IO模型就是用什么样的通道进行数据的发送和接收,很大程度上决定了程序通信的性能。
Java共支持3种网络编程模型/IO模式:BIO,NIO,AIO
1. IO模型介绍
- Java BIO
- Blocking IO,阻塞io
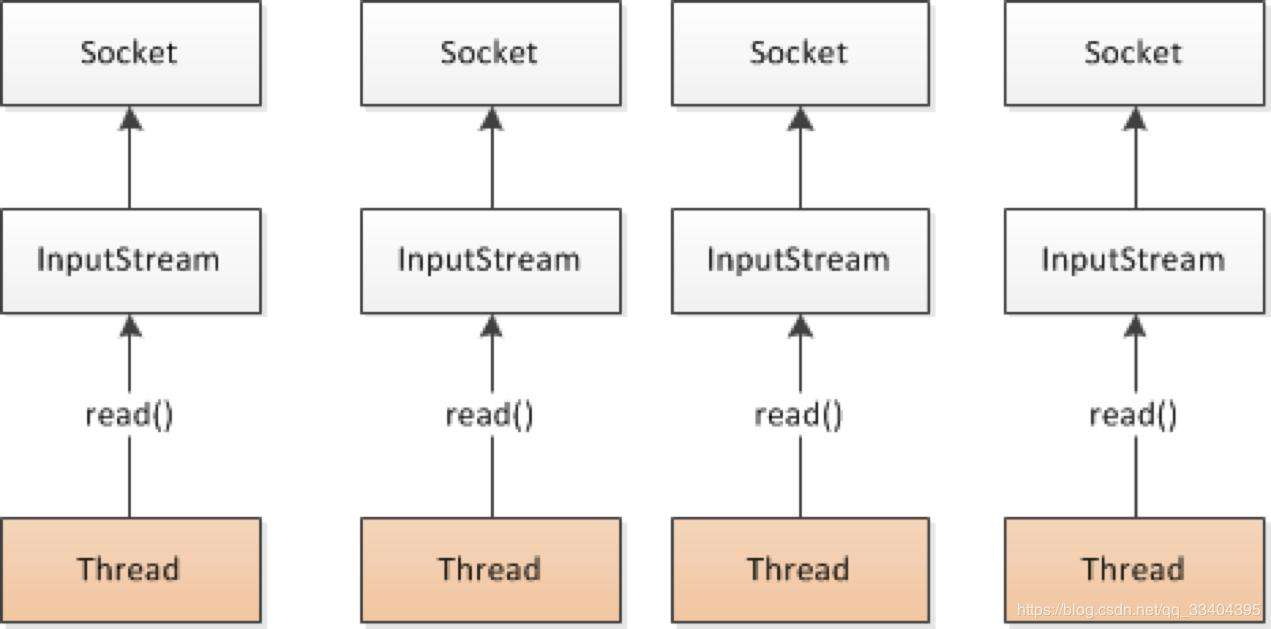
- 服务器实现模式为一个连接一个线程,即客户端有连接请求时服务器端就需要启动一个线程进行处理,如果这个连接不做任何事情就会造成不必要的连接开销。
- Java NIO
- Non-Blocking IO,同步非阻塞io
- 服务器实现模式为一个线程处理多个请求(连接),即客户端发送的连接请求都会注册到多路复用器上,多路复用器轮询到连接有I/O请求就进行处理。
- Java AIO(NIO 2)
- Async IO 异步非阻塞
- AIO引入了异步通道的概念,采用了Proactor模式,简化了程序编写,有效的请求才启动线程,它的特点是先由操作系统完成后才通知服务端程序启动线程去处理,一般适用于连接数较多且连接时间较长的应用。
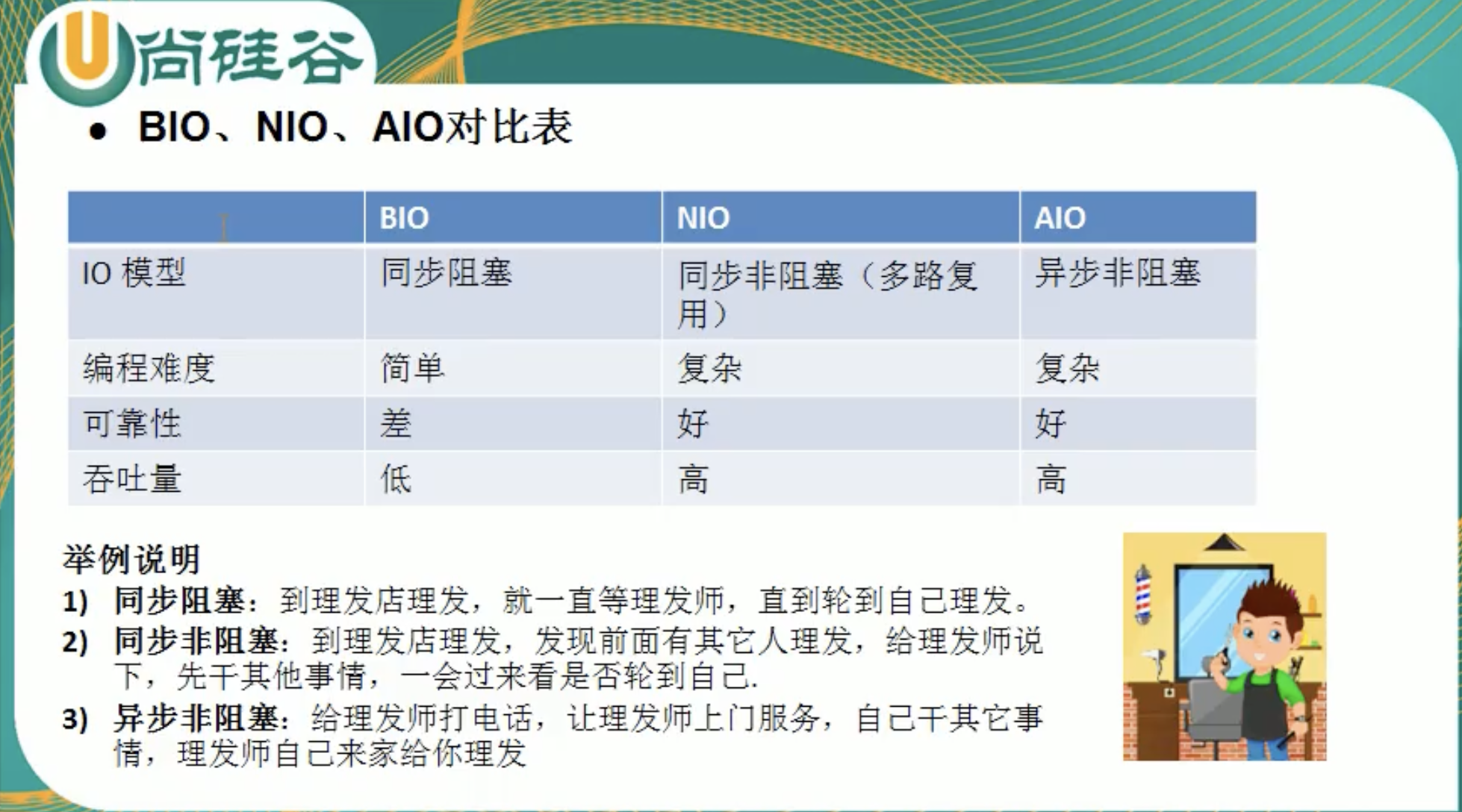
2. BIO、NIO、AIO使用场景分析
- BIO方式适用于连接树木比较小且固定的架构,这种方式对服务器资源要求比较高,并发局限于应用中,JDK1.4以前的唯一选择,程序简单易理解。
- NIO方式适用于连接数目多且连接比较短(轻操作)的架构,比如聊天服务器,弹幕系统,服务器间通讯等。编程比较复杂,JDK1.4开始支持。
- AIO方式适用于连接数目多且连接比较长(重操作)的架构,比如相册服务器,充分调用OS参与并发操作,编程比较复杂,JDK7开始支持。
3. IO模型详解
3.1 Java BIO模型详解
- 传统的Java io 编程
- package java.io.*
- BIO(blocking i/o): 同步阻塞,务器实现模式为一个连接一个线程,即客户端有连接请求时服务器端就需要启动一个线程进行处理,如果这个连接不做任何事情就会造成不必要的连接开销。可以通过线程池机制改善
- BIO适用于连接数目比较小且固定的架构,这种方式对服务器资源要求比较高,并发局限于应用中,JDK1.4以前的唯一选择,程序简单易理解。
example
/**
* @author kern
*/
public class ExampleBioServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(6666);
while (true) {
//阻塞监听客户端
final Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
//创建一个新的线程处理连接
executorService.execute(() -> {
handle(socket);
});
}
}
private static void handle(final Socket socket) {
try {
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
while (true) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
if (inputStream.read(bytes) != -1) {
String str = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(str);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
BIO问题
- 每个请求都需要创建独立的线程,当并发数较大时,需要创建大量线程来处理连接,系统资源占用较大。
- 连接建立后,如果当前线程暂时没有数据可读,则线程就阻塞在Read操作上,造成线程资源浪费
3.2 Java NIO详解
3.2.1 Java NIO 基本介绍
- Java non-blocking IO Java非阻塞 io 编程
- package java.nio.*
- NIO三大核心
- Channel 通道
- Buffer 缓冲区
- 底层使用Unsafe类直接操作内存,Buffer中写入的所有数据jvm都不进行管理,不能被gc回收。
- Selector 选择器
- NIO是事件驱动的
- NIO是面向缓冲区编程的。数据总是写到缓冲区,需要时可以从缓冲区中获取,增加了处理过程中的灵活性
- Java NIO的非阻塞模式,使一个线程从某通道发送请求或者读取数据,只有有数据可以进行读写时,才调用一个线程进行读写。
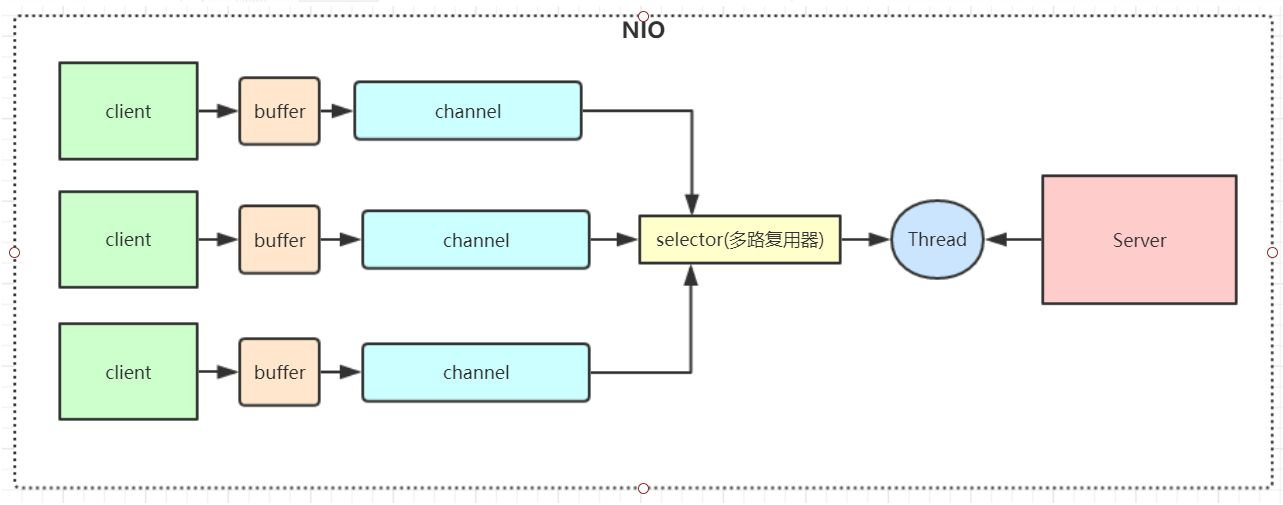
图示说明:
- 每个channel 都会对应一个buffer,buffer是一个内存快,底层维护了一个数组。
- selector 对应一个线程,一个线程/selector对应多个channel
- selector在channel间切换,切换是由event事件触发的
- selector会根据不同的event,在各个通道上切换,并完成事件event操作
3.2.2 NIO组件介绍
3.2.2.1 缓冲区Buffer
缓冲区本质上是一个可以读写数据的内存快,可以理解成是一个容器对象(含数组),该对象提供了一组方法,可以更轻松地使用内存块,缓冲区对象内置了一些机制,能够跟踪和记录缓冲区的状态变化情况,Channel提供从文件,网络读取数据的渠道,但是读取或写入的数据都必须经由buffer。
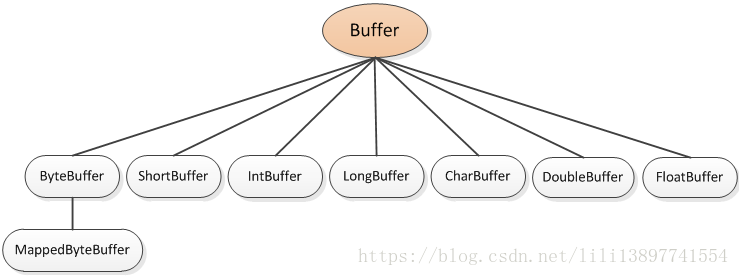
java.nio 下buffer实现了缓冲区,并根据数据类型进行了不同的子类实现
- java.nio.Buffer
- java.nio.ShortBuffer
- java.nio.ByteBuffer
- java.nio.IntBuffer
- java.nio.LongBuffer
- java.nio.FloatBuffer
- java.nio.DoubleBuffer
- java.nio.CharBuffer
public abstract class Buffer {
//mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
//标记
private int mark = -1;
//当前位置下标
private int position = 0;
//当前终点下标
private int limit;
//容量
private int capacity;
//使用直接内存时的内存地址
long address;
}
/**
* @author kern
*/
public class ExampleBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
//创建一个容量为5的int buffer
//堆内存中分配空间
//position = 0, limit = 5, capacity = 5, mark = -1
IntBuffer buffer = IntBuffer.allocate(5);
//position = 1, limit = 5, capacity = 5, mark = -1
buffer.put(random.nextInt());
//position = 2, limit = 5, capacity = 5, mark = -1
buffer.put(random.nextInt());
//position = 3, limit = 5, capacity = 5, mark = -1
buffer.put(random.nextInt());
//读写切换
/*
limit = position
position = 0
mark = -1
*/
//position = 0, limit = 3, capacity = 5, mark = -1
buffer.flip();
//position = 1, limit = 3, capacity = 5, mark = -1
System.out.println(buffer.get());
//position = 2, limit = 3, capacity = 5, mark = -1
System.out.println(buffer.get());
//position = 3, limit = 3, capacity = 5, mark = -1
System.out.println(buffer.get());
/*
清除缓冲区,仅重置下标
position = 0;
limit = capacity;
mark = -1;
*/
//position = 0, limit = 5, capacity = 5, mark = -1
buffer.clear();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
buffer.put(random.nextInt());
}
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.println(buffer.get());
}
}
}
ByteBuffer
/**
* @author kern
*/
public class ExampleByteBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//堆内存
ByteBuffer heapBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//直接内存,不需要操作系统进行内存拷贝
ByteBuffer directBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
String filePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/io-mode/src/main/resources/nio/file-channel.log";
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(filePath, "rw");
FileChannel fileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
/**
* 获取MappedByteBuffer直接加载到堆外内存
* mode – FileChannel.MapMode类中定义的常量READ_ONLY 、 READ_WRITE或PRIVATE之一,分别根据文件是只读、读/写还是私有(写时复制)映射
* position – 文件中映射区域开始的位置; 必须是非负数
* size -- 要映射的区域的大小; 必须为非负数且不大于Integer.MAX_VALUE
*/
MappedByteBuffer buffer = fileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 20);
buffer.put(0, (byte) 'F');
buffer.put(1, (byte) 'U');
buffer.put(2, (byte) 'C');
buffer.put(3, (byte) 'K');
buffer.put(4, (byte) ' ');
byte[] bytes = new byte[20];
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
if (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
bytes[i] = buffer.get();
} else {
break;
}
}
System.out.println(new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
}
Scattering:将数据写入到buffer时,可以采用buffer数组,依次写入[分散]
Gathering:从buffer读取数据时,可以采用buffer数组,依次读取[聚合]
/**
* @author kern
*/
public class ExampleGatheringAndScatteringBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//一个线程池处理连接
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//Socket监听6666端口
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(6666));
while (true) {
System.out.println("服务器启动,等待监听");
final SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
executorService.execute(() -> {
//一个buffer数组,分别是容量5和容量3的两个buffer
ByteBuffer[] buffers = new ByteBuffer[2];
buffers[0] = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
buffers[1] = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
int readBytes = 0;
try {
//循环读取,每次只读满8个字节
long read = 0;
while ((read = socketChannel.read(buffers)) < 8 && read != 0 ) {
readBytes += read;
System.out.printf("ReadBytes=%d, %s %n", readBytes, Arrays.asList(buffers).stream().map(
b -> String.format("position=%s, limit=%s", b.position(), b.limit())
).collect(Collectors.joining(" ")));
}
/*
Connected to the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:50267', transport: 'socket'
服务器启动,等待监听
服务器启动,等待监听
ReadBytes=1, position=1, limit=5 position=0, limit=3
ReadBytes=4, position=4, limit=5 position=0, limit=3
ReadBytes=5, position=5, limit=5 position=0, limit=3
ReadBytes=6, position=5, limit=5 position=1, limit=3
ReadBytes=7, position=5, limit=5 position=2, limit=3
ReadBytes=8, position=5, limit=5 position=3, limit=3
服务器启动,等待监听
ReadBytes=1, position=1, limit=5 position=0, limit=3
ReadBytes=2, position=2, limit=5 position=0, limit=3
ReadBytes=3, position=3, limit=5 position=0, limit=3
ReadBytes=4, position=4, limit=5 position=0, limit=3
ReadBytes=5, position=5, limit=5 position=0, limit=3
ReadBytes=6, position=5, limit=5 position=1, limit=3
ReadBytes=7, position=5, limit=5 position=2, limit=3
ReadBytes=8, position=5, limit=5 position=3, limit=3
*/
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
}
?? 注意事项
- ByteBuffer支持类型化的put和get,put放入的是什么数据类型,get就应该使用相应的数据类型来取出,否则可能有BufferUnderflowException
https://blog.csdn.net/lili13897741554/article/details/82734656
| 基本数据类型 | 缓冲区 |
|---|---|
| byte | ByteBuffer |
| short | ShortBuffer |
| int | IntBuffer |
| long | LongBuffer |
| boolean | - |
| char | CharBuffer |
| float | FloatBuffer |
| double | DoubleBuffer |
3.2.2.2 通道Channel
- NIO的通道(Channel)类似于流,但通道(Channel)可以同时进行读写,而流只能是写入流(OutputStream)或读取流(InputStream)
- Channel是一个nio包中的接口,实现了Closeable接口
public interface Channel extends Closeable {}
- 常用的Channel实现
- FileChannel 文件数据读写
- DatagramChannel UDP数据读写
- ServerSocketChannel TCP数据读写
- SocketChannel TCP数据读写
FileChannel
- 文件读写
/**
* @author kern
*/
public class ExampleNioFileChannel {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/io-mode/src/main/resources/nio/file-channel.log";
//获取FIleChannel FileOutputStream -> Channel
FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
FileChannel channel = os.getChannel();
//数据写入Buffer中,并反转Buffer以进行读取
String str = "Hello Nio";
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buffer.put(str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
buffer.flip();
//Channel读取Buffer
channel.write(buffer);
os.close();
buffer.clear();
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(filePath);
channel = is.getChannel();
channel.read(buffer);
//注意反转
buffer.flip();
if (buffer.hasArray()) {
System.out.println(new String(buffer.array(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.limit()];
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
bytes[i] = buffer.get();
}
System.out.println(new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
}
- 文件复制
/**
* @author kern
*/
public class ExampleNioFileChannelCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//copy file
String filePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/io-mode/src/main/resources/nio/file-channel.log";
Path sourcePath = Paths.get(URI.create("file://" + filePath));
FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(sourcePath, StandardOpenOption.READ);
ByteBuffer copyBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) sourcePath.toFile().length());
fileChannel.read(copyBuffer);
copyBuffer.flip();
String targetFilePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/io-mode/src/main/resources/nio/file-channel-bak.log";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(targetFilePath);
FileChannel newFileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
newFileChannel.write(copyBuffer);
fileChannel.close();
newFileChannel.close();
String pictureFilePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/io-mode/src/main/resources/nio/Java虚拟器家族.png";
FileInputStream pictureIs = new FileInputStream(pictureFilePath);
String targetPictureFilePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/io-mode/src/main/resources/nio/Java虚拟器家族01.png";
FileOutputStream pictureOs = new FileOutputStream(targetPictureFilePath);
FileChannel isChannel = pictureIs.getChannel();
FileChannel osChannel = pictureOs.getChannel();
// osChannel.transferFrom(isChannel, 0, isChannel.size());
isChannel.transferTo(0, isChannel.size(), osChannel);
pictureIs.close();;
pictureOs.close();;
isChannel.close();
osChannel.close();
}
}
[
](https://blog.csdn.net/lili13897741554/article/details/82734656)
ServerSocketChannel

SocketChannel
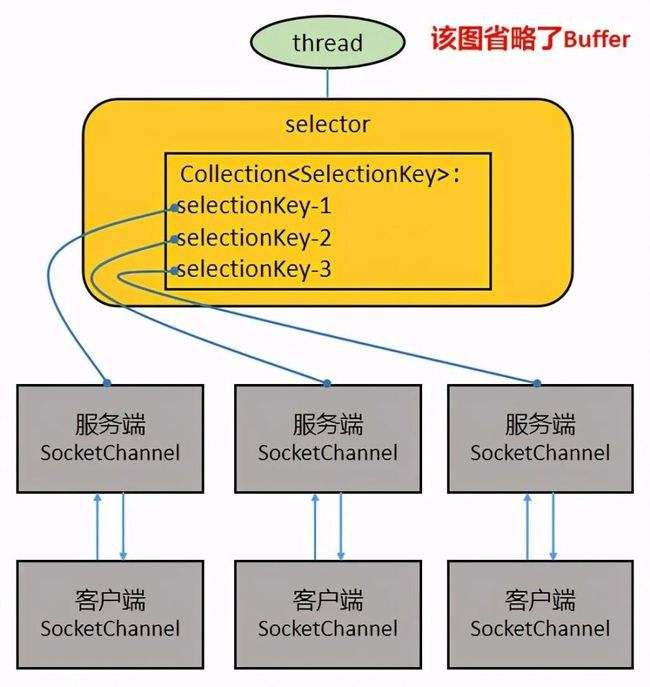
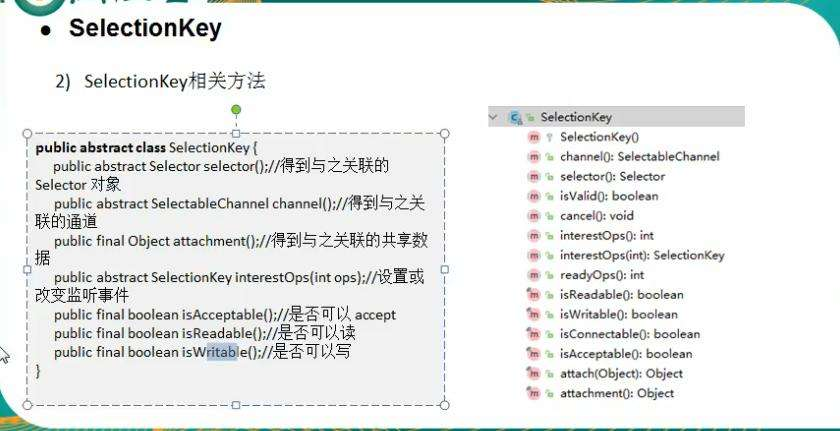
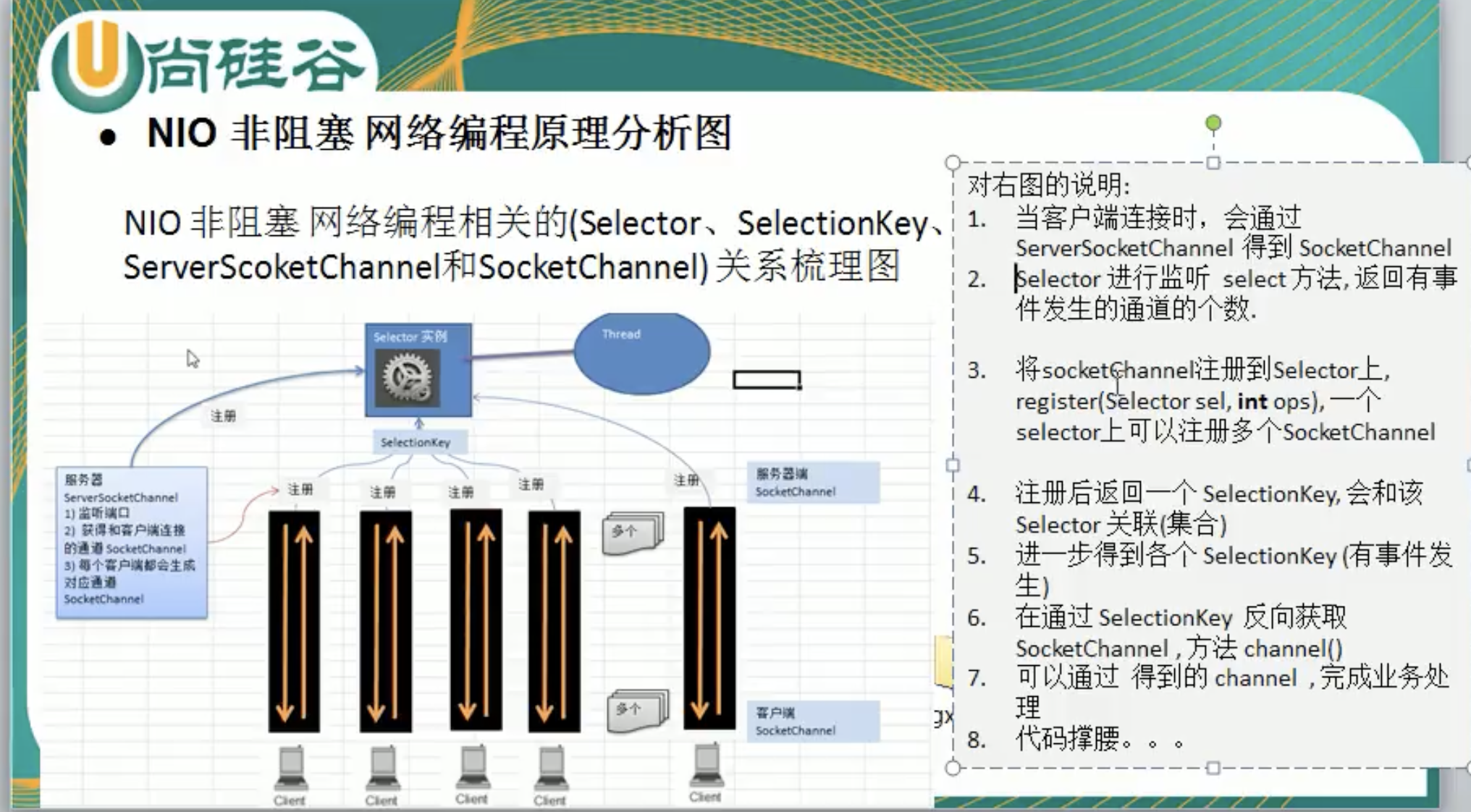
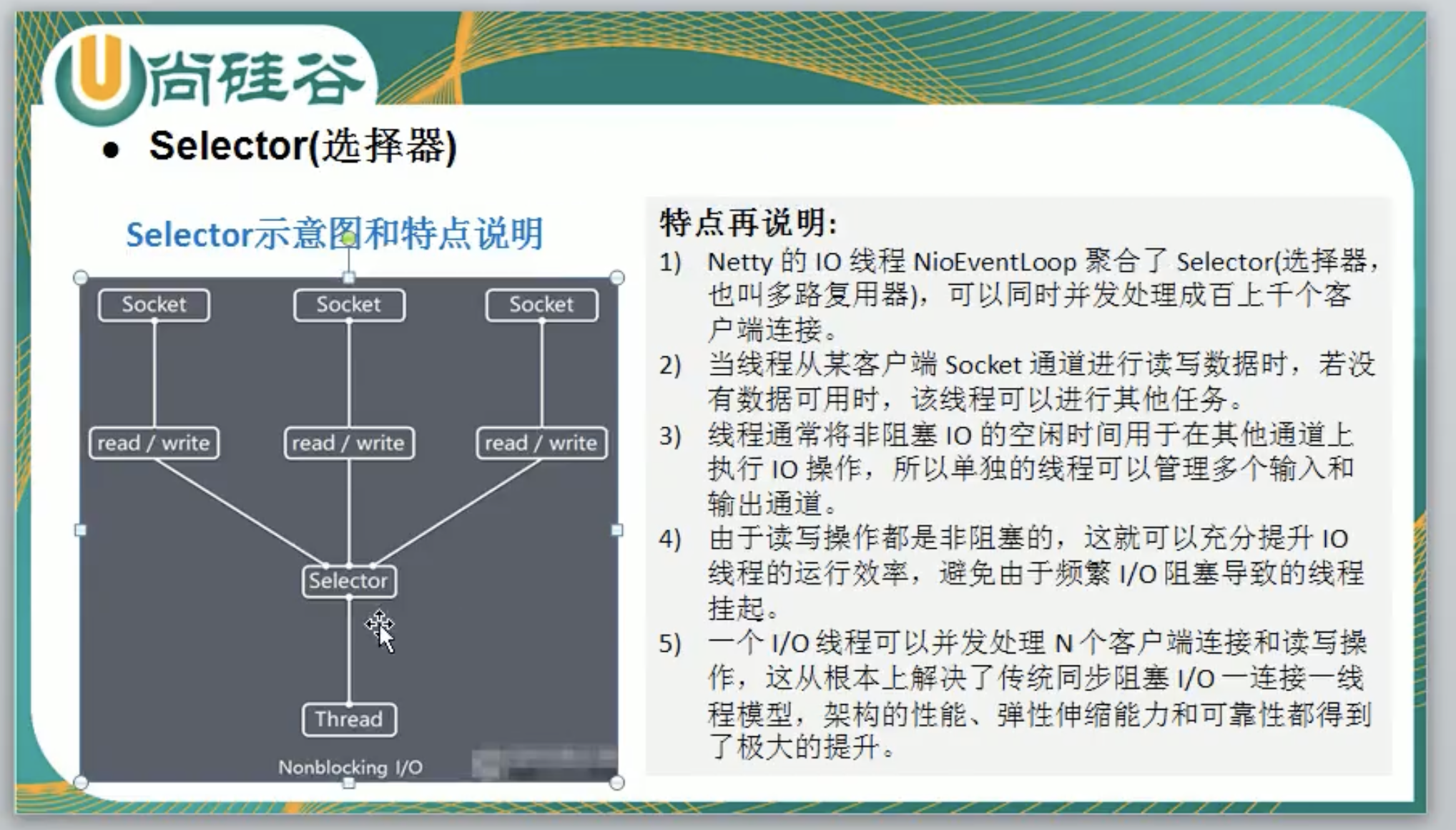
3.2.2.3 Selector
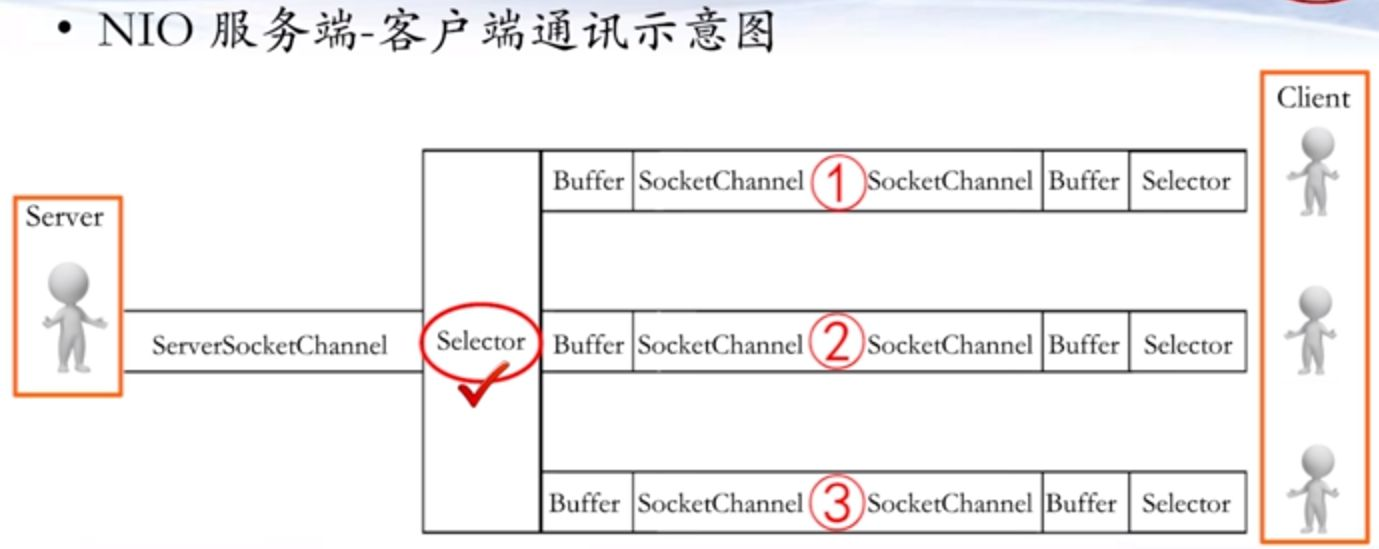
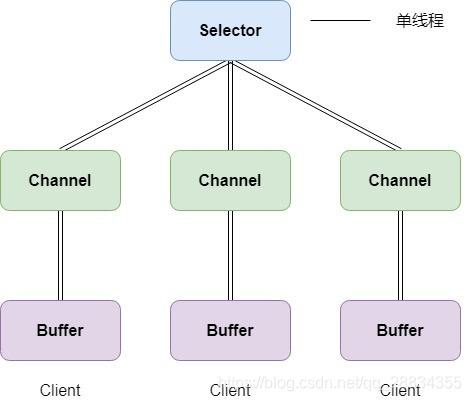
- Java的NIO用非阻塞的IO方式,可以用一个线程,处理多个客户端连接,就会使用到Selector(选择器)
- Selector能够检测多个注册的通道上是否有事件发生(注意:多个Channel以事件的方式可以注册到同一个Selector),如果有事件发生,便获取事件然后针对每个事件进行相应的处理。这样就可以只用一个单线程去管理多个通道,也就是管理多个连接和请求。
- 只有在连接真正有读写事件发生时,才会进行读写,就大大地减少了系统开销,并且不必为每个连接都创建一个线程,不用去维护多个线程,避免了多线程之间的上下文切换导致的开销。

3.2.3 NIOServer 和 NIOClient 编程实战
读写响应
/**
* @author kern
*/
public class ExampleNioServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//绑定端口
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(6666));
//声明非阻塞模式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//声明Selector选择器
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//Server注册到Selector,关注连接事件
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("启动服务");
//循环遍历是否有事件发生
//单线程不断轮询,如果有某个任务有阻塞也将导致程序阻塞
while (true) {
//无连接
if (selector.select(5000) == 0) {
System.out.println("服务端等待了5s, 无连接");
continue;
}
//有事件发生
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
//连接事件
if (key.isValid() && key.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
System.out.printf("连接事件: %s%n", socketChannel.socket().getInetAddress().getHostAddress());
//声明非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
}
//读事件
if (key.isValid() && key.isReadable()) {
System.out.printf("读事件 %s %n", Thread.currentThread().getName());
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
//读取请求写入buffer
int recount = 0;
try {
recount = socketChannel.read(buffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.printf("断开连接 %s %n", socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
socketChannel.close();
break;
}
if (recount == -1) {
System.out.printf("断开连接 %s %n", socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
socketChannel.close();
break;
}
String message = new String(buffer.array(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(message);
//重置下标
buffer.clear();
ByteBuffer respBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(String.format("Server Accept Msg=%s", message).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//读取buffer写入响应
socketChannel.write(respBuffer);
}
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
/**
* @author kern
*/
public class ExampleNioClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入服务端IP");
String ip = scanner.nextLine();
if ("close".equals(ip)) {
break ;
}
if ("".equals(ip)) {
ip = "127.0.0.1";
}
InetAddress address;
try {
address = InetAddress.getByName(ip);
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.out.println("IP错误");
continue;
}
int port = 6666;
while (true){
System.out.println("请输入服务端端口");
try {
port = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("端口错误");
continue;
}
break ;
}
System.out.println("准备连接");
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
SocketAddress socketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(address, port);
if (!socketChannel.connect(socketAddress)) {
while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()) {
System.out.println("连接中。。。");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
if (socketChannel.isConnected()) {
System.out.println("连接成功");
while (true) {
String line = scanner.nextLine();
if ("close".equals(line)) {
break ;
}
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(line.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//读取buffer并写入请求
socketChannel.write(buffer);
//重置下标
buffer.clear();
Thread.sleep(100);
//读取响应写入buffer
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readByte = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
byte[] bytes = new byte[readByte];
//读取模式
byteBuffer.flip();
byteBuffer.get(bytes);
byteBuffer.clear();
String message = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(message);
}
socketChannel.close();
System.out.println("连接结束");
}
}
}
}
聊天室
/**
* @author kern
*/
public class ExampleNioServer {
private final int port;
private final ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
private final Selector selector;
private volatile boolean isClose;
public ExampleNioServer(int port) throws IOException {
this.port = port;
this.isClose = false;
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//绑定端口
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
//声明非阻塞模式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//声明Selector选择器
selector = Selector.open();
//Server注册到Selector,关注连接事件
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("启动服务");
}
public void listen() throws IOException {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
while (!isClose) {
//无连接
if (selector.select(5000) == 0) {
System.out.println("服务端等待了5s, 无连接");
continue;
}
//有事件发生
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
//连接事件
if (key.isValid() && key.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
System.out.printf("连接事件: %s%n", socketChannel.socket().getInetAddress().getHostAddress());
//声明非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
//读事件
if (key.isValid() && key.isReadable()) {
System.out.printf("读事件 %s %n", Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
new ReadMassTextingHandle().read(selector, key);
} catch (IOException e) {
continue;
}
}
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("异常关闭" + e.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
shutDown();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
public void shutDown() throws IOException {
this.isClose = true;
selector.close();
System.out.println("服务关闭");
}
public interface ReadHandle {
String read(Selector selector, SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException;
}
public static class ReadOnlyHandle implements ReadHandle {
@Override
public String read(Selector selector, SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//读取请求写入buffer
int recount = 0;
try {
recount = socketChannel.read(buffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.printf("断开连接 %s %n", socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
socketChannel.close();
throw new IOException();
}
if (recount == -1) {
System.out.printf("断开连接 %s %n", socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
socketChannel.close();
throw new IOException();
}
String message = new String(buffer.array(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(message);
//重置下标
buffer.clear();
return message;
}
}
public static class ReadAndResponseHandle implements ReadHandle {
private final ReadHandle basicReadHandle = new ReadOnlyHandle();
@Override
public String read(Selector selector, SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException {
String message = basicReadHandle.read(selector, selectionKey);
ByteBuffer respBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(String.format("Server Accept Msg=%s", message).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//读取buffer写入响应
((SocketChannel)selectionKey.channel()).write(respBuffer);
return message;
}
}
public static class ReadMassTextingHandle implements ReadHandle {
private final ReadHandle basicReadHandle = new ReadOnlyHandle();
@Override
public String read(Selector selector, SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException {
String message = basicReadHandle.read(selector, selectionKey);
byte[] bytes = message == null ? null : message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
if (bytes != null) {
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.keys();
keys.forEach(e -> {
if (e.isValid() && e.channel() instanceof SocketChannel) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes);
try {
((SocketChannel)e.channel()).write(buffer);
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
return message;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ExampleNioServer nioServer = new ExampleNioServer(6666);
nioServer.listen();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
scanner.nextLine();
//一旦获取输入即关闭
nioServer.shutDown();
}
}
/**
* @author kern
*/
public class ExampleNioClient {
public ExampleNioClient(String name, String ip, int port) throws IOException {
this.name = name;
this.ip = ip;
this.port = port;
this.isClose = false;
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
if (!socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(ip, port))) {
while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()) {
System.out.println("连接中。。。");
}
}
System.out.println(name + " --> 连接成功");
}
private final String name;
private final String ip;
private final int port;
private final SocketChannel socketChannel;
private volatile boolean isClose;
public void listenReading() {
new Thread(() -> {
while (!isClose) {
//读取响应写入buffer
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readByte = 0;
try {
readByte = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("读取消息异常,服务关闭");
shutDown();
}
if (readByte == -1) {
System.out.println("读取消息异常,服务关闭");
shutDown();
}
if (readByte > 0) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[readByte];
//读取模式
byteBuffer.flip();
byteBuffer.get(bytes);
byteBuffer.clear();
String message = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(message);
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
public void listenWriting(Scanner scanner) throws IOException{
while (!isClose) {
String line = scanner.nextLine();
if ("close".equals(line)) {
shutDown();
}
line = name + ": " + line;
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(line.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//读取buffer并写入请求
socketChannel.write(buffer);
//重置下标
buffer.clear();
}
}
public void shutDown() {
try {
socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
isClose = true;
System.out.println("连接结束");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入账号");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
if ("close".equals(name)) {
System.out.println("关闭窗口");
break;
}
System.out.println("准备连接");
ExampleNioClient nioClient = new ExampleNioClient(name, "127.0.0.1", 6666);
nioClient.listenReading();
nioClient.listenWriting(scanner);
}
}
}
3.2.4 NIO与零拷贝
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46589575/article/details/117440450
- 零拷贝是网络编程的关键,很多性能优化都离不开零拷贝。
- 常用的零拷贝技术
- mmap(内存映射)
- sendFile
- Java NIO的零拷贝
channel.transferTo()channel.transferFrom()
传统IO文件读写
File file = new File("");
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");
byte[] bytes = new byte[(int) file.length()];
//1. 用户态切换到内核态 -> 进行 DMA拷贝(直接内存拷贝)到内核空间 -> 进行CPU拷贝到用户空间
raf.read(bytes);
//对读取到的字节数组进行操作
//2. 内核态切换到用户态
Socket socket = new ServerSocket(8080).accept();
//3. 用户态切换到内核态 -> 进行CPU拷贝到内核空间 -> 进行DMA拷贝到协议栈
socket.getOutputStream().write(bytes);
//用户态和内核态的切换总共三次,拷贝4次
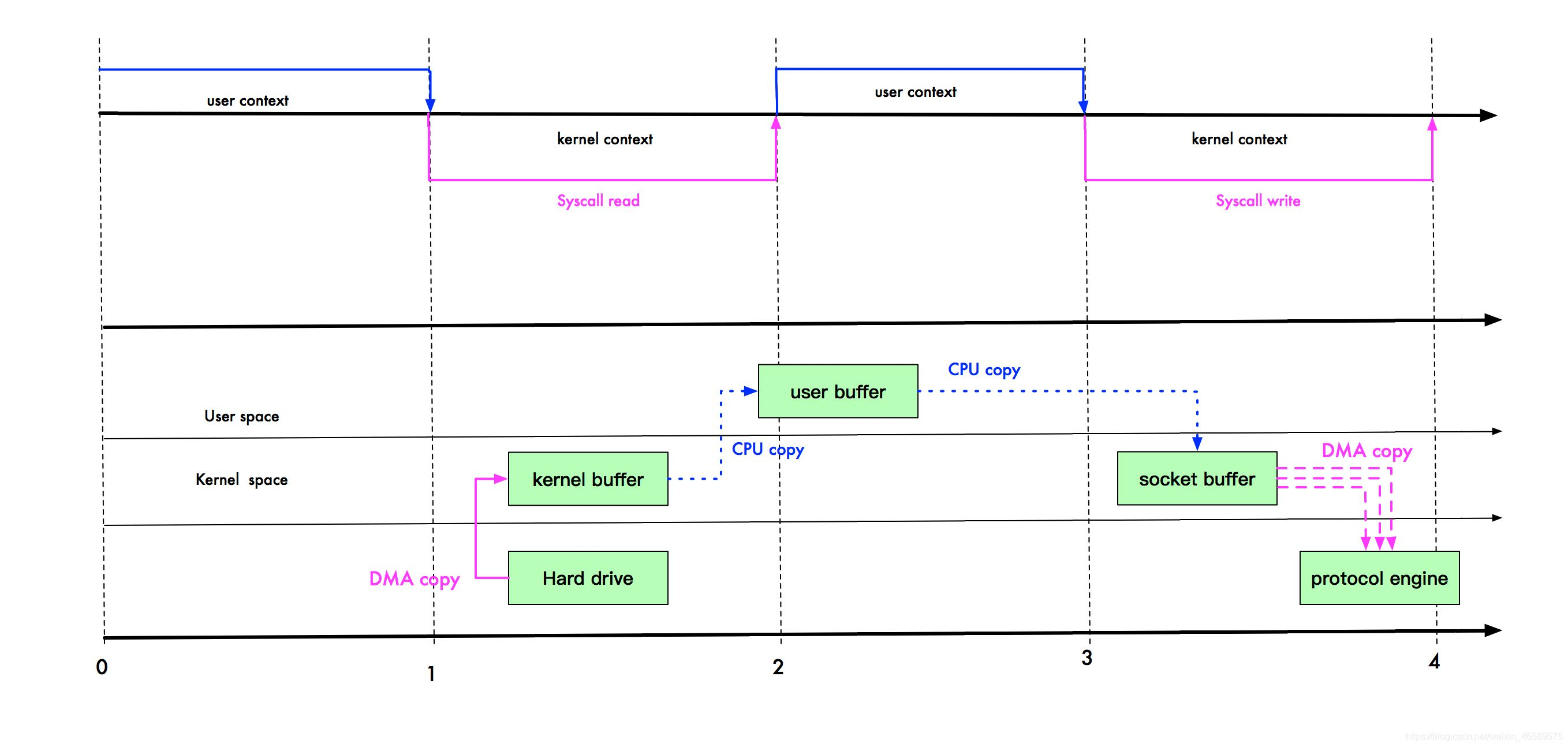
**mmap优化 **
通过内存映射,将文件映射到内核缓冲区,同时,用户空间可以共享内核空间的数据。这样,在进行网络传输时,就可以减少内核空间到用户空间的拷贝次数。
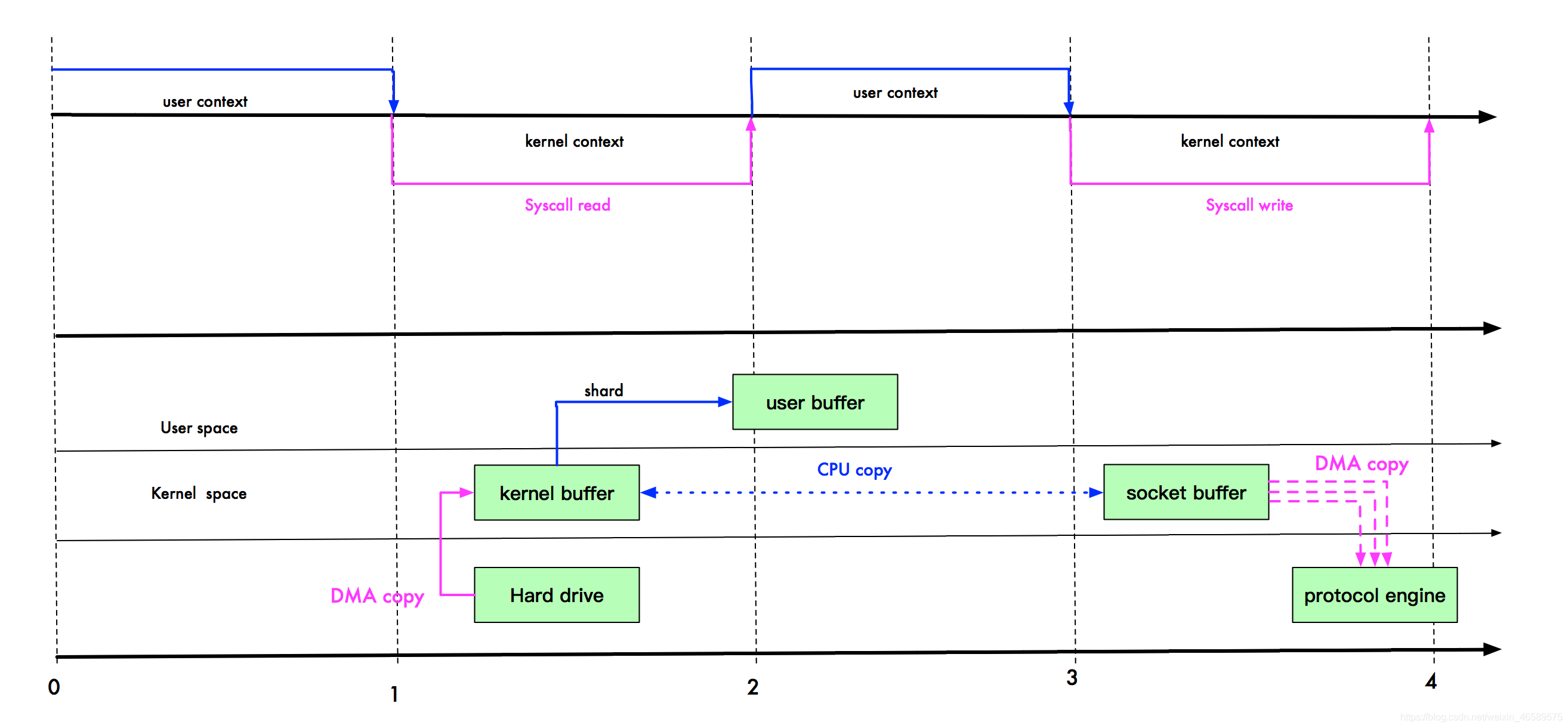
user buffer 和 kernel buffer 共享 index.html。如果你想把硬盘的 index.html 传输到网络中,再也不用拷贝到用户空间,再从用户空间拷贝到 Socket 缓冲区。
现在,你只需要从内核缓冲区拷贝到 Socket 缓冲区即可,这将减少一次内存拷贝(从 4 次变成了 3 次),但不减少上下文切换次数。
sendFile优化
Linux 2.1 版本 提供了 sendFile 函数,其基本原理如下:数据根本不经过用户态,直接从内核缓冲区进入到 Socket Buffer,同时,由于和用户态完全无关,就减少了一次上下文切换。
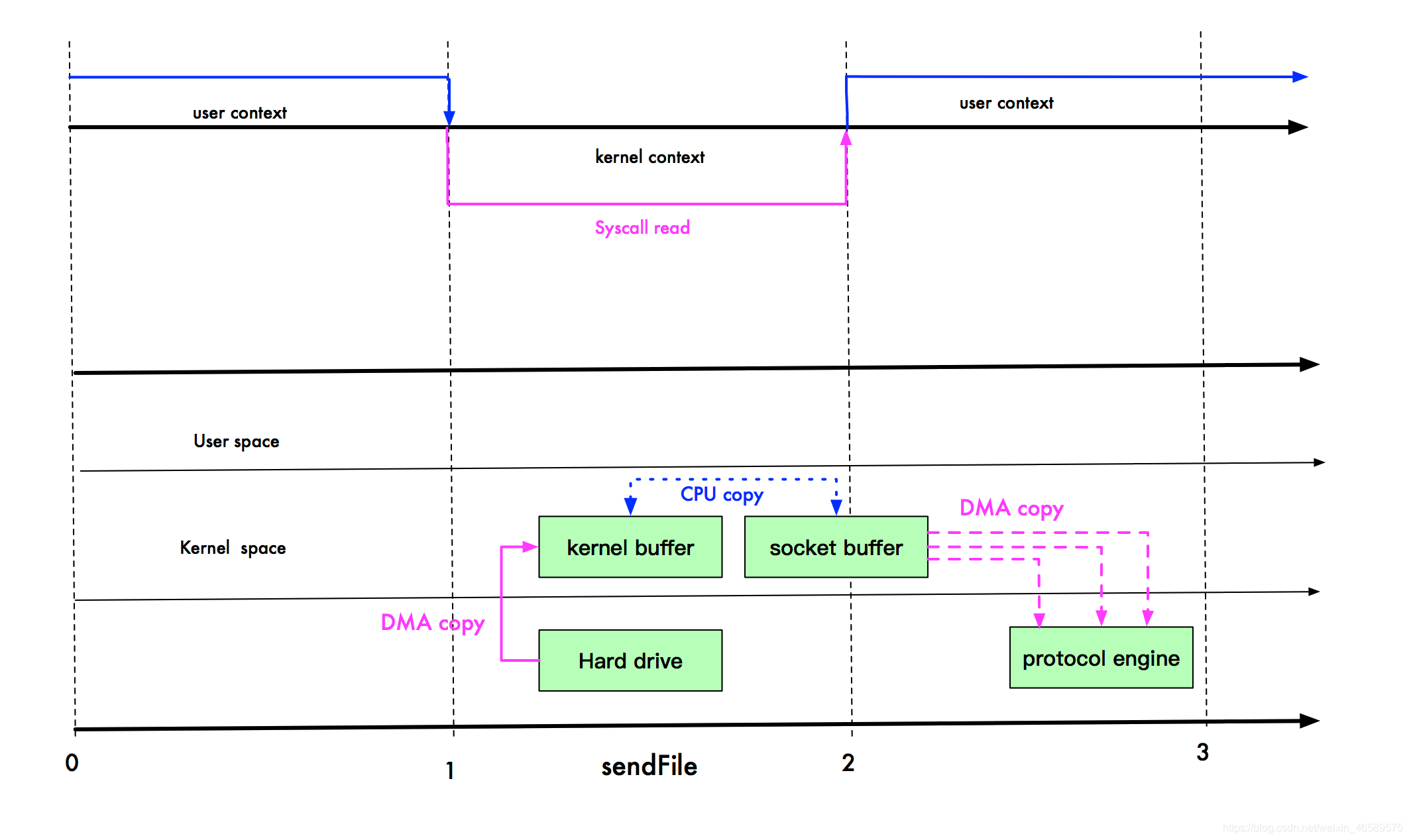
我们进行 sendFile 系统调用时,数据被 DMA 引擎从文件复制到内核缓冲区,然后调用 write 方法时,从内核缓冲区进入到 Socket,这时,是没有上下文切换的,因为都在内核空间。
最后,数据从 Socket 缓冲区进入到协议栈。此时,数据经过了 3 次拷贝,3 次上下文切换。那么,还能不能再继续优化呢? 例如直接从内核缓冲区拷贝到网络协议栈?
实际上,Linux 在 2.4 版本中,做了一些修改,避免了从内核缓冲区拷贝到 Socket buffer 的操作,直接拷贝到协议栈,从而再一次减少了数据拷贝。具体如下图:
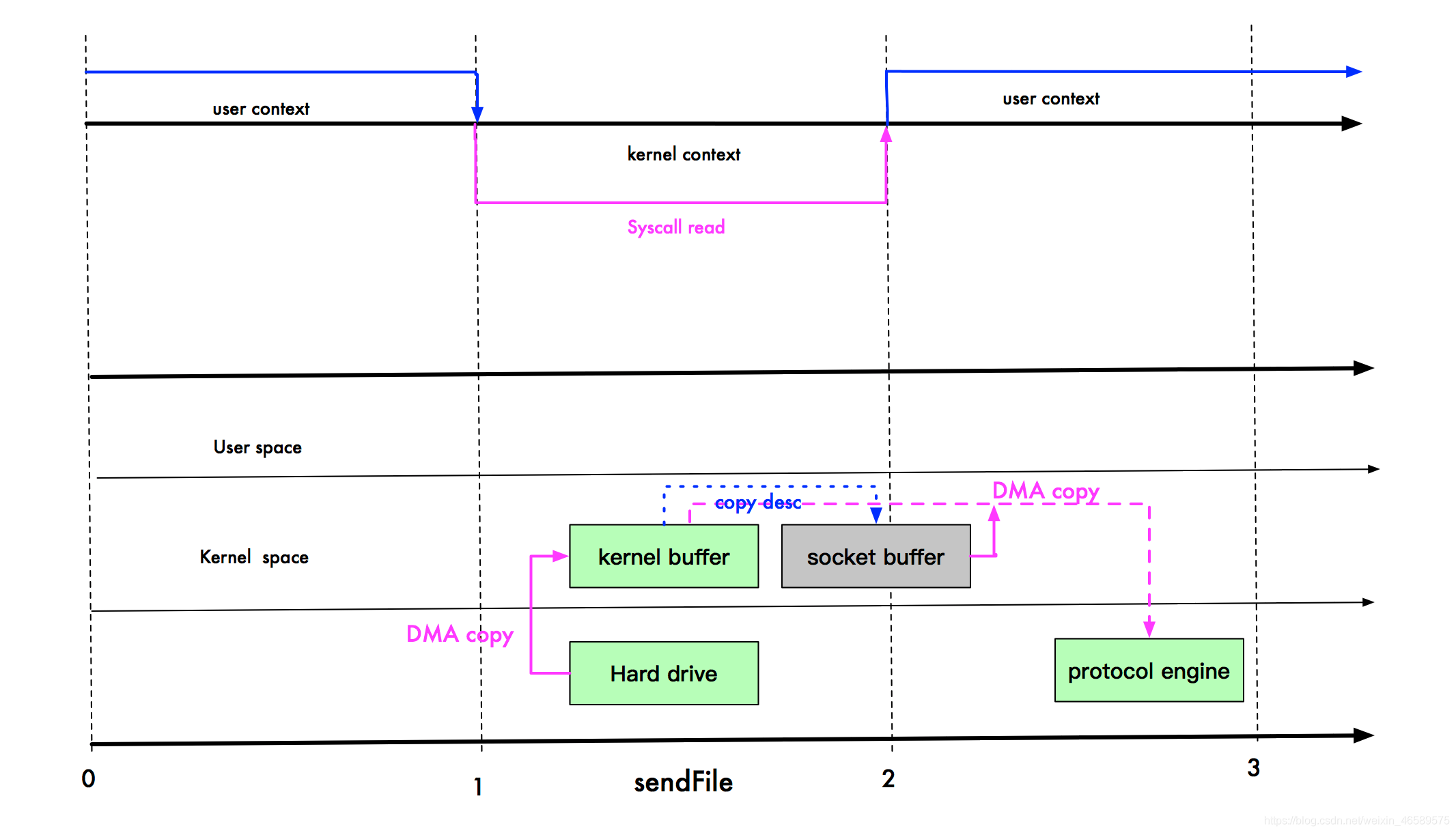
现在,index.html 要从文件进入到网络协议栈,只需 2 次拷贝:第一次使用 DMA 引擎从文件拷贝到内核缓冲区,第二次从内核缓冲区将数据拷贝到网络协议栈;内核缓存区只会拷贝一些 offset 和 length 信息到 SocketBuffer,基本无消耗。
等一下,不是说零拷贝吗?为什么还是要 2 次拷贝?
首先我们说零拷贝,是从操作系统的角度来说的。因为内核缓冲区之间,没有数据是重复的(只有 kernel buffer 有一份数据,sendFile 2.1 版本实际上有 2 份数据,算不上零拷贝)。例如我们刚开始的例子,内核缓存区和 Socket 缓冲区的数据就是重复的。
而零拷贝不仅仅带来更少的数据复制,还能带来其他的性能优势,例如更少的上下文切换,更少的 CPU 缓存伪共享以及无 CPU 校验和计算。
再稍微讲讲 mmap 和 sendFile 的区别。
mmap 适合小数据量读写,sendFile 适合大文件传输。
mmap 需要 4 次上下文切换,3 次数据拷贝;sendFile 需要 3 次上下文切换,最少 2 次数据拷贝。
sendFile 可以利用 DMA 方式,减少 CPU 拷贝,mmap 则不能(必须从内核拷贝到 Socket 缓冲区)。
在这个选择上:rocketMQ 在消费消息时,使用了 mmap。kafka 使用了 sendFile。
bio vs nio 文件拷贝实战测试
mac pro 16M ram 文件大小 160m
BIO实战耗时平均7s
/**
*
* @author kern
*/
public class ExampleBioFileCopyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(7001);
while (true) {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
DataInputStream inputStream = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
List<Byte> list = new ArrayList<>();
byte[] bytes = new byte[4096];
int readTotal = 0;
int readCount;
while ((readCount = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
readTotal += readCount;
for (byte aByte : bytes) {
list.add(aByte);
}
}
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("/Users/kern/IdeaRepo/gitee/netty-demo/io-mode/src/main/resources/nio/代码大全2中文版-copy.pdf");
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(outputStream);
byte[] allBytes = new byte[list.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
allBytes[i] = list.get(i);
}
dos.write(allBytes);
dos.flush();
dos.close();
socket.close();
System.out.println("总共读取字节:" + readTotal);
}
}
}
/**
* 平均耗时7s左右
* 6959 7668 10585
* @author kern
*/
public class ExampleBioFileCopyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
long millisTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
File file = new File("/Users/kern/IdeaRepo/gitee/netty-demo/io-mode/src/main/resources/nio/代码大全2中文版(高清晰完美PDF版,索引完整).pdf");
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");
byte[] bytes = new byte[(int) file.length()];
//1. 用户态切换到内核态 -> 进行 DMA拷贝(直接内存拷贝)到内核空间 -> 进行CPU拷贝到用户空间
raf.read(bytes);
//对读取到的字节数组进行操作
//2. 内核态切换到用户态
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 7001);
//3. 用户态切换到内核态 -> 进行CPU拷贝到内核空间 -> 进行DMA拷贝到协议栈
socket.getOutputStream().write(bytes);
//用户态和内核态的切换总共三次,拷贝4次
System.out.printf("总共耗时: %d millis", System.currentTimeMillis() - millisTime);
}
}
NIO实战耗时平均0.15s
/**
* @author kern
*/
public class ExampleNioFileCopyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(7002));
while (true) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
FileChannel fileChannel = new FileOutputStream("/Users/kern/IdeaRepo/gitee/netty-demo/io-mode/src/main/resources/nio/代码大全2中文版-copy.pdf").getChannel();
fileChannel.transferFrom(socketChannel, 0, 161366016);
System.out.println("总共读取字节:" + fileChannel.size());
}
}
}
/**
* 平均耗时 0.15秒左右
* 182 154 127 125 128
* @author kern
*/
public class ExampleNioFileCopyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
long millisTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("/Users/kern/IdeaRepo/gitee/netty-demo/io-mode/src/main/resources/nio/代码大全2中文版(高清晰完美PDF版,索引完整).pdf");
FileChannel fileChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 7002));
fileChannel.transferTo(0, fileChannel.size(), socketChannel);
//用户态和内核态的切换总共三次,拷贝4次
System.out.printf("总共耗时: %d millis", System.currentTimeMillis() - millisTime);
}
}
bio的服务端编码可能有些问题,但总的还是能感受到性能差异。
3.4 Java AIO详解
- JDK 7 引入 Asynchronous I/O。在进行io编程中,常用到两种模式:Reactor 和 Proactor。Java 的 NIO 就是 Reactor,当有事件触发时,服务端得到通知,进行相应的处理。
- AIO 即 NIO2.0,即异步不阻塞IO。AIO引入异步通道的概念,采用了系统完成后才通知服务端程序启动线程去处理,一般适用于连续数较多且连续时间较长的应用。
- 目前AIO还没有广泛应用。
4. BIO/NIO/AIO对比