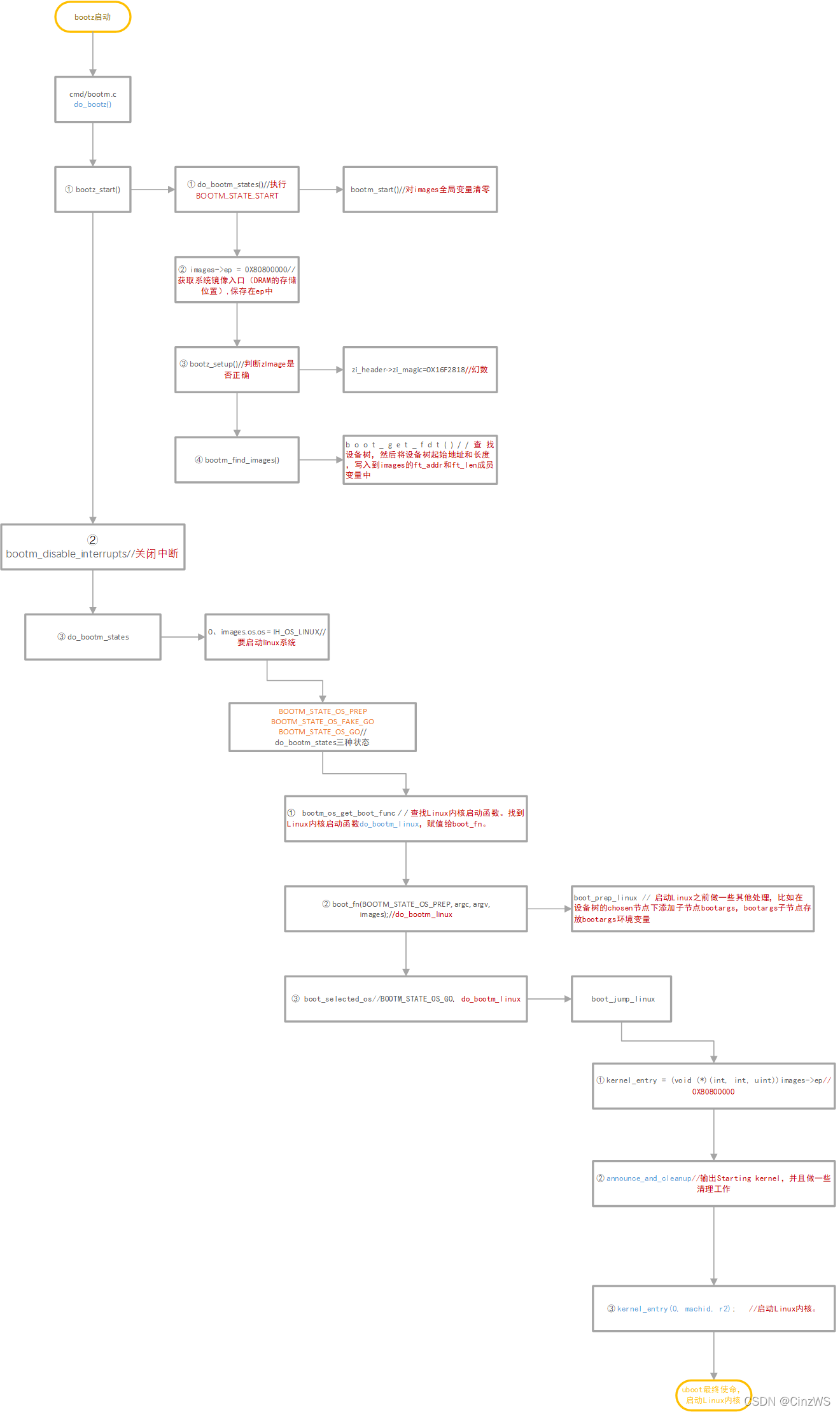
分析完uboot启动流程,该篇分析bootz启动linux内核。如下图所示,bootz 命令的执行函数为 do_bootz,主要分为三个阶段:①bootz_start;②bootm_disable_interruptes;③do_bootm_states。

1、bootz_start函数
bootz_start()主要分为四个阶段:① do_bootm_states();② images->ep;③ bootz_setup();④ bootm_find_images()
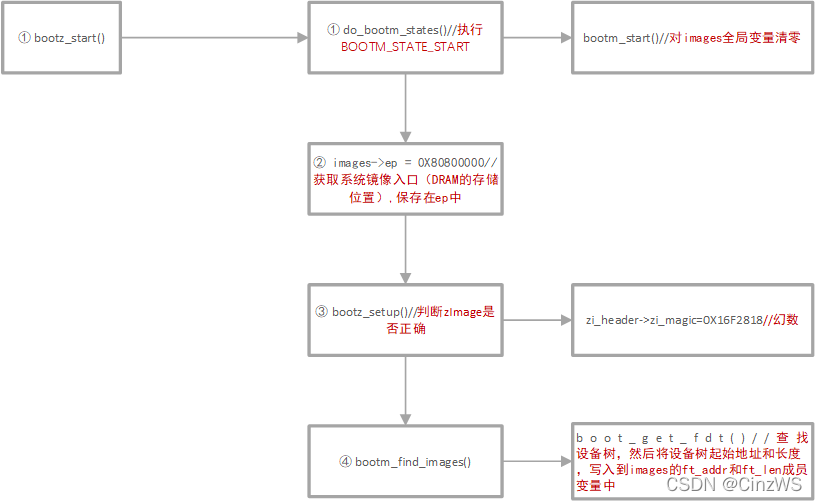
(1) do_bootm_states函数,用于执行 BOOTM_STATE_START 状态。事实上do_bootm_states函数有下面四种状态:
BOOTM_STATE_OS_PREP
BOOTM_STATE_OS_FAKE_GO
BOOTM_STATE_OS_GO
BOOTM_STATE_START
但是本阶段只执行执行 BOOTM_STATE_START 状态,该状态会调用bootm_start()函数,函数代码如下:
static int bootm_start(cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag, int argc,
char * const argv[])
{
memset((void *)&images, 0, sizeof(images));//清空images
images.verify = getenv_yesno("verify");//初始化verfify成员
boot_start_lmb(&images);
bootstage_mark_name(BOOTSTAGE_ID_BOOTM_START, "bootm_start");
images.state = BOOTM_STATE_START;//设置状态为BOOTM_STATE_START
return 0;
}
由代码可知,bootm_start()函数用于对images全局变量清零。
(2) images->ep = simple_strtoul(argv[0], NULL, 16);该行用于设置 images 的 ep 成员变量,也就是系统镜像的入口点,使用 bootz 命令启动系统的时候就会设置系统在 DRAM 中的存储位置,这个存储位置就是系统镜像的入口点,因此 images->ep=0X80800000。
(3) bootz_setup()函数,该函数用于判断当前的系统镜像文件是否为 Linux 的镜像文件,并且打印出镜像相关信息。
(4) bootm_find_images()函数,该函数中最重要的函数为boot_get_fdt()函数,用于查找设备树,然后将设备树起始地址和长度,写入到images的ft_addr和ft_len成员变量中。并且在使用 bootz 启动 Linux 的时候设备树存放在DRAM 中,因此 images.ft_addr=0X83000000,长度根据具体的设备树文件而定,如设备树文件长度为 0X8C81,则 images.ft_len=0X8C81。
2、bootm_disable_interrupts函数
bootm_disable_interrupts函数用于关闭中断
3、do_bootm_states函数
在执行do_bootm_states函数之前,先执行命令images.os.os = IH_OS_LINUX,表示要启动linux系统。do_bootm_states函数执行过程如下所示:
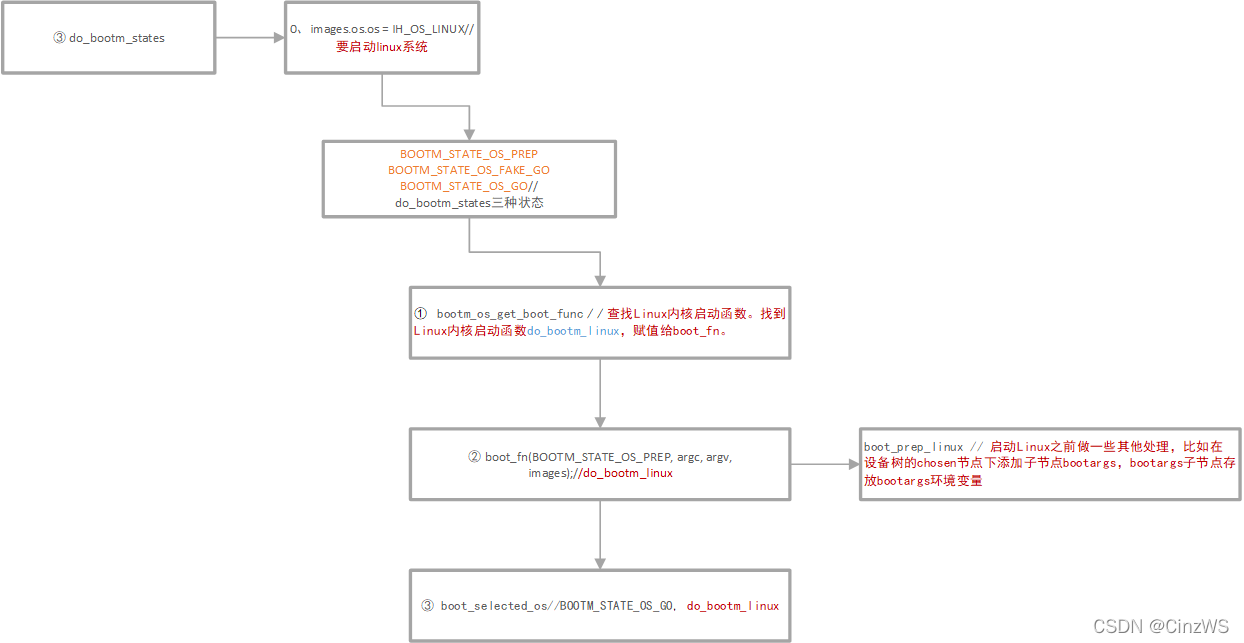
do_bootz 最后调用函数do_bootm_states,而在此之前bootz_start函数就调用过该函数,只不过执行的状态是BOOTM_STATE_START,剩下的三种状态将在该函数执行。
BOOTM_STATE_OS_PREP
BOOTM_STATE_OS_FAKE_GO//该状态由于没用使能TRACE功能,所以没有被执行
BOOTM_STATE_OS_GO
(1) bootm_os_get_boot_func函数,用于查找Linux内核启动函数。找到 Linux内核启动函数do_bootm_linux,赋值给boot_fn。
(2) boot_fn(BOOTM_STATE_OS_PREP, argc, argv, images);处理 BOOTM_STATE_OS_PREP 状态时,函数实际上是执行实际上是执行的 do_bootm_linux 函数,do_bootm_linux调用boot_prep_linux函数启动Linux之前做一些其他处理,比如在设备树的chosen节点下添加子节点bootargs,bootargs子节点存放bootargs环境变量。
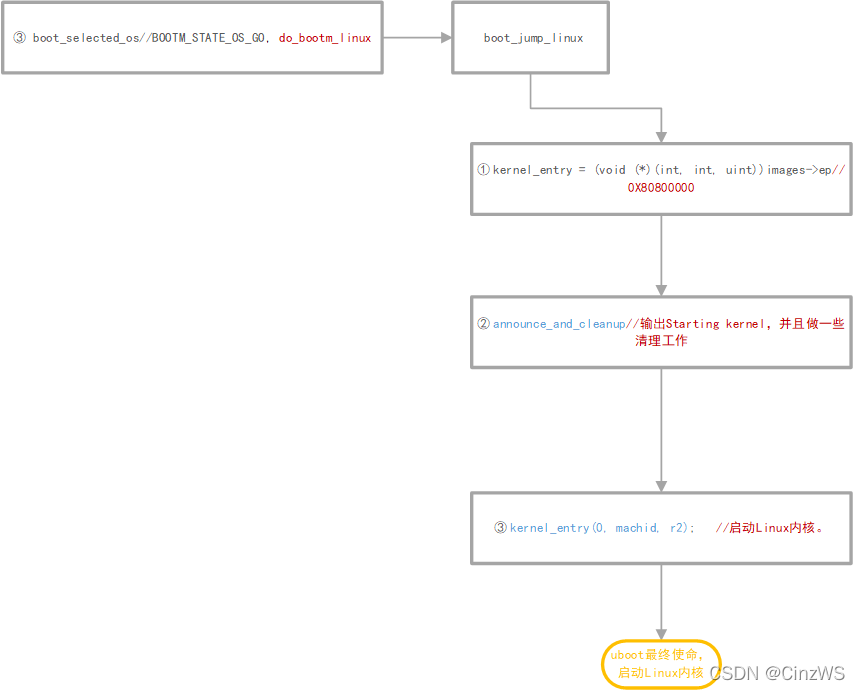
(3)boot_selected_os函数,当状态处于BOOTM_STATE_OS_GO时,boot_selected_os被执行,由boot_selected_os第 5 个参数为 Linux 系统启动函数 do_bootm_linux,可知 boot_selected_os用于启动 Linux 内核。
int boot_selected_os(int argc, char * const argv[], int state,
bootm_headers_t *images, boot_os_fn *boot_fn)
3.1 do_bootm_linux
do_bootm_linux 为最终启动 Linux 内核的函数,结合下面代码分析可知:当参数flag等于BOOTM_STATE_OS_GO或者BOOTM_STATE_OS_FAKE_GO的话就执行 boot_jump_linux 函数。 boot_selected_os 函数在调用 do_bootm_linux 的时候会将 flag设置为 BOOTM_STATE_OS_GO。
int do_bootm_linux(int flag, int argc, char * const argv[],
bootm_headers_t *images)
{
/* No need for those on ARM */
if (flag & BOOTM_STATE_OS_BD_T || flag & BOOTM_STATE_OS_CMDLINE)
return -1;
if (flag & BOOTM_STATE_OS_PREP) {
boot_prep_linux(images);
return 0;
}
if (flag & (BOOTM_STATE_OS_GO | BOOTM_STATE_OS_FAKE_GO)) {
boot_jump_linux(images, flag);
return 0;
}
boot_prep_linux(images);
boot_jump_linux(images, flag);
return 0;
}
执行函数 boot_jump_linux,该函数主要由三个阶段:
(1) kernel_entry,该函数有三个参数: zero, arch, params,第一个参数 zero 同样为 0;第二个参数为机器 ID; 第三个参数 ATAGS 或者设备树(DTB)首地址, ATAGS 是传统的方法,用于传递一些命令行信息,如果使用设备树的话就要传递设备树(DTB)。实际上通常使用设备树,故第三个参数最重要。并且kernel_entry 并不是 uboot 定义的,而是 Linux 内核定义的,Linux 内核镜像文件的第一行代码就是函数 kernel_entry,而 images->ep 保存着 Linux内核镜像的起始地址,起始地址保存的正是 Linux 内核第一行代码。
void (*kernel_entry)(int zero, int arch, uint params);
...
kernel_entry = (void (*)(int, int, uint))images->ep;
(2) announce_and_cleanup函数,用于输出Starting kernel,并且做一些清理工作。
(3) kernel_entry(0, machid, r2), 该函数启动Linux内核。
4、整体流程详细图
至此,uboot 启动Linux内核完成。事实上,uboot启动流程与bootz启动Linux内核看不懂对uboot移植也没有关系,了解就行,不必强求。最后附上bootz启动Linux内核全部流程图: