1 Pod介绍
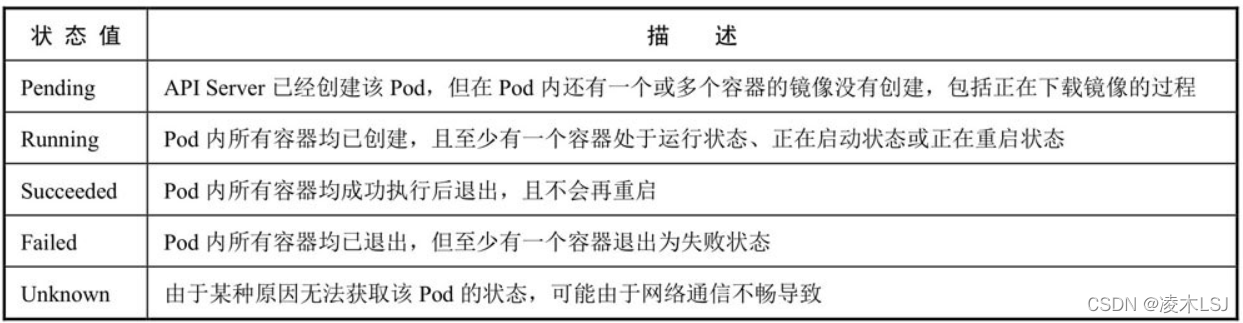
Pod在整个生命周期中被系统定义为各种状态,熟悉Pod的各种状态对于理解如何设置Pod的调度策略、重启策略是很有必要的。
?Pod的重启策略(RestartPolicy)应用于Pod内的所有容器,并且仅在Pod所处的Node上由kubelet进行判断和重启操作。
当某个容器异常退出或者健康检查失败时,kubelet将根据RestartPolicy的设置来进行相应的操作。
◎ Always:当容器失效时,由kubelet自动重启该容器。
◎ OnFailure:当容器终止运行且退出码不为0时,由kubelet自动重启该容器。
◎ Never:不论容器运行状态如何,kubelet都不会重启该容器。
Kubernetes对Pod的健康状态可以通过两类探针来检查: LivenessProbe和ReadinessProbe,kubelet定期执行这两类探针来诊断容器的健康状况。
- LivenessProbe探针:用于判断容器是否存活(Running状态),如果LivenessProbe探针探测到容器不健康,则kubelet将杀掉该容器,并根据容器的重启策略做相应的处理。
- ReadinessProbe探针:用于判断容器服务是否可用(Ready状态),达到Ready状态的Pod才可以接收请求。
在Kubernetes平台上,我们很少会直接创建一个Pod,在大多数情况下会通过RC、Deployment、DaemonSet、Job等控制器完成对一组Pod副本的创建、调度及全生命周期的自动控制任务
2 Pod基本使用
2.1 创建容器
在使用Docker时,可以使用docker run命令创建并启动一个容器。而在Kubernetes系统中对长时间运行容器的要求是:其主程序需要一直在前台执行。对于无法改造为前台执行的应用,可以使用开源工具Supervisor辅助进行前台运行的功能。
Pod可以由1个或多个容器组合而成,如下案例Pod只由一个容器组成,配置文件frontend-localredis-pod.yaml的内容如下:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: frontend
labels:
name: frontend
spec:
containers:
- name: frontend
image: kubeguide/guestbook-php-frontend
env:
- name: GET_HOSTS_FROM
value: env
ports:
- containerPort: 80
另一种场景是,当frontend和redis两个容器应用为紧耦合的关系,并组合成一个整体对外提供服务时,应将这两个容器打包为一个Pod:
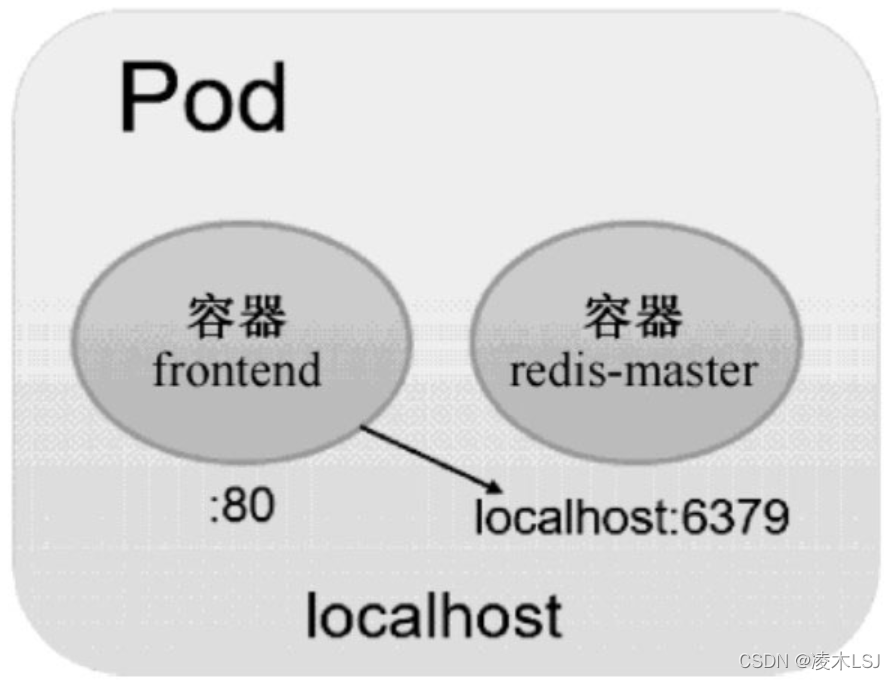
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: redis-php
labels:
name: redis-php
spec:
containers:
- name: frontend
image: kubeguide/guestbook-php-frontend:localredis
ports:
- containerPort: 80
- name: redis
image: kubeguide/redis-master
ports:
- containerPort: 6379kubectl create -f frontend-localredis-pod.yam? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?//创建pod
kubectl get pods? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? // 查看已创建的pod
kubectl describe pod <pod名>? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? //查看具体pod的信息
2.2 静态Pod
静态Pod是由kubelet进行管理的仅存在于特定Node上的Pod。它们不能通过API Server进行管理,无法与ReplicationController、Deployment或者DaemonSet进行关联,并且kubelet无法对它们进行健康检查。
最常见的 Static Pod:
- etcd
- kube-apiserver
- kube-controller-manager
- kube-scheduler
在配置文件/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml 里找到staticPodPath


?在目录 staticPodPath 中放入一个static-web.yaml文件
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: static-web
labels:
name: static-web
spec:
containers:
- name: static-web
image: nginx
ports:
- name: web
containerPort: 80重启 kubelet
systemctl stop kubelet
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start kubelet
等待一会儿,查看本机中已经启动的容器,可以看到一个Nginx容器已经被kubelet成功创建了出来。
删除该Pod的操作只能将static-web.yaml文件删除。
2.3 Pod配置管理
应用部署的一个最佳实践是将应用所需的配置信息与程序进行分离,这样可以使应用程序被更好地复用。
ConfigMap将应用打包为容器镜像后,可以通过环境变量或者外挂文件的方式在创建容器时进行配置注入。
ConfigMap供容器使用的典型用法如下:
- 生成为容器内的环境变量。
- 设置容器启动命令的启动参数(需设置为环境变量)。
- 以Volume的形式挂载为容器内部的文件或目录。
使用yaml文件创建
cm-appconfigfile.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: cm-appconfigfile
data:
key-serverxml: |
<...>
key-logproperity: "..."kubectl create -f cm-appconfigfile.yaml
kubectl get?ConfigMap
kubectl get?ConfigMap?cm-appconfigfile -o yaml
kubectl describe configmap?cm-appconfigfile??
通过kubectl命令行方式创建,使用参数--from-file或--from-literal指定内容通过kubectl create configmap创建ConfigMap。
kubectl create configmap -h
kubectl create configmap config-name --from-file=[key-name]=directory或者file
kubectl create configmap config-name --from-literal=key-name=value
kubectl create configmap config-name --from-env-file=envfile
????????--from-env-file只能跟文件,不能是目录,并且文件里key/value有格式的要求,会做参数的校验。
在Pod“cm-test-pod”的定义中,将ConfigMap“cm-appconfigfile”中的内容以环境变量(APPLOGLEVEL和APPDATADIR)方式设置为容器内部的环境变量,容器的启动命令将显示这两个环境变量的值("env | grep APP"):
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: cm-test-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: cm-test
image: busybox
command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "env | grep APP" ]
env:
- name: APPLOGLEVEL # 定义环境变量的名称
valueFrom: # key“apploglevel”对应的值
configMapKeyRef:
name: cm-appconfigfile? # 环境变量的值取自cm-appconfigfile
key: apploglevel # key为apploglevel
- name: APPDATADIR # 定义环境变量的名称
valueFrom: # key“appdatadir”对应的值
configMapKeyRef:
name: cm-appconfigfile? # 环境变量的值取自cm-appconfigfile
key: appdatadir # key为appdatadir
restartPolicy: Neverkubectl create -f?cm-test-pod.yaml
kubectl get pods ---show-all
Kubernetes从1.6版本开始,引入了一个新的字段envFrom,实现了在Pod环境中将ConfigMap(也可用于Secret资源对象)中所有定义的key=value自动生成为环境变量:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: cm-test-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: cm-test
image: busybox
command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "env" ]
envFrom:
- configMapRef
name: cm-appconfigfile? # 根据cm-appvars中的key=value自动生成环境变量
restartPolicy: Never2.4?共享Volume
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: volume-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: tomcat
image: tomcat
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
volumeMounts:
- name: app-logs
mountPath: /usr/local/tomcat/logs
- name: logreader
image: logreader
command: ["sh", "-c", "tail -f /logs/catalina*.log"]
volumeMounts:
- name: app-logs
mountPath: /logs
volumes:
- name: app-logs
emptyDir: {}
这里设置的Volume名为app-logs,类型为emptyDir。挂载到tomcat容器内的/usr/local/tomcat/logs目录,同时挂载到logreader容器内的/logs目录。tomcat容器在启动后会向/usr/local/tomcat/logs目录写文件,logreader容器就可以读取其中的文件了。
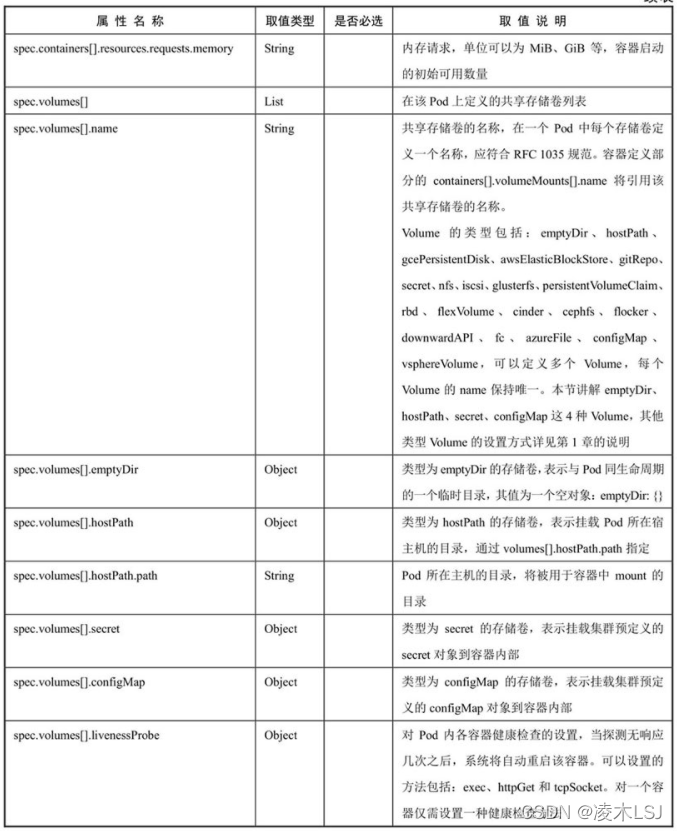
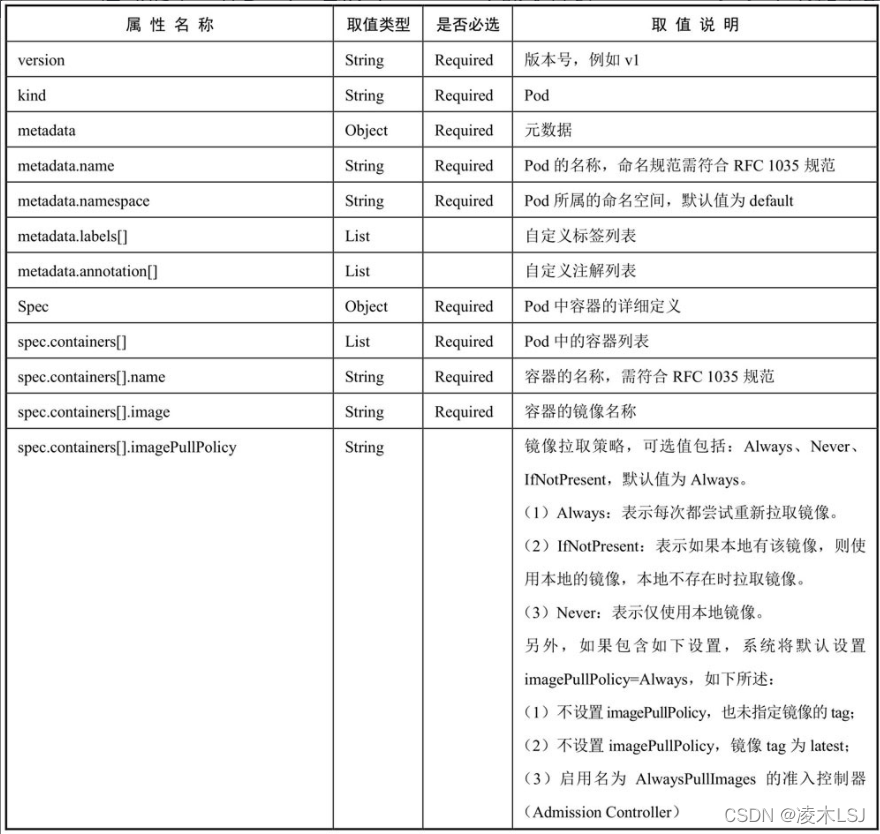
附录:Pod定义文件?
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: string
namespace: string
labels:
- name: string
annotations:
- name: string
spec:
containers:
- name: string
image: string
imagePullPolicy: [Always | Never | IfNotPresent]
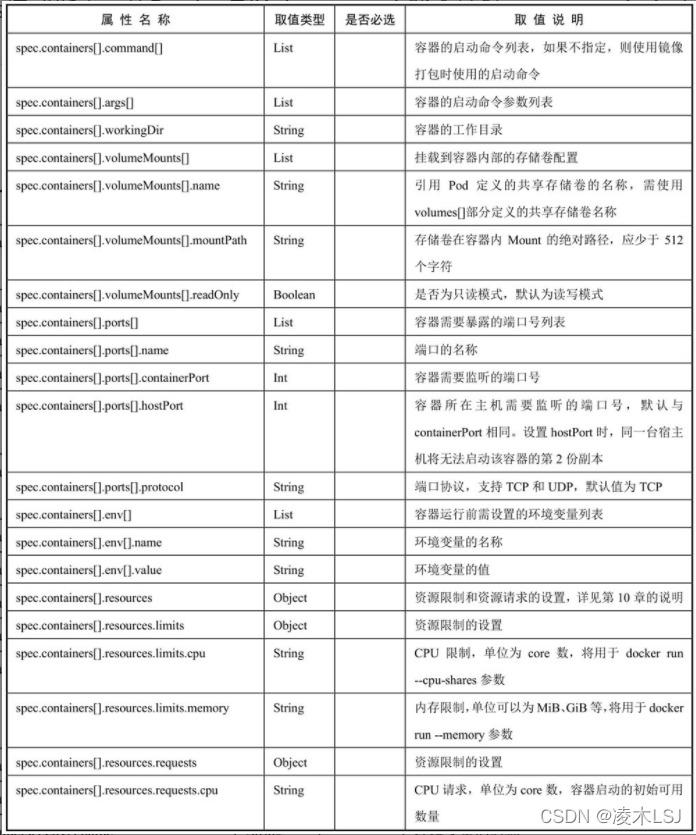
command: [string]
args: [string]
workingDir: string
volumeMounts:
- name: string
mountPath: string
readOnly: boolean
ports:
- name: string
containerPort: int
hostPort: int
protocol: string
env:
- name: string
value: string
resources:
limits:
cpu: string
memory: string
requests:
cpu: string
memory: string
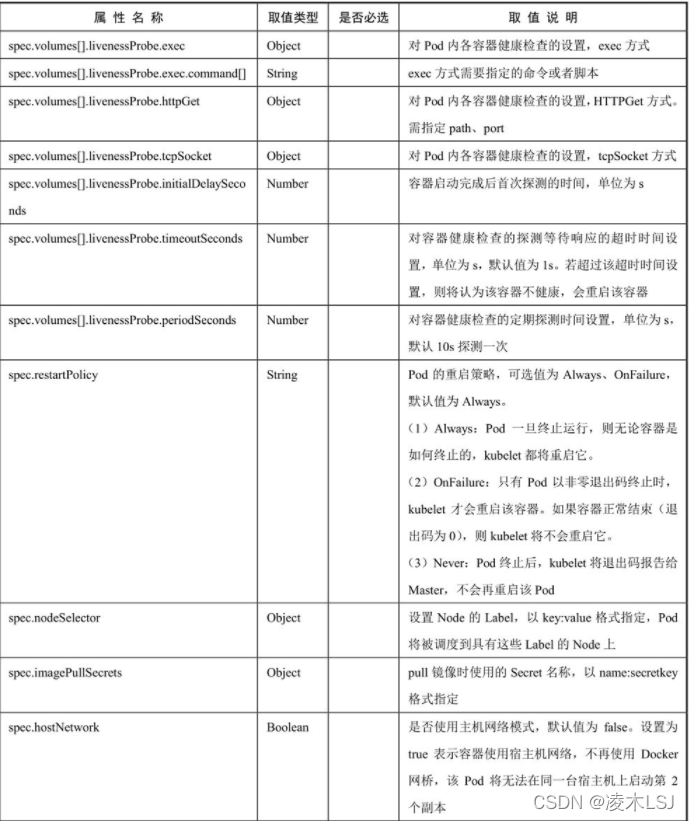
livenessProbe:
exec:
command: [string]
httpGet:
path: string
port: number
host: string
scheme: string
httpHeaders:
- name: string
value: string
tcpSocket:
port: number
initialDelaySeconds: 0
timeoutSeconds: 0
periodSeconds: 0
successThreshold: 0
failureThreshold: 0
securityContext:
privileged: false
restartPolicy: [Always | Never | OnFailure]
nodeSelector: object
imagePullSecrets:
- name: string
hostNetwork: false
volumes:
- name: string
emptyDir: {}
hostPath:
path: string
secret:
secretName: string
items:
- key: string
path: string
configMap:
name: string
items:
- key: string
path: string
?