总体时序
先概述一下总体运行流程,当按电源键,首先是加载系统引导程序BootLoader,然后启动linux内核,再启动init进程,最后Zygote进程启动完成。理论上Android系统中的所有应用程序理论上都是由Zygote启动的。Zygote前期启动启动服务,后期主要fork程序。
init启动流程
- 用户空间的第一个进程,进程号为1(在《深入理解安卓内核思想》的257页里面写的是0,在这记录一下).
- 职责
- 创建Zygote
- 初始化属性服务
- init文件位于源码目录system/core/init中
init进程的启动三个阶段
- 启动电源以及系统的启动,加载引导程序BootLoader。
- 启动Linux内核
- 启动init进程。
- 启动Zygote进程
- 初始化启动属性服务。
入口函数
Linux内核启动,启动init进程,进入init的入口函数中,加载init.rc文件:
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "ueventd")) {
return ueventd_main(argc, argv);
}
if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "watchdogd")) {
return watchdogd_main(argc, argv);
}
if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) {
install_reboot_signal_handlers();
}
add_environment("PATH", _PATH_DEFPATH);
bool is_first_stage = (getenv("INIT_SECOND_STAGE") == nullptr);
if (is_first_stage) {
boot_clock::time_point start_time = boot_clock::now();
// Clear the umask. 清理umask
umask(0);
// Get the basic filesystem setup we need put together in the initramdisk
// on / and then we'll let the rc file figure out the rest.
//创建挂在启动所需要的文件目录
mount("tmpfs", "/dev", "tmpfs", MS_NOSUID, "mode=0755");
mkdir("/dev/pts", 0755);
mkdir("/dev/socket", 0755);
mount("devpts", "/dev/pts", "devpts", 0, NULL);
#define MAKE_STR(x) __STRING(x)
mount("proc", "/proc", "proc", 0, "hidepid=2,gid=" MAKE_STR(AID_READPROC));
// Don't expose the raw commandline to unprivileged processes.
chmod("/proc/cmdline", 0440);
gid_t groups[] = { AID_READPROC };
setgroups(arraysize(groups), groups);
mount("sysfs", "/sys", "sysfs", 0, NULL);
mount("selinuxfs", "/sys/fs/selinux", "selinuxfs", 0, NULL);
mknod("/dev/kmsg", S_IFCHR | 0600, makedev(1, 11));
mknod("/dev/random", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(1, 8));
mknod("/dev/urandom", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(1, 9));
// Now that tmpfs is mounted on /dev and we have /dev/kmsg, we can actually
// talk to the outside world...
InitKernelLogging(argv);
LOG(INFO) << "init first stage started!";
if (!DoFirstStageMount()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to mount required partitions early ...";
panic();
}
SetInitAvbVersionInRecovery();
// Set up SELinux, loading the SELinux policy.
selinux_initialize(true);
// We're in the kernel domain, so re-exec init to transition to the init domain now
// that the SELinux policy has been loaded.
if (restorecon("/init") == -1) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "restorecon failed";
security_failure();
}
setenv("INIT_SECOND_STAGE", "true", 1);
static constexpr uint32_t kNanosecondsPerMillisecond = 1e6;
uint64_t start_ms = start_time.time_since_epoch().count() / kNanosecondsPerMillisecond;
setenv("INIT_STARTED_AT", StringPrintf("%" PRIu64, start_ms).c_str(), 1);
char* path = argv[0];
char* args[] = { path, nullptr };
execv(path, args);
// execv() only returns if an error happened, in which case we
// panic and never fall through this conditional.
PLOG(ERROR) << "execv(\"" << path << "\") failed";
security_failure();
}
// At this point we're in the second stage of init.
InitKernelLogging(argv);
LOG(INFO) << "init second stage started!";
// Set up a session keyring that all processes will have access to. It
// will hold things like FBE encryption keys. No process should override
// its session keyring.
keyctl(KEYCTL_GET_KEYRING_ID, KEY_SPEC_SESSION_KEYRING, 1);
// Indicate that booting is in progress to background fw loaders, etc.
close(open("/dev/.booting", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_CLOEXEC, 0000));
//初始化和启动属性服务
property_init();
// If arguments are passed both on the command line and in DT,
// properties set in DT always have priority over the command-line ones.
process_kernel_dt();
process_kernel_cmdline();
// Propagate the kernel variables to internal variables
// used by init as well as the current required properties.
export_kernel_boot_props();
// Make the time that init started available for bootstat to log.
property_set("ro.boottime.init", getenv("INIT_STARTED_AT"));
property_set("ro.boottime.init.selinux", getenv("INIT_SELINUX_TOOK"));
// Set libavb version for Framework-only OTA match in Treble build.
const char* avb_version = getenv("INIT_AVB_VERSION");
if (avb_version) property_set("ro.boot.avb_version", avb_version);
// Clean up our environment.
unsetenv("INIT_SECOND_STAGE");
unsetenv("INIT_STARTED_AT");
unsetenv("INIT_SELINUX_TOOK");
unsetenv("INIT_AVB_VERSION");
// Now set up SELinux for second stage.
selinux_initialize(false);
selinux_restore_context();
//创建epoll句柄
epoll_fd = epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC);
if (epoll_fd == -1) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "epoll_create1 failed";
exit(1);
}
//设置进程信号处理,用于设置子进程信号处理函数,如果子进程异常退出,init进程会调用
//中设定的信号处理函数处理。
signal_handler_init();
//导入默认的环境变量
property_load_boot_defaults();
export_oem_lock_status();
start_property_service();
set_usb_controller();
const BuiltinFunctionMap function_map;
Action::set_function_map(&function_map);
Parser& parser = Parser::GetInstance();
parser.AddSectionParser("service",std::make_unique<ServiceParser>());
parser.AddSectionParser("on", std::make_unique<ActionParser>());
parser.AddSectionParser("import", std::make_unique<ImportParser>());
std::string bootscript = GetProperty("ro.boot.init_rc", "");
if (bootscript.empty()) {
//解析init.rc配置文件
parser.ParseConfig("/init.rc");
parser.set_is_system_etc_init_loaded(
parser.ParseConfig("/system/etc/init"));
parser.set_is_vendor_etc_init_loaded(
parser.ParseConfig("/vendor/etc/init"));
parser.set_is_odm_etc_init_loaded(parser.ParseConfig("/odm/etc/init"));
} else {
parser.ParseConfig(bootscript);
parser.set_is_system_etc_init_loaded(true);
parser.set_is_vendor_etc_init_loaded(true);
parser.set_is_odm_etc_init_loaded(true);
}
// Turning this on and letting the INFO logging be discarded adds 0.2s to
// Nexus 9 boot time, so it's disabled by default.
if (false) parser.DumpState();
ActionManager& am = ActionManager::GetInstance();
am.QueueEventTrigger("early-init");
// Queue an action that waits for coldboot done so we know ueventd has set up all of /dev...
am.QueueBuiltinAction(wait_for_coldboot_done_action, "wait_for_coldboot_done");
// ... so that we can start queuing up actions that require stuff from /dev.
am.QueueBuiltinAction(mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng_action, "mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(set_mmap_rnd_bits_action, "set_mmap_rnd_bits");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(set_kptr_restrict_action, "set_kptr_restrict");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(keychord_init_action, "keychord_init");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(console_init_action, "console_init");
// Trigger all the boot actions to get us started.
am.QueueEventTrigger("init");
// Repeat mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng in case /dev/hw_random or /dev/random
// wasn't ready immediately after wait_for_coldboot_done
am.QueueBuiltinAction(mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng_action, "mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng");
// Don't mount filesystems or start core system services in charger mode.
std::string bootmode = GetProperty("ro.bootmode", "");
if (bootmode == "charger") {
am.QueueEventTrigger("charger");
} else {
am.QueueEventTrigger("late-init");
}
// Run all property triggers based on current state of the properties.
am.QueueBuiltinAction(queue_property_triggers_action, "queue_property_triggers");
while (true) {
// By default, sleep until something happens.
int epoll_timeout_ms = -1;
if (!(waiting_for_prop || ServiceManager::GetInstance().IsWaitingForExec())) {
//内部遍历执行每个action中携带的command对应的执行函数
am.ExecuteOneCommand();
}
if (!(waiting_for_prop || ServiceManager::GetInstance().IsWaitingForExec())) {
//重启死去的进程
restart_processes();
// If there's a process that needs restarting, wake up in time for that.
if (process_needs_restart_at != 0) {
epoll_timeout_ms = (process_needs_restart_at - time(nullptr)) * 1000;
if (epoll_timeout_ms < 0) epoll_timeout_ms = 0;
}
// If there's more work to do, wake up again immediately.
if (am.HasMoreCommands()) epoll_timeout_ms = 0;
}
epoll_event ev;
int nr = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(epoll_wait(epoll_fd, &ev, 1, epoll_timeout_ms));
if (nr == -1) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "epoll_wait failed";
} else if (nr == 1) {
((void (*)()) ev.data.ptr)();
}
}
return 0;
}
main函数中做了很多事情,主要做的事情如下:
- 初始化和启动属性服务
- 信号处理,详见system/core/init/signal_handler_init.cpp文件
- 解析init.rc文件,详见system/core/init/init_parse.cpp文件
property_init
代码详见:\system\core\init\property_service.cpp
void property_init() {
if (__system_property_area_init()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to initialize property area";
exit(1);
}
}
void start_property_service() {
property_set("ro.property_service.version", "2");
property_set_fd = create_socket(PROP_SERVICE_NAME, SOCK_STREAM | SOCK_CLOEXEC | SOCK_NONBLOCK,
0666, 0, 0, NULL);//创建非阻塞的Socket
if (property_set_fd == -1) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "start_property_service socket creation failed";
exit(1);
}
listen(property_set_fd, 8);//调用listen函数对对属性进行监听
register_epoll_handler(property_set_fd, handle_property_set_fd);//当有数据更新时,init进程会调用handle_property_set_fd函数进行处理
}
- 属性服务的初始化
- 创建非阻塞的Socket
- 调用listen函数对对属性进行监听
- 当有数据更新时,init进程会调用handle_property_set_fd函数进行处理
handle_property_set
代码详见:\system\core\init\property_service.cpp
static void handle_property_set(SocketConnection& socket,
const std::string& name,
const std::string& value,
bool legacy_protocol) {
const char* cmd_name = legacy_protocol ? "PROP_MSG_SETPROP" : "PROP_MSG_SETPROP2";
if (!is_legal_property_name(name)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(" << cmd_name << "): illegal property name \"" << name << "\"";
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_INVALID_NAME);
return;
}
struct ucred cr = socket.cred();
char* source_ctx = nullptr;
getpeercon(socket.socket(), &source_ctx);
//ctl开头为控制属性
if (android::base::StartsWith(name, "ctl.")) {
//校验客户端权限
if (check_control_mac_perms(value.c_str(), source_ctx, &cr)) {
//设置控制属性
handle_control_message(name.c_str() + 4, value.c_str());
if (!legacy_protocol) {
socket.SendUint32(PROP_SUCCESS);
}
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(" << cmd_name << "): Unable to " << (name.c_str() + 4)
<< " service ctl [" << value << "]"
<< " uid:" << cr.uid
<< " gid:" << cr.gid
<< " pid:" << cr.pid;
if (!legacy_protocol) {
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_HANDLE_CONTROL_MESSAGE);
}
}
} else {//普通属性
//校验客户端权限
if (check_mac_perms(name, source_ctx, &cr)) {
uint32_t result = property_set(name, value);
if (!legacy_protocol) {
socket.SendUint32(result);
}
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(" << cmd_name << "): permission denied uid:" << cr.uid << " name:" << name;
if (!legacy_protocol) {
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_PERMISSION_DENIED);
}
}
}
freecon(source_ctx);
}
static void handle_property_set_fd() {
static constexpr uint32_t kDefaultSocketTimeout = 2000; /* ms */
int s = accept4(property_set_fd, nullptr, nullptr, SOCK_CLOEXEC);
if (s == -1) {
return;
}
struct ucred cr;
socklen_t cr_size = sizeof(cr);
if (getsockopt(s, SOL_SOCKET, SO_PEERCRED, &cr, &cr_size) < 0) {
close(s);
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop: unable to get SO_PEERCRED";
return;
}
SocketConnection socket(s, cr);
uint32_t timeout_ms = kDefaultSocketTimeout;
uint32_t cmd = 0;
if (!socket.RecvUint32(&cmd, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop: error while reading command from the socket";
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_READ_CMD);
return;
}
switch (cmd) {
case PROP_MSG_SETPROP: {
char prop_name[PROP_NAME_MAX];
char prop_value[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
//如果Socket读取不到数据就返回
if (!socket.RecvChars(prop_name, PROP_NAME_MAX, &timeout_ms) ||
!socket.RecvChars(prop_value, PROP_VALUE_MAX, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(PROP_MSG_SETPROP): error while reading name/value from the socket";
return;
}
prop_name[PROP_NAME_MAX-1] = 0;
prop_value[PROP_VALUE_MAX-1] = 0;
handle_property_set(socket, prop_value, prop_value, true);
break;
}
case PROP_MSG_SETPROP2: {
std::string name;
std::string value;
if (!socket.RecvString(&name, &timeout_ms) ||
!socket.RecvString(&value, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(PROP_MSG_SETPROP2): error while reading name/value from the socket";
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_READ_DATA);
return;
}
handle_property_set(socket, name, value, false);//处理客户端的请求
break;
}
default:
LOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop: invalid command " << cmd;
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_INVALID_CMD);
break;
}
}
- 处理客户端请求
- 服务属性接收到客户端请求时调用handle_property_set_fd()处理数据
- 根据属性分类处理:普通属性、控制属性
init.rc文件
官方注解文档详见system/core/init/Readme.txt
init.rc文件详见system/core/rootdir,其用到了AIL(Android Init Language)语言,其详细含义请自行百度。
在Android8.0中对init.rc文件进行了拆分,每个服务对应一个rc文件。
解析init.rc
zygote启动脚本路径为:system/core/rootdir/init.zygote64.rc
service zygote /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
class main
priority -20
user root
group root readproc
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart cameraserver
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
onrestart restart wificond
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks
启动脚本中参数介绍:
- zygote:创建的进程名称
- /system/bin/app_process64 :执行的文件路径
- class main:表示Zygote的classname为main,后面会根据main查找Zygote服务
- onrestart:当服务启动时需要重启的服务
Service类型语句采用ServiceParser进行解析,ServiceParser代码在system/core/init/service.cpp中,其会针对启动脚本中的每个服务创建对应的实例,然后将所有的对象实例缓存在Service链表中,在启动服务时就会从此列表中查找对应的服务对象。
class main代表的是Zygote服务,所以会遍历前面保存解析Service的链表,查找classname为main()的服务,然后执行Service中的start()方法。
Result<Success> Service::Start() {
pid_t pid = -1;
if (namespace_flags_) {
pid = clone(nullptr, nullptr, namespace_flags_ | SIGCHLD, nullptr);
} else {
pid = fork();
}
if (pid == 0) {
if (!ExpandArgsAndExecv(args_)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "cannot execve('" << args_[0] << "')";
}
}
}
static bool ExpandArgsAndExecv(const std::vector<std::string>& args) {
return execv(c_strings[0], c_strings.data()) == 0; //3、
}
在statr()方法中,首先判断进程是否已经运行,对未运行的进程通过fork()创建子进程,创建成功后调用ExpandArgsAndExecv()方法,在ExpandArgsAndExecv()中调用执行execv()后Service进程就被启动并进入Service的main()方法,Zygote进程对应的程序路径为app_main.cpp,在app_main.cpp的main()方法中调用runtime.start()启动进程。
路径:frameworks\base\cmds\app_process\app_main.c
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
if (!LOG_NDEBUG) {
String8 argv_String;
for (int i = 0; i < argc; ++i) {
argv_String.append("\"");
argv_String.append(argv[i]);
argv_String.append("\" ");
}
ALOGV("app_process main with argv: %s", argv_String.string());
}
AppRuntime runtime(argv[0], computeArgBlockSize(argc, argv));
// Process command line arguments
// ignore argv[0]
argc--;
argv++;
// Everything up to '--' or first non '-' arg goes to the vm.
//
// The first argument after the VM args is the "parent dir", which
// is currently unused.
//
// After the parent dir, we expect one or more the following internal
// arguments :
//
// --zygote : Start in zygote mode
// --start-system-server : Start the system server.
// --application : Start in application (stand alone, non zygote) mode.
// --nice-name : The nice name for this process.
//
// For non zygote starts, these arguments will be followed by
// the main class name. All remaining arguments are passed to
// the main method of this class.
//
// For zygote starts, all remaining arguments are passed to the zygote.
// main function.
//
// Note that we must copy argument string values since we will rewrite the
// entire argument block when we apply the nice name to argv0.
//
// As an exception to the above rule, anything in "spaced commands"
// goes to the vm even though it has a space in it.
const char* spaced_commands[] = { "-cp", "-classpath" };
// Allow "spaced commands" to be succeeded by exactly 1 argument (regardless of -s).
bool known_command = false;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < argc; i++) {
if (known_command == true) {
runtime.addOption(strdup(argv[i]));
ALOGV("app_process main add known option '%s'", argv[i]);
known_command = false;
continue;
}
for (int j = 0;
j < static_cast<int>(sizeof(spaced_commands) / sizeof(spaced_commands[0]));
++j) {
if (strcmp(argv[i], spaced_commands[j]) == 0) {
known_command = true;
ALOGV("app_process main found known command '%s'", argv[i]);
}
}
if (argv[i][0] != '-') {
break;
}
if (argv[i][1] == '-' && argv[i][2] == 0) {
++i; // Skip --.
break;
}
runtime.addOption(strdup(argv[i]));
ALOGV("app_process main add option '%s'", argv[i]);
}
// Parse runtime arguments. Stop at first unrecognized option.
bool zygote = false;
bool startSystemServer = false;
bool application = false;
String8 niceName;
String8 className;
++i; // Skip unused "parent dir" argument.
while (i < argc) {
const char* arg = argv[i++];
if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) {//当前进程是否在Zygote中
zygote = true;
niceName = ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0) {//是否是systemserver进程
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0) {
application = true;
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--nice-name=", 12) == 0) {
niceName.setTo(arg + 12);
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--", 2) != 0) {
className.setTo(arg);
break;
} else {
--i;
break;
}
}
Vector<String8> args;
if (!className.isEmpty()) {
// We're not in zygote mode, the only argument we need to pass
// to RuntimeInit is the application argument.
//
// The Remainder of args get passed to startup class main(). Make
// copies of them before we overwrite them with the process name.
args.add(application ? String8("application") : String8("tool"));
runtime.setClassNameAndArgs(className, argc - i, argv + i);
if (!LOG_NDEBUG) {
String8 restOfArgs;
char* const* argv_new = argv + i;
int argc_new = argc - i;
for (int k = 0; k < argc_new; ++k) {
restOfArgs.append("\"");
restOfArgs.append(argv_new[k]);
restOfArgs.append("\" ");
}
ALOGV("Class name = %s, args = %s", className.string(), restOfArgs.string());
}
} else {
// We're in zygote mode.
maybeCreateDalvikCache();
if (startSystemServer) {
args.add(String8("start-system-server"));
}
char prop[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
if (property_get(ABI_LIST_PROPERTY, prop, NULL) == 0) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: Unable to determine ABI list from property %s.",
ABI_LIST_PROPERTY);
return 11;
}
String8 abiFlag("--abi-list=");
abiFlag.append(prop);
args.add(abiFlag);
// In zygote mode, pass all remaining arguments to the zygote
// main() method.
for (; i < argc; ++i) {
args.add(String8(argv[i]));
}
}
if (!niceName.isEmpty()) {
runtime.setArgv0(niceName.string(), true /* setProcName */);
}
if (zygote) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
} else if (className) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
}
}
由于zygote进程是通过forke自己来创建进程,这样zygote进程和他的子进程都可以进入app_main.cpp的main函数中,因此需要去人一下当前进程是在哪个进程。
在app_main文件的main()方法中,首先根据进程的名称判断当前是否为Zyote进程,并赋值zygote为true,然后调用runtime.start()启动进程,注意这里的参数传入的是ZygoteInit类的全路径,最后是根据全路径反射执行ZygoteInit方法。
AndroidRuntime
代码路径:frameworks\base\core\jni\AndroidRuntime.cpp
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote)
{
ALOGD(">>>>>> START %s uid %d <<<<<<\n",
className != NULL ? className : "(unknown)", getuid());
static const String8 startSystemServer("start-system-server");
/*
* 'startSystemServer == true' means runtime is obsolete and not run from
* init.rc anymore, so we print out the boot start event here.
*/
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
if (options[i] == startSystemServer) {
/* track our progress through the boot sequence */
const int LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START = 3000;
LOG_EVENT_LONG(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START, ns2ms(systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC)));
}
}
const char* rootDir = getenv("ANDROID_ROOT");
if (rootDir == NULL) {
rootDir = "/system";
if (!hasDir("/system")) {
LOG_FATAL("No root directory specified, and /android does not exist.");
return;
}
setenv("ANDROID_ROOT", rootDir, 1);
}
//const char* kernelHack = getenv("LD_ASSUME_KERNEL");
//ALOGD("Found LD_ASSUME_KERNEL='%s'\n", kernelHack);
/* start the virtual machine */
JniInvocation jni_invocation;
jni_invocation.Init(NULL);
JNIEnv* env;
//启动java虚拟机
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote) != 0) {
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);
/*为Java虚拟机注册jni方法
* Register android functions.
*/
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
/*
* We want to call main() with a String array with arguments in it.
* At present we have two arguments, the class name and an option string.
* Create an array to hold them.
*/
jclass stringClass;
jobjectArray strArray;
jstring classNameStr;
stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
assert(stringClass != NULL);
strArray = env->NewObjectArray(options.size() + 1, stringClass, NULL);
assert(strArray != NULL);
//从app_main的main函数中找到className为com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit
classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
assert(classNameStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
jstring optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options.itemAt(i).string());
assert(optionsStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, i + 1, optionsStr);
}
/*讲className的“.”替换为“/”
* Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
* not return until the VM exits.
*/
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className);
//找到ZygoteInit
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
/* keep going */
} else {
//ZytoteInit的main方法。
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
/* keep going */
} else {
//执行main方法。
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
#if 0
if (env->ExceptionCheck())
threadExitUncaughtException(env);
#endif
}
}
free(slashClassName);
ALOGD("Shutting down VM\n");
if (mJavaVM->DetachCurrentThread() != JNI_OK)
ALOGW("Warning: unable to detach main thread\n");
if (mJavaVM->DestroyJavaVM() != 0)
ALOGW("Warning: VM did not shut down cleanly\n");
}
在AndroidRuntime的start()方法中,执行了Zygote进程的主要逻辑:
- 启动Java虚拟机
- 为Java虚拟机注册JNI方法
- 通过JNI调用Java层ZygoteInit类中的方法完成进程的启动,此时程序由native进入Java层
代码路径:frameworks/base/core/java/com.android.internal.os/ZygoteInit
public static void main(String argv[]) {
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer();//首先创建并注册Service端的Socket,此Socket用于相应AMS请求创建进程
// Mark zygote start. This ensures that thread creation will throw
// an error.
ZygoteHooks.startZygoteNoThreadCreation();
// Zygote goes into its own process group.
try {
Os.setpgid(0, 0);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to setpgid(0,0)", ex);
}
final Runnable caller;
try {
// Report Zygote start time to tron unless it is a runtime restart
if (!"1".equals(SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed"))) {
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_zygote_init",
(int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
}
String bootTimeTag = Process.is64Bit() ? "Zygote64Timing" : "Zygote32Timing";
TimingsTraceLog bootTimingsTraceLog = new TimingsTraceLog(bootTimeTag,
Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.enableDdms();
boolean startSystemServer = false;
String socketName = "zygote";
String abiList = null;
boolean enableLazyPreload = false;
for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if ("--enable-lazy-preload".equals(argv[i])) {
enableLazyPreload = true;
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {
abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {
socketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
}
}
if (abiList == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");
}
zygoteServer.registerServerSocketFromEnv(socketName);
// In some configurations, we avoid preloading resources and classes eagerly.
// In such cases, we will preload things prior to our first fork.
if (!enableLazyPreload) {
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygotePreload");
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);//预加载类和资源
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygotePreload
} else {
Zygote.resetNicePriority();
}
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PostZygoteInitGC");
gcAndFinalize();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PostZygoteInitGC
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygoteInit
// Disable tracing so that forked processes do not inherit stale tracing tags from
// Zygote.
Trace.setTracingEnabled(false, 0);
Zygote.nativeSecurityInit();
// Zygote process unmounts root storage spaces.
Zygote.nativeUnmountStorageOnInit();
ZygoteHooks.stopZygoteNoThreadCreation();
if (startSystemServer) {
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer);//调用forkSystemServer()启动SystemServer进程
// {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and {@code r != null} in the
// child (system_server) process.
if (r != null) {
r.run();
return;
}
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
// The select loop returns early in the child process after a fork and
// loops forever in the zygote.
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);//执行zygoteServer.runSelectLoop()循环等待AMS请求创建新的应用进程
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
}
// We're in the child process and have exited the select loop. Proceed to execute the
// command.
if (caller != null) {
caller.run();
}
}
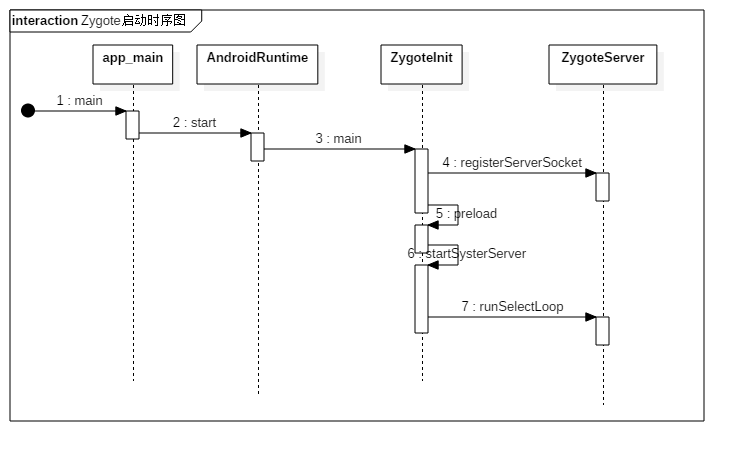
程序进入Java层执行ZygoteInit.main()方法,在main()中主要执行:
- 首先创建并注册Service端的Socket,此Socket用于相应AMS请求创建进程
- 预加载类和资源
- 调用forkSystemServer()启动SystemServer进程
- 执行zygoteServer.runSelectLoop()循环等待AMS请求创建新的应用进程
