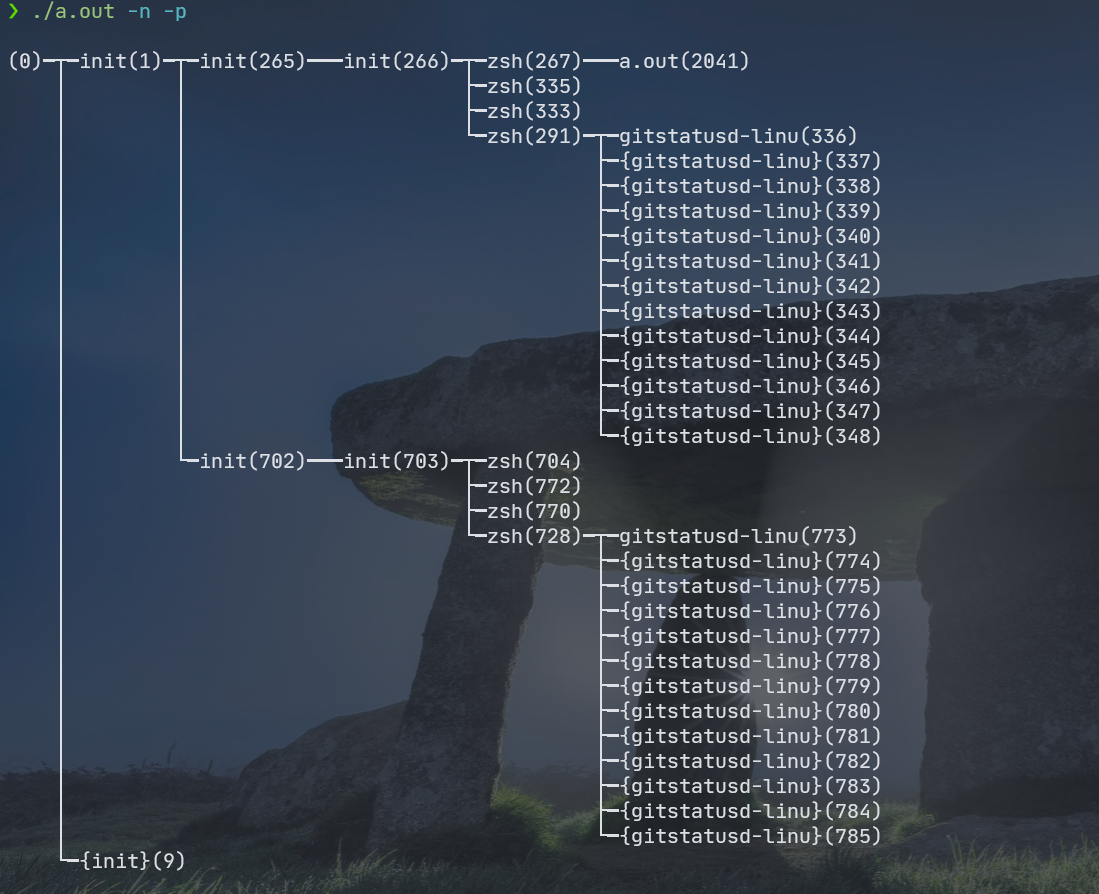
一个查看进程树的小栗子
可以打印进程数,并且可以加参数 -n 显示pid,加参数-p 显示线程信息 ( 和pstree 的参数并不一样)
准备工作
step 1 处理进程信息
想办法找到所有当前进程
在Linux下
proc 文件系统 (procfs) 是类 Unix 操作系统中的一种特殊文件系统,它以分层文件结构呈现有关进程的信息和其他系统信息,为动态访问内核中保存的进程数据提供了一种更方便和标准化的方法。传统的跟踪方法或直接访问内核内存。 (翻译自维基百科)
所以说,我们每一个进程其实存放在Linux下的/proc文件夹下,以进程号作为文件夹名称
接下来,我们要想办法读取这个文件夹下的所有文件夹
这里我们需要用到Linux下读取文件夹的一些操作 其包含的操作在dirent.h下。
其函数原型有:

struct dirent 结构

struct DIR 结构

在这里,我们利用
opendir函数和readdir函数遍历目录
int listdir(const char *path) {
DIR *dir;
struct dirent *entry;
dir = opendir(path);
if (dir == NULL) {
perror("fail opendir");
return -1;
}
while ((entry = readdir(dir)))
if (DT_DIR == entry -> d_type)
puts(entry->d_name);
closedir(dir);
return 0;
}
接下来我们要去status里读取这个进程的信息,同时去task文件夹下面读取这个进程的线程
/proc/PID/statuscontains basic information about a process including its run state and memory usage.
FILE* fp;
char ch[size];
strcpy(ch, "/proc/");
strcat(ch, path);
strcat(ch, "/status");
fp = fopen(ch, "r");
char pid[size], ppid[size], name[size];
while((fscanf(fp, "%s", ch)) != EOF) {
if (strcmp(ch, "Pid:") == 0) {
fscanf(fp, "%s", pid);
}
if (strcmp(ch, "PPid:") == 0) {
fscanf(fp, "%s", ppid);
}
if (strcmp(ch, "Name:") == 0) {
fscanf(fp, "%s", name);
}
}
进入task目录下遍历目录我们可以使用listdir一样的代码
step 2 建树
我们需要一颗多叉树,来供我们保存父子节点信息方便打印,以及建树的几个函数
struct process {
char *p_name;
char *p_pid;
struct process *bro;
struct process *son;
};
typedef struct process process;
process* create_p(const char*, const char*);
int insert(process*, process*, const char*);
int print_tree(process*, int, int*, int);
这部分就是数据结构的问题,所有就不多叙述
step 3 打印树
我们需要控制一下打印格式 且需要使用一些Unicode特殊字符
如:\u2500, \u2502, \u252c, \u2514 等字符
然后递归打印这颗树即可
int print_tree(process* head, int len, int* buf, int flag) {
if (head == NULL) return -1;
while (head) {
printf("%s", head->p_name);
if (flag) printf("(%s)", head->p_pid);
if (head->son) {
if(!head->son->bro) printf("\u2500\u2500\u2500");
else printf("\u2500\u252c\u2500");
int size = strlen(head->p_name) + len + 3 + (flag * (strlen(head->p_pid) + 2));
if (head->son->bro) buf[size - 2] = 1;
print_tree(head->son, size, buf, flag);
}
head = head->bro;
if (head) {
printf("\n");
if (!head->bro) buf[len - 2] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len - 2; ++ i)
if (buf[i]) printf("\u2502");
else printf(" ");
if (!head->bro) printf("\u2514\u2500");
else printf("\u251c\u2500");
}
}
return 0;
}
总体代码
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: demo.c
> Author: amjieker
> Mail: secrecy
> Created Time: Sun Mar 14 20:58:37 2022
************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct process {
char *p_name;
char *p_pid;
struct process *bro;
struct process *son;
};
typedef struct process process;
// tools
int listdir(const char*, const char*, process**, int, int);
int check_digital(const char*);
int build_tree(const char*, process*, int dep);
// struct process function
process* create_p(const char*, const char*);
int insert(process*, process*, const char*);
int print_tree(process*, int, int*, int);
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
// listdir("/proc");
// process* head = create_p("init", "1");
// insert(head, create_p("zsh", "2"), "1");
// insert(head, create_p("ass", "3"), "1");
// insert(head, create_p("ssssssssssssssssb", "4"), "1");
// insert(head, create_p("cdsds", "5"), "2");
// insert(head, create_p("dwe2", "6"), "5");
// insert(head, create_p("fdpsaa", "7"), "5");
// insert(head, create_p("e3wq", "8"), "4");
// insert(head, create_p("gxps", "9"), "4");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "10"), "8");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "11"), "8");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "12"), "8");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "13"), "8");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "14"), "8");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "15"), "10");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "16"), "10");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "17"), "10");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "18"), "10");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "19"), "14");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "20"), "14");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "21"), "14");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "22"), "14");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "23"), "14");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "24"), "14");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "25"), "20");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "26"), "20");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "27"), "20");
// insert(head, create_p("wwewqm", "28"), "27");
int buf[1024] = {0};
int state_n = 0, state_p = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < argc; ++ i) {
if (strcmp(argv[i], "-n") == 0) state_n = 1;
else if (strcmp(argv[i], "-p") == 0) state_p = 1;
else {
puts(argv[i]);
puts("errof command");
exit(0);
}
}
process** head = (process**)malloc(sizeof(process*));
listdir("/proc", " ", head, 0, state_p);
printf("\n");
print_tree((*head), 0, buf, state_n);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
int listdir(const char* path, const char* father, process** head, int dep, int flag) {
struct dirent *entry;
DIR *dir;
dir = opendir(path);
if (dir == NULL) {
perror("fail opendir");
return -1;
}
if (dep == 0) *head = create_p("", "0"); // init process
while ((entry = readdir(dir)))
if (DT_DIR == entry -> d_type)
if (check_digital(entry->d_name) != -1) {
if (dep == 1 && !strcmp(entry->d_name, father))
continue;
build_tree(entry->d_name, *head, dep);
if (0 == dep && flag) {
char buf[1024];
strcpy(buf, "/proc/");
strcat(buf, entry->d_name);
strcat(buf, "/task");
listdir(buf, entry->d_name, head, 1, flag);
}
}
closedir(dir);
return 0;
}
int check_digital(const char* s) {
int flag = 0;
for (; *s; ++ s)
if (*s < '0' || *s > '9')
return -1;
return 0;
}
int build_tree(const char* path, process* head, int dep) {
const int size = 1024;
FILE* fp;
char ch[size];
strcpy(ch, "/proc/");
strcat(ch, path);
strcat(ch, "/status");
fp = fopen(ch, "r");
char pid[size], ppid[size], name[size];
while((fscanf(fp, "%s", ch)) != EOF) {
if (strcmp(ch, "Pid:") == 0) {
fscanf(fp, "%s", pid);
}
if (strcmp(ch, "PPid:") == 0) {
fscanf(fp, "%s", ppid);
}
if (strcmp(ch, "Name:") == 0) {
fscanf(fp, "%s", name);
}
}
ch[0] = 0;
if (dep) strcpy(ch, "{");
strcat(ch, name);
if (dep) strcat(ch, "}");
insert(head, create_p(ch, pid), ppid);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
void check_memory(void* p) {
if (p == NULL) {
perror("malloc error");
exit(0);
}
}
process* create_p(const char* p_name, const char* p_pid) {
process* p = (process*)malloc(sizeof(process));
check_memory(p);
p->p_name = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (strlen(p_name) + 1));
p->p_pid = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (strlen(p_pid) + 1));
check_memory(p->p_name);
check_memory(p->p_pid);
strcpy(p->p_name, p_name);
strcpy(p->p_pid, p_pid);
p->bro = NULL;
p->son = NULL;
return p;
}
// tools
int cmp(const char* a, const char *b) {
int tempa = atoi(a), tempb = atoi(b);
if (a == b) return 0;
if (a > b) return 1;
return -1;
}
void insert_node(process* head, process* node) {
/*help insert node function*/
process* cur = head->bro;
process* prv = head;
while (cur) {
int state = strcmp(head->p_name, node->p_name);
if ( 1 == state ||
(0 == state && -1 == cmp(head->p_pid, node->p_name))
) {
prv->bro = node;
node->bro = cur;
return;
}
prv = cur;
cur = cur->bro;
}
prv->bro = node;
return;
}
int insert(process* head, process* node, const char* fp_pid) {
if (node == NULL) return -1;
if (head == NULL) return -1;
while (head) {
if (0 == strcmp(head->p_pid, fp_pid)) {
if (head->son)
insert_node(head->son, node);
else
head->son = node;
return 0;
} else {
if (0 == insert(head->son, node, fp_pid))
return 0;
}
head = head->bro;
}
return -1;
}
int print_tree(process* head, int len, int* buf, int flag) {
if (head == NULL) return -1;
while (head) {
printf("%s", head->p_name);
if (flag) printf("(%s)", head->p_pid);
if (head->son) {
if(!head->son->bro) printf("\u2500\u2500\u2500");
else printf("\u2500\u252c\u2500");
int size = strlen(head->p_name) + len + 3 + (flag * (strlen(head->p_pid) + 2));
if (head->son->bro) buf[size - 2] = 1;
print_tree(head->son, size, buf, flag);
}
head = head->bro;
if (head) {
printf("\n");
if (!head->bro) buf[len - 2] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len - 2; ++ i)
if (buf[i]) printf("\u2502");
else printf(" ");
if (!head->bro) printf("\u2514\u2500");
else printf("\u251c\u2500");
}
}
return 0;
}
最后效果