1.ls指令
对于目录,列出该目录下的所有子目录与文件
对于文件,列出文件名及其他信息
【常用选项】
- -a? 列出目录下所有文件,包括开头隐含的文件
- -l?? 列出文件详细信息
- -d? 将目录像文件一样显示,而不是显示其下的文件
- -F? 显示文件并在后面附上一个用来说明该文件类型的字符,*代表可执行普通文件,/代表目录,@表示符号链接,|表示FIFOs,=表示套接字。
- -i?? 输出文件的 i 节点的索引信息。 如 ls –ai 指定文件
- -k? 以 k 字节的形式表示文件的大小。ls –alk 指定文件
- -n 用数字的 UID,GID 代替名称。
- -r 对目录反向排序
- -t 以时间排序
- -s 在l文件名后输出该文件的大小
- -R 列出所有子目录下的文件
- -1 一行只输出一个文件
【例】
[root@VM-24-9-centos testLinux]# ls
test01
[root@VM-24-9-centos testLinux]# ls -l
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 23 19:46 test01
[root@VM-24-9-centos testLinux]# ls -a
. .. test01
[root@VM-24-9-centos testLinux]# ls -l -a
total 12
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Jan 23 19:46 .
dr-xr-x---. 7 root root 4096 Jan 23 19:46 ..
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 23 19:46 test01
?.和..就是隐藏文件
?【ps1】
[root@VM-24-9-centos testLinux]# ls -a -l test01
total 24
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 23 20:22 .
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Jan 23 20:20 ..
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 8360 Jan 23 20:22 a.out
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 75 Jan 23 20:22 test.c
[root@VM-24-9-centos testLinux]# ls -a -l test01/
total 24
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 23 20:22 .
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Jan 23 20:20 ..
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 8360 Jan 23 20:22 a.out
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 75 Jan 23 20:22 test.c?ls -a -l [目录],这个命令会优先显示目录里面的文件内容,不会优先显示目录
若只想看目录的属性那么再加一个属性-d
[root@VM-24-9-centos testLinux]# ls -a -l -d test01
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 23 20:22 test01
?【ps2】
[root@VM-24-9-centos testLinux]# which ls
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
/usr/bin/ls
[root@VM-24-9-centos testLinux]# ls /usr/bin/ls
/usr/bin/ls
[root@VM-24-9-centos testLinux]# ls -al /usr/bin/ls
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 117608 Nov 17 2020 /usr/bin/ls
[root@VM-24-9-centos testLinux]# which ll
alias ll='ls -l --color=auto'
/usr/bin/ls
[root@VM-24-9-centos testLinux]# alias back='cd ..'
[root@VM-24-9-centos testLinux]# back
[root@VM-24-9-centos ~]# ls
a.out test.c testLinux
?1.我们通过which命令查看特定指令的系统路径,发现ls指令也是一个文件,他的本质也就是LInux上面的一些程序。这种文件也就是window中的.exe文件/可执行程序
2.令人注意的一点是alias这个命令可以取到别名,ls就是ls --color=auto的别名,ll就是ls -l的别名,这就是为什么ll和ls这么相像的原因。
同样也可以对一个命令自定义别名,但是这个别名的作用时间仅限于本次虚拟机的开关机,也就是说他是一次性的,如果想要永久,那么就在磁盘的源文件中改,但是这样会破坏环境,还是不要这样。
2.pwd命令
显示用户当前目录
[root@VM-24-9-centos testLinux]# pwd
/root/testLinux
3.cd指令
Linux系统中,磁盘上的文件和目录被组成一棵目录树,每个节点都是目录或文件。几乎所有操作系统管理文件方式,都是采用多叉树形式
【功能】:改变工作目录,将当前工作目录改变到指定目录下。
[root@VM-24-9-centos test01]# pwd
/root/testLinux/test01 #绝对路径
[root@VM-24-9-centos test01]# cd ../../ #相对路径
[root@VM-24-9-centos test01]# ./a.out #相对路径
hello world
[root@VM-24-9-centos test01]# /root/testLinux/test01/a.out #绝对路径
hello world
绝对路径:具有唯一性,从根目录找到这个文件唯一的道路,每一个节点只有一个父节点。
相对路径:相对于“我”现处的位置的文件,不具有唯一性,因为从多条路径都可以找到一个文件。
./a.out代表的就是相对路径,./代表当前文件
【cd用法举例】
- cd ..? :返回上级目录
- cd /home/linux/ : 绝对路径
- cd /../test01 :相对路径
- cd ~ :进入回家目录
- cd - :返回最近访问目录
通过cd ~进入回家目录
[root@VM-24-9-centos test01]# cd ~
[root@VM-24-9-centos ~]# whoami
root
【注意】:
root对印的工作目录是:/root
普通用户默认所处的工作路径是:/home/XXX
4.touch指令
【功能】:
- 创建文件,普通文本文件
- 更新文件的最新创建时间、修改时间(默认是一样的时间)
[root@VM-24-9-centos test01]# touch myfile.txt
[root@VM-24-9-centos test01]# ll
total 16
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 8360 Jan 23 20:22 a.out
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 23 23:59 myfile.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 75 Jan 23 20:22 test.c
[root@VM-24-9-centos test01]# touch myfile.txt
[root@VM-24-9-centos test01]# ll
total 16
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 8360 Jan 23 20:22 a.out
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 24 00:00 myfile.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 75 Jan 23 20:22 test.c
[root@VM-24-9-centos test01]# stat myfile.txt
File: ‘myfile.txt’
Size: 0 Blocks: 0 IO Block: 4096 regular empty file
Device: fd01h/64769d Inode: 658248 Links: 1
Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root)
Access: 2022-01-24 00:00:41.605727840 +0800
Modify: 2022-01-24 00:00:41.605727840 +0800
Change: 2022-01-24 00:00:41.605727840 +0800
Birth: -
在这里可以看到,touch不仅创建了myfile.txt文件,而且修改了第二次的时间,用stat查看默认的创建时间和修改时间是一样的
5.mkdir指令
【功能】:在当前目录下创建一个文件目录
【常用命令】:
- -p/--parents? :可以是一个路径名称,若此时路径中还没有此目录,加上这个选项,将创建一条路径,即一次可以建立多个目录
mkdir –p test/test1 : 递归建立多个目录【小拓展】
下载tree的命令:
yum install -y tree6.rmdir指令和rm指令
6.1rmdir
rmdir是一个与mkdir相对应的命令,mkdir是建立目录,rmdir是删除命令
【适用对象】:
具有当前目录操作权限的所有使用者
【功能】:
删除空目录
【常用选项】:
- -p 当子目录被删除后如果父目录也变成空目录的话,就连带父目录一起删除。
[root@VM-24-9-centos d2]# ls
d3
[root@VM-24-9-centos d2]# rmdir d3
[root@VM-24-9-centos d2]# ls
[root@VM-24-9-centos d2]#
[root@VM-24-9-centos d2]# mkdir -p d3/d4
[root@VM-24-9-centos d2]# ls
d3
[root@VM-24-9-centos d2]# cd d3
[root@VM-24-9-centos d3]# ls
d4
[root@VM-24-9-centos d3]# cd ..
[root@VM-24-9-centos d2]# rmdir d3
rmdir: failed to remove ‘d3’: Directory not empty我们发现当d3中有文件时,删除d3不成功,rmdir只能删除空目录。
如果想要删除非空文件怎么办呢?
6.2rm
【常用选项】
- -f? 即使文件属性为只读,也可直接删除
- -i? 删除前逐一询问
- -r? 删除目录及其下所有文件
[root@VM-24-9-centos d2]# rm -r d3
rm: descend into directory ‘d3’? y
rm: remove directory ‘d3/d4’? y
rm: remove directory ‘d3’? y
[root@VM-24-9-centos d2]# ls
[root@VM-24-9-centos d2]#
7.man指令
Linux的命令有很多参数,有的我们记不住,那么可以通过man命令查看联机手册获取帮助
【常用选项】:
- -k? 根据关键字搜索联机帮助
- num? 只找num章节
- -a? 将所有章节都显示出来
man可以查看linux内部指令,如果想要查看其它语言的用法,需要下载一个源
yum install -y man-pages如果不成功上面显示pip更新,需要下载更新一下pip。
下载好之后,就可以查看其他相应库中查看想要的内容。
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos ~]$ man man #这个命令下查看man的用法
1 Executable programs or shell commands #默认
2 System calls (functions provided by the kernel) #系统调用函数
3 Library calls (functions within program libraries) #库函数
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos ~]$ man 3 printf
这里的1,2,3代表的是想要查看命令用法的命令的库
- 1是普通命令
- 2是系统调用(如open,write)
- 3是库函数,如printf这种C/C++的库函数
前三个是比较常用的

按q就可以退出
8.cp指令
【功能】:赋值文件或目录? ?? 用法:[cp 源文件? 目的文件]
【说明】:cp指令用于复制文件或目录,
【常用选项】:
- -f/--force? 强行复制文件或目录,不论目的文件或目录是否已经存在
- -i/--interactive? 覆盖文件之前先询问用户
- -r? 递归处理,将指定目录下的文件与子目录一并处理。若源文件或目录的形态,不属于目录或符号链接,则一律视为普通文件处理。
- -R/--recursive? 递归处理,将指定目录下的文件及子目录一并处理
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ cp test.c ../
#拷贝到目的路径,没有指明文件,自动生成一个一样的文件
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ ll ../
total 8
drwxrwxr-x 2 wjy wjy 4096 Jan 24 16:23 test01
-rw-rw-r-- 1 wjy wjy 78 Jan 24 19:26 test.c
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ cp test.c name.c
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ ll ../
total 8
drwxrwxr-x 2 wjy wjy 4096 Jan 24 19:26 test01
-rw-rw-r-- 1 wjy wjy 78 Jan 24 19:26 test.c
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos LinuxTest]$ cp test01 test01_backup
cp: omitting directory ‘test01’
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos LinuxTest]$ cp -r test01 test01_backup
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos LinuxTest]$ ll
total 8
drwxrwxr-x 2 wjy wjy 4096 Jan 24 19:32 test01
drwxrwxr-x 2 wjy wjy 4096 Jan 24 19:36 test01_backup?单纯用cp指令并不能复制目录,如果想要递归复制目录,需要加-r,当test01文件中有权限访问提示,rf命令可强制将test01的内容都拷贝到test01_backup进行备份。
9.mv指令
mv命令是move的缩写,可以用来移动文件或将文件改名,也就是windows下的剪切
【功能】:
- 剪切普通文件或目录,可以不用选项,直接将目录剪切
- 可以将普通文件或目录重命名
【常用选项】:
- -f? :force,如果目标文件已经存在,不会询问直接覆盖
- -i? :若目标文件已经存在,会询问是否覆盖
10.cat命令
【功能】:查看目标文件的内容
【常用选项】:
- -b? :对非空输出行编号
- -n? :对输出的所有行编号
- -s? :不输出多行空行
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ cat -n test.c
1 #include <stdio.h>
2
3 int main()
4 {
5 printf("hello world\n");
6 return 0;
7 }
tac就是查看cat的逆序
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ cat test.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello world\n");
return 0;
}
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ tac test.c
}
return 0;
printf("hello world\n");
{
int main()
#include <stdio.h>
?如果只输入一个cat
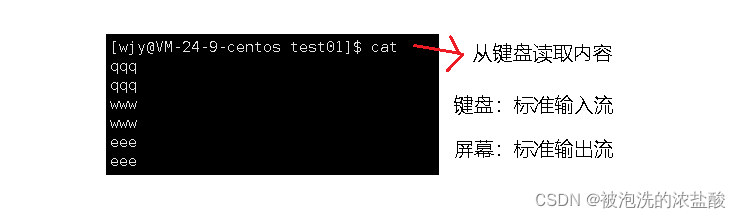
?
如果想在文件中写内容,除了 nano命令,还有echo
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ echo "hello world"
hello world
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ echo "hello this is my first echo" > log.txt
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ ls
a.out log.txt test.c
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ cat log.txt
hello this is my first echo
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ echo "AAAAAAA" > log.txt
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ cat log.txt
AAAAAAA
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ echo "AAAAAAA" >> log.txt
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ cat log.txt
AAAAAAA
AAAAAAA
[wjy@VM-24-9-centos test01]$ cat < log.txt
AAAAAAA
AAAAAAA
仅仅在echo后些内容,就会在页面中打印出来,想要向指定文件些内容,格式为 【echo 内容 > 文件】,如果没有这个文件,系统自动创建。当再次向这个文件中写入内容,发现原来的内容没有了,被第二次写的覆盖了。
我们称这个为输出重定向
输出重定向:本来应该显示到显示器的内容,重定向写入目标文件中
如果不想被覆盖,我们写两个大于号,我们称之为追加重定向
cat后面加小于号,这个叫输入重定向 ,就是将源文件内容传入程序,让程序处理该数据
11.more指令
【功能】:与cat命令类似,可分批查看很长的内容,每次向下看,不能向上翻找。
【常用选项】:
- -n 对输出的所有行编号
q退出查看
more -5 test.c
12.less指令
与less相比more太鸡肋,more只能乡下翻找,如果想要向上翻找,要用less命令。
【选项】:
- -i 忽略搜索时的大小写
- -N 显示每行的行号
- / :向下搜索字符串
- ?:向上搜索字符串
- n :重复前一个搜索
- N : 反向重复前一个搜索
- q :退出
/和?可以搜索想要的内容
总结:如果想要查看大文件,不想全部打开它,使用more/less
【应用场景】:
- 日志:保存软件运行过程中的数据
- 别人写好的代码
13.head和tail指令
head:查看内容前10行
tail:查看内容后10行
如果就想看前3行或后3行,这种固定行数,那么
tail -3 test.c
head -3 test.c【选项】:-n显示行号
【问题】:
如果想要查看1000行命令中的第100-120行命令怎么办?
1.方法一,通过上面提到的输出重定向,可以先将前120行重定向到tmp.txt这个临时文件,查看后20行命令,这样就看到100-120行命令,但是,这样拆开看有点麻烦
2.方法二:直接通过一个命令用“|”隔开,我们称之为管道 ,通过管道,将第一个命令传递给第二个命令
head -120 file.txt > tmp.txt
tail -20 tmp.txt
head -120 file.txt > tmp.txt | tail -20 #管道命令
cat file.txt | head -10 | tail - 5 #第5-10行命令使用管道的时候,隐式的发生了重定向