在generateLayoutParams()和 generateDefaultLayoutParams()方法中返回自定义的布局参数PositionLayoutParams,其中在generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs)方法将attrs传入PositionLayoutParams构造方法,所以PositionLayoutParams 才能读取到 layout_position 的属性值。
2.1.8 在CornerLayout的onLayout方法中根据布局参数的方位来布局
在 onLayout()方法中,我们需要根据当前子组件的 PositionLayoutParams 的 position 属性来确定方位,这里有两种情况:一种是没有为组件定义方位时,依旧按照从左往右、从上往下的方式进行放置;另一种是如果组件定义了特定方位,如 right_bottom,则将该组件显示在容器的右下角。
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int count = getChildCount();
// 内边距
int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();
int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
PositionLayoutParams params = (PositionLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 外边距
int leftMargin = params.leftMargin;
int rightMargin = params.rightMargin;
int topMargin = params.topMargin;
int bottomMargin = params.bottomMargin;
// 布局方位
int position = params.position;
// 子View宽高
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
if (i == 0 && position == PositionLayoutParams.NONE
|| position == PositionLayoutParams.LEFT_TOP) {
// 左上角
int left = paddingLeft + leftMargin;
int top = paddingTop + topMargin;
child.layout(left, top, left + childWidth, top + childHeight);
} else if (i == 1 && position == PositionLayoutParams.NONE
|| position == PositionLayoutParams.RIGHT_TOP) {
// 右上角
int left = getMeasuredWidth() - paddingRight - rightMargin - childWidth;
int top = paddingTop + topMargin;
child.layout(left, top, left + childWidth, top + childHeight);
} else if (i == 2 && position == PositionLayoutParams.NONE
|| position == PositionLayoutParams.LEFT_BOTTOM) {
// 左下角
int left = paddingLeft + leftMargin;
int top = getMeasuredHeight() - paddingBottom - bottomMargin - childHeight;
child.layout(left, top, left + childWidth, top + childHeight);
} else if (i == 3 && position == PositionLayoutParams.NONE
|| position == PositionLayoutParams.RIGHT_BOTTOM) {
// 右下角
int left = getMeasuredWidth() - paddingRight - rightMargin - childWidth;
int top = getMeasuredHeight() - paddingBottom - bottomMargin - childHeight;
child.layout(left, top, left + childWidth, top + childHeight);
}
}
}
为了更加清晰地看明白 CornerLayout3 容器内子组件的位置,我们为子组件 TextView 分别添加了 A、B、C、D 四个字符作为 text 属性的值,在没有为子组件指定方位的情况下,修改activity_main.xml 布局文件,内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.mchenys.viewmodel.CornerLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:padding="20dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_bright"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="A"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="B"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="C"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="D"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF" />
</com.mchenys.viewmodel.CornerLayout>
效果图:
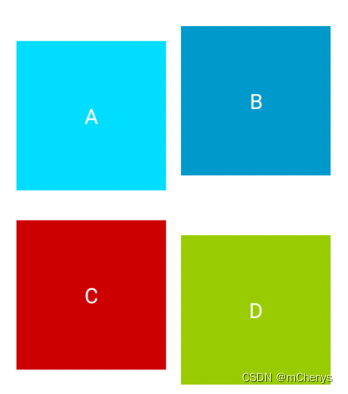
接下来,我们为每个子组件都指定一个不同的方位(方位相同会重叠),修改如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.mchenys.viewmodel.CornerLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:padding="20dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_bright"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="A"
app:layout_position="right_bottom"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="B"
app:layout_position="left_bottom"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="C"
app:layout_position="left_top"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
app:layout_position="right_top"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="D"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF" />
</com.mchenys.viewmodel.CornerLayout>
效果图:

2.2 流式布局(FlowLayout)
在 Java Swing 中,有一种布局,叫流式布局(FlowLayout),这种布局的特点是子组件按照从左往右、从上往下的顺序依次排序,如果一行放不下,自动显示到下一行,和 HTML 中的float 效果类似,但在,Android 中没有提供这样的布局,本节,我们将一起来实现这种布局。
对于 FlowLayout 来说,难点有二:一是要事先预测组件的宽度和高度,这个和 CornerLayout有明显的不同,FlowLayout 中的组件数是不固定的,而 CornerLayout 中最多只支持 4 个子组件,前者的难度系数更大,也需要更灵活的处理;二是对子组件进行定位时,也是个头痛的问题,子组件的大小不一,数量多少不一,每一个组件放在哪一行、放在一行中的什么位置都需要计算,最重要的是要找到规律,不可能一个一个去处理。
测量 FlowLayout 容器的宽度时,不允许子组件的宽度比容器的宽度还大,这是前提。当子组件个数很少,总宽度比容器的 layout_width 为 match_parent 时的宽度小,那么容器的layout_width 为 wrap_content 时就是子组件的宽度之和。但是如果子组件个数很多,总宽度超出容器的最大宽度,则就算容器的 layout_width 为 wrap_content 最终测量宽度也要采用match_parent 值,并且需要另起一行继续显示上一行余下的子组件。
2.2.1 重写FlowLayout的onMeasure方法确定容器的宽高
1)测量 FlowLayout 容器的宽度时,不允许子组件的宽度比容器的宽度还大,这是前提。当子组件个数很少,总宽度比容器的layout_width=match_parent时的宽度,或者小于容器写死的宽度dp,那么当容器的layout_width=wrap_content时,它的实际宽度就是所有子组件的宽度之和。但是如果子组件个数很多,总宽度超出容器的最大宽度,则容器的实际宽度是最大宽度,并且需要另起一行继续显示上一行余下的子组件。
2)FlowLayout容器高度是每一行最高的组件的高度之和。因为测量时并不需要显示子组件,所以我们采用预测的方法判断是否需要换行,换行后计算出当前行最高的组件高度并进行累加,最后算出所有行的最高高度之和。
3) 除此之外,我们还需要考虑容器的内边距和子View的外边距,谈到外边距就离不开MarginLayoutParams,因此我们还的重写容器的generateLayoutParams方法,前面有介绍过原因,这里就不赘述了.
具体代码如下:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 先测量所有子View
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 计算容器的宽高
int width = calcSelfWidth(widthMeasureSpec);
int height = calcSelfHeight(heightMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
// 计算容器的宽度
private int calcSelfWidth(int widthMeasureSpec) {
int mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
if (mode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
// 只处理wrap_content即可,其他情况使用容器的最大宽度或者写死的dp宽度
int count = getChildCount();
int childrenWidth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth()+ params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin;
//单个子组件的宽度不能超过容器宽度
if (childWidth > width) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Subview is too large.");
}
childrenWidth += childWidth;
}
//在wrap_content 的情况下,如果子组件占的总宽度<容器的最大宽度,则应该取所有子容器的宽度之和
if (childrenWidth < width) {
width = childrenWidth;
}
//padding
width += this.getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
}
return width;
}
// 计算容器的高度
private int calcSelfHeight(int heightMeasureSpec) {
int mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if (mode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
// 只处理wrap_content
int count = getChildCount();
// 由于onMeasure会多次触发,因此这里是可以的到测量后的宽度的,第一次会是0
int maxWidth = getMeasuredWidth() - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight();
int currLineHeight = 0;//当前行的子组件的最大高度
int usedLineWidth = 0;//当前行的子组件的总宽度
int totalHeight = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
// 累加当前行宽
usedLineWidth += (childWidth + params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin);
// 记录当前行最大的高度
currLineHeight = Math.max(childHeight + params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin, currLineHeight);
// 预测是否需要换行,需要换行则累加高度
if (i + 1 < count) {
View next = getChildAt(i + 1);
params = (MarginLayoutParams) next.getLayoutParams();
int nextWidth = next.getMeasuredWidth() + params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin;
if (usedLineWidth + nextWidth > maxWidth) {
totalHeight += currLineHeight;
currLineHeight = 0;
usedLineWidth = 0;
}
} else if (i == count - 1) {
// 最后一个行高别忘记了
totalHeight += currLineHeight;
}
}
height = totalHeight + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
}
return height;
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(p);
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new MarginLayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
2.2.2 重写FlowLayout的onLayout方法确定子View的位置
重写 onLayout()方法定位子组件时,是一个逻辑性比较强的工作。从第 0 个子组件开始,一个个进行定位,如果当前行的已占宽度加上当前子组件的宽度大于容器的宽度,则要换行,换行后下一行的top就需要累加变化.
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int count = getChildCount();
int currLineHeight = 0; //当前行的子组件的最大高度
int usedLineWidth = 0; //当前行的子组件的总宽度
int usedTotalHeight = 0; //累计高度
int width = getMeasuredWidth() - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight(); //容器宽度
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin;
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin;
if (usedLineWidth + childWidth > width) {
//换行后需累计当前行的行高
usedTotalHeight += currLineHeight;
//新起一行,新行的已占宽度和高度重置为 0
currLineHeight = 0;
usedLineWidth = 0;
}
// 布局子View
int left = usedLineWidth + params.leftMargin;
int top = usedTotalHeight + params.topMargin;
int right = left + child.getMeasuredWidth();
int bottom = top + child.getMeasuredHeight();
layoutChildView(child, left, top, right, bottom);
// 获取当前行的最高高度
currLineHeight = Math.max(childHeight, currLineHeight);
// 累加当前行的宽度
usedLineWidth += childWidth;
}
}
private void layoutChildView(View child, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// 所有子组件要统一向右和向下平移指定的 padding
child.layout(l + getPaddingLeft(), t + getPaddingTop(), r + getPaddingLeft(), b + getPaddingTop());
}
效果图如下:

布局文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.mchenys.viewmodel.FlowLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/black"
android:padding="20dp">
<TextView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_bright"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="A"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="B"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="C"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="D"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_bright"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="A"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="B"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="C"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="D"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_bright"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="A"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="B"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="C"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="D"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_bright"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="A"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="B"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="C"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="D"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_bright"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="A"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="B"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="C"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="D"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_bright"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="A"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="B"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="C"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="D"
android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
/>
</com.mchenys.viewmodel.FlowLayout>