一、Callbacks.h
#pragma once
#include <memory>
#include <functional>
class Buffer;
class TcpConnection;
class Timestamp;
using TcpConnectionPtr = std::shared_ptr<TcpConnection>;
using ConnectionCallback = std::function<void(const TcpConnectionPtr&)>;
using CloseCallback = std::function<void(const TcpConnectionPtr&)>;
using WriteCompleteCallback = std::function<void(const TcpConnectionPtr&)>;
using MessageCallback = std::function<void(const TcpConnectionPtr&, Buffer*, Timestamp)>;
using HighWaterMarkCallback = std::function<void (const TcpConnectionPtr&, size_t)>;
二、TcpServer.h
#pragma once
#include "Acceptor.h"
#include "Logger.h"
#include "InetAddress.h"
#include "noncopyable.h"
#include "EventLoop.h"
#include "EventLoopThreadPool.h"
#include "Callbacks.h"
#include "TcpConnection.h"
#include "Buffer.h"
#include <functional>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
#include <atomic>
#include <unordered_map>
class TcpServer : noncopyable{
public:
using ThreadInitCallback = std::function<void(EventLoop*)>;
// 预置两个是否重用port的选项
enum Option{
kNoReusePort,
kReusePort,
};
// 构造函数,用户需要传入一个EventLoop,即mainLoop,还有服务器的ip和监听的端口
TcpServer(EventLoop* loop, const InetAddress& listenAddr, const std::string& nameArg, Option = kNoReusePort);
~TcpServer();
// 线程初始化回调
void setThreadInitCallback(const ThreadInitCallback& cb){ threadInitCallback_ = cb; }
void setConnectionCallback(const ConnectionCallback& cb){ connectionCallback_ = cb; }
void setMessageCallback(const MessageCallback& cb){ messageCallback_ = cb; }
void setWriteCompleteCallback(const WriteCompleteCallback& cb){ writeCompleteCallback_ = cb; }
// 设置subloop的数量
void setThreadNum(int numThreads);
// 开启服务器监听
void start();
private:
void newConnection(int connfd, const InetAddress& peerAddr); // 一条新连接到来
void removeConnection(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn); // 连接已断开,从ConnectionMap里面移除
void removeConnectionInLoop(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn); // 从事件循环中删除连接
using ConnectionMap = std::unordered_map<std::string, TcpConnectionPtr>;
const std::string ipPort_; // 保存服务器的ip port
const std::string name_; // 保存服务器的name
EventLoop* loop_; // 用户传入的baseloop
std::unique_ptr<Acceptor> acceptor_; // 运行在mainloop的Acceptor,用于监听listenfd,等待新用户连接
std::shared_ptr<EventLoopThreadPool> threadPool_; // one loop per thread
ThreadInitCallback threadInitCallback_; // loop线程初始化的回调
ConnectionCallback connectionCallback_; // 有新连接的回调处理函数
MessageCallback messageCallback_; // 已连接用户的读写消息回调处理函数
WriteCompleteCallback writeCompleteCallback_; // 消息发送完成的回调处理函数
std::atomic_int started_;
int nextConnId_;
ConnectionMap connections_; // 保存所有的连接
};
三、TcpServer类
首先TcpServer对象创建一个Acceptor对象,Acceptor创建listenfd,并将listenfd封装成acceptChannel,先设置acceptChannel的读事件,然后通过loop把acceptChannel注册到当前EventLoop的Poller(Poller封装poll/epoll),Poller就监听acceptChannel上的事件。一旦acceptChannel上有事件发生,acceptChannel就会执行相应的回调函数,即Acceptor::handleRead()
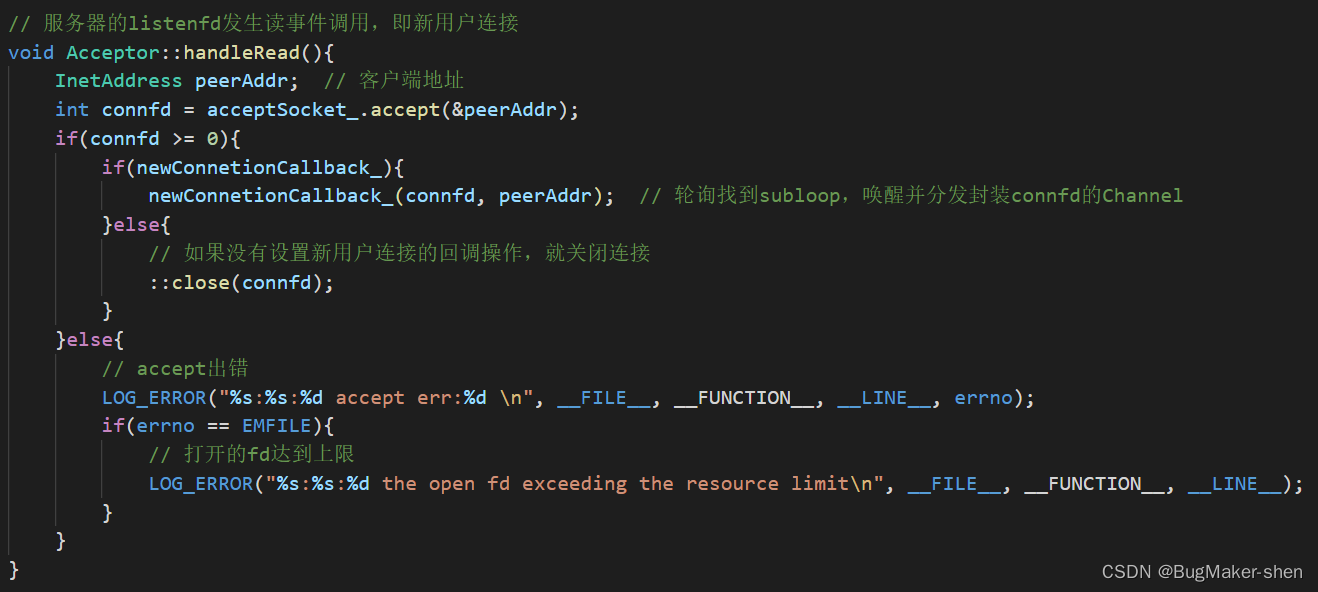
这个回调函数首先将新用户的地址保存在peerAddr,并获取和客户端通信的fd,然后传入Acceptor::newConnetionCallback_并执行,而这个回调就是TcpServer对象的成员acceptor_提前调用Acceptor::setNewConnectionCallback设置的

新用户到来就会执行TcpServer提前注册的回调函数,这个回调函数就会将与客户通信的connfd封装成Channel(实际上mainLoop封装成了TcpConnection,包含一个成员变量Channel),采用轮询算法选择一个subloop,通过其数据成员wakeupFd_写8字节数据来唤醒,然后分发Channel
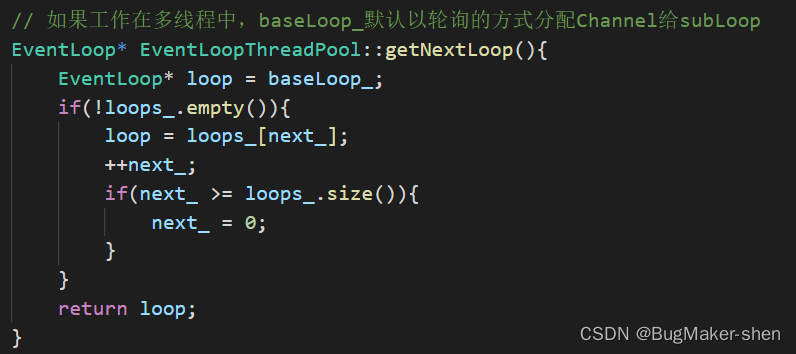
运行在主线程的mainLoop调用TcpServer注册好的回调函数TcpServer::newConnection,选择一个ioLoop,但是每个线程的事需要等到CPU调度到这个线程的时候才能处理,所以EventLoop提供了两个方法runInLoop和queueInLoop

- runInLoop:如果当前执行线程就是创建EventLoop对象的线程,就直接执行回调cb
- queueInLoop:当前执行的线程并不是创建EventLoop对 象的线程,先把回调cb放到队列,然后往该EventLoop对象的wakeupFd_上写数据通知对应线程
为什么我们总要使用EventLoop::isInLoopThread判断执行线程的是否就是创建EventLoop对象的线程呢?
因为muduo网络库并没有在mainLoop和subLoop之间添加同步队列,没有使用mainLoop生产Channel和subLoop消费Channel的生产者——消费者模型,而是采用了one loop per thread的方法,让每个线程监听自己的wakeupFd_,执行mainLoop的线程往wakeupFd_上写数据就是通知subLoop,需要处理新的Channel
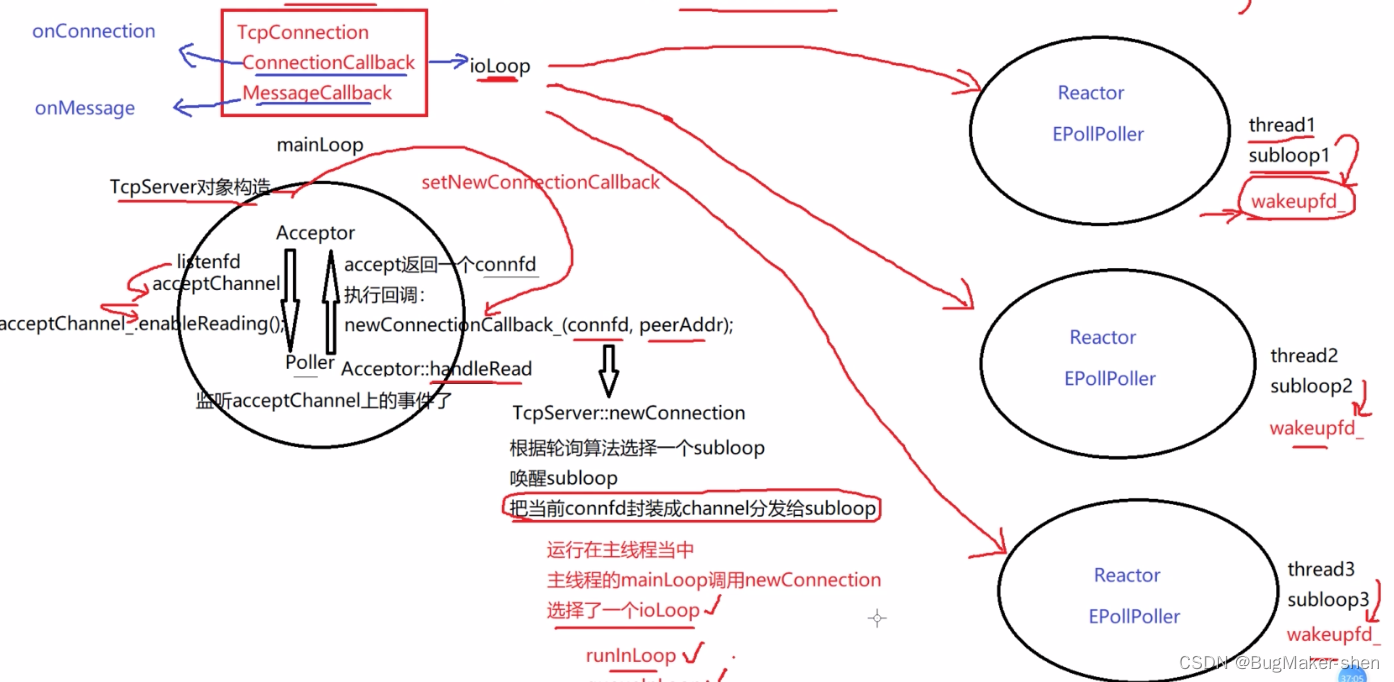
mainLoop传递给sunLoop的TcpConnection包含两个成员:
- connectionCallback_:就是我们使用muduo编程时,给服务器注册用户连接的创建和断开回调,当有新连接到来或者断开时subLoop就会调用
- messageCallback_:使用muduo编程时,给服务器注册的用户读写事件回调,TcpConnection里的Channel有读写事件时会被调用
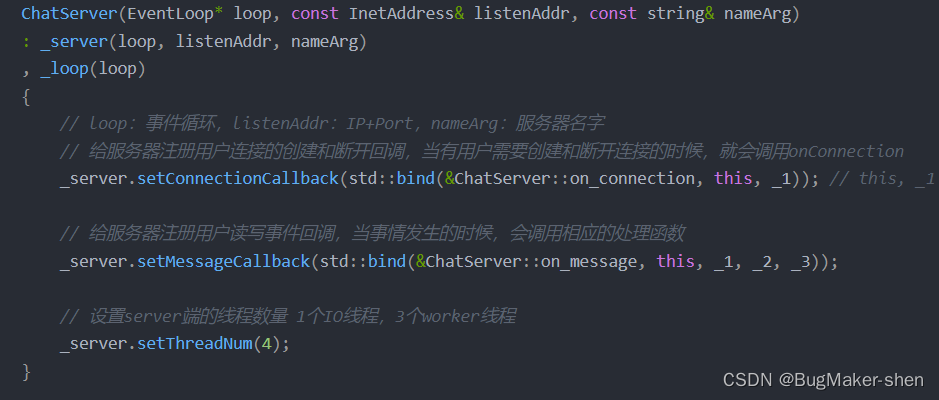
1. 建立连接
TcpServer对象构造的时候,就会同时构造Acceptor对象和threadPool_对象,并调用Acceptor::setNewConnectionCallback方法,把TcpServer::newConnection传给成员Acceptor::newConnetionCallback_,Acceptor::newConnetionCallback_又会在新连接到来时在Acceptor::handleRead中调用
即TcpServer::newConnection最终调用处是在Acceptor::handleRead
TcpServer::newConnection主要做:组装新连接的名字、创建TcpConnection连接对象、并设置相应的一系列回调函数
// 一条新连接到来,Acceptor根据轮询算法选择一个subloop并唤醒,把和客户端通信的connfd封装成Channel分发给subloop
// TcpServer要把newConnection设置给Acceptor,让Acceptor对象去调用,工作在mainLoop
// connfd是用于和客户端通信的fd,peerAddr封装了客户端的ip port
void TcpServer::newConnection(int connfd, const InetAddress& peerAddr){
// 轮询算法获取一个subloop指针
EventLoop* ioLoop = threadPool_->getNextLoop();
char buff[64];
snprintf(buff, sizeof(buff), "-%s#%d", ipPort_.c_str(), nextConnId_);
++nextConnId_;
// newConnection的名称
std::string connName = name_ + buff;
LOG_INFO("TcpServer::newConnection [%s] - new connection [%s] from %s \n", name_.c_str(), connName.c_str(), peerAddr.toIpPort().c_str());
// 通过sockfd获取其绑定的本机ip和port
sockaddr_in local;
memset(&local, 0, sizeof(local));
socklen_t addr_len = sizeof(local);
// getsockname通过connfd拿到本地的sockaddr地址信息写入local
if(::getsockname(connfd, (sockaddr*)&local, &addr_len) < 0){
LOG_ERROR("sockets::getLocalAddr \n");
}
InetAddress localAddr(local);
// 将connnfd封装成TcpConnection,TcpConnection有一个Channel的成员变量,这里就相当于把一个TcpConnection对象放入了一个subloop
TcpConnectionPtr conn(new TcpConnection(ioLoop, connName, connfd, localAddr, peerAddr));
// 将新的TcpConnectionPtr存入TcpServer::connections_
connections_[connName] = conn;
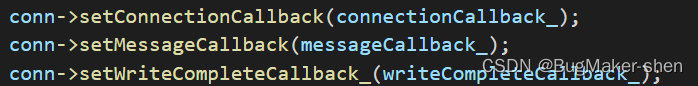
// 下面的回调都是用户设置给TcpServer的,然后TcpServer => TcpConnection => Channel,Channel会把自己封装的fd和events注册到Poller,发生事件时Poller调用Channel的handleEvent方法处理
// 就比如这个messageCallback_,用户把on_message(messageCallback_)传给TcpServer,TcpServer会调用TcpConnection::setMessageCallback,那么TcpConnection的成员messageCallback_就保存了on_message
// TcpConnection会把handleRead设置到Channel的readCallBack_,而handleRead就包括了TcpConnection::messageCallback_(on_message)
conn->setConnectionCallback(connectionCallback_);
conn->setMessageCallback(messageCallback_);
conn->setWriteCompleteCallback_(writeCompleteCallback_);
// 设置了如何关闭连接的回调 conn->shutDown()
conn->setCloseCallback(std::bind(&TcpServer::removeConnection, this, std::placeholders::_1));
// 直接调用TcpConnection::connectEstablished
ioLoop->runInLoop(std::bind(&TcpConnection::connectEstablished, conn));
}
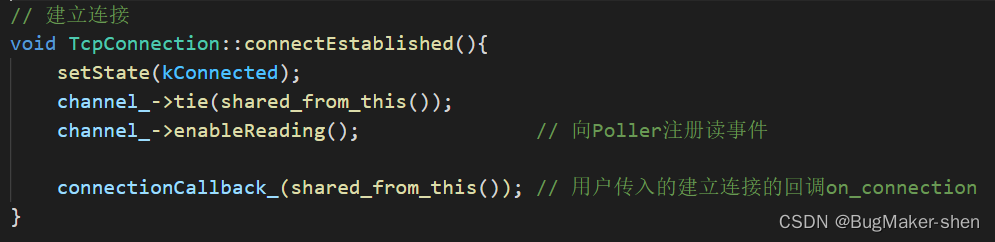
这一系列的回调方法都是用户传递给TcpServer,TcpServer => TcpConnection => Channel,Channel会把自己封装的fd和events注册到Poller,发生事件时Poller调用Channel的handleEvent方法处理
我们来说一下,用户在使用muduo编程时通常会写一个on_message函数,这个函数是怎么被调用的
用户调用TcpServer::setMessageCallback将on_message传递给TcpServer::messageCallback_,TcpServer会调用TcpConnection::setMessageCallback,那么TcpConnection的成员messageCallback_就保存了on_message,TcpConnection会把handleRead设置到Channel的readCallBack_,而handleRead就包括了TcpConnection::messageCallback_(on_message)


2. 断开连接
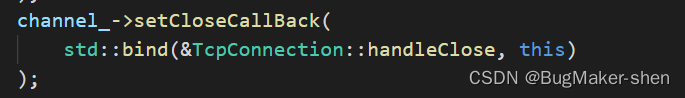
断开连接时,Poller会设置Channel的revents并将发生事件的Channel对象放入activateChannels_,EventLoop会遍历activateChannels_,并通过自己的Channel成员调用Channel::handleEvent处理EPOLLHUP事件,handleEvent会调用Channel::closeCallBack_,而这个Channel::closeCallBack_就是TcpConnection::handleClose
// 连接已断开,从ConnectionMap里面移除
void TcpServer::removeConnection(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn){
loop_->runInLoop(std::bind(&TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop, this, conn));
}
// 从事件循环中删除连接
void TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn){
LOG_INFO("TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop [%s] - connection %s\n", name_.c_str(), conn->name().c_str());
connections_.erase(conn->name());
EventLoop* ioLoop = conn->getLoop();
ioLoop->queueInLoop(std::bind(&TcpConnection::connectDestroyed, conn));
}


四、TcpServer.cc
#include "TcpServer.h"
#include "TcpConnection.h"
static EventLoop* CheckLoopNotNull(EventLoop* loop){
if(loop == nullptr){
LOG_FATAL("%s:%s%d mainloop is null! \n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
}
return loop;
}
// 构造函数,用户需要传入一个EventLoop,即mainLoop,还有服务器的ip和监听的端口
TcpServer::TcpServer(EventLoop* loop, const InetAddress& listenAddr, const std::string& nameArg, Option option)
: loop_(CheckLoopNotNull(loop))
, ipPort_(listenAddr.toIpPort())
, name_(nameArg)
, acceptor_(new Acceptor(loop, listenAddr, option == kReusePort))
, threadPool_(new EventLoopThreadPool(loop, name_)) // EventLoopThreadPool线程池
, connectionCallback_() //
, messageCallback_()
, nextConnId_(1)
, started_(0)
{
// 有新用户连接时,会调用Acceptor::handleRead,然后handleRead调用TcpServer::newConnection,
// 使用两个占位符,因为TcpServer::newConnection方法需要新用户的connfd以及新用户的ip port
acceptor_->setNewConnectionCallback(std::bind(&TcpServer::newConnection, this, std::placeholders::_1, std::placeholders::_2));
}
TcpServer::~TcpServer(){
for (auto& item : connections_){
// 这个局部的shared_ptr智能指针对象,出右括号,可以自动释放new出来的TcpConnection对象资源了
TcpConnectionPtr tmp_conn(item.second);
// TcpServer::connections_的值是shared_ptr,让TcpServer::connections_的值,即item.second不再指向TcpConnection对象,然后就只剩局部TcpConnectionPtr指向TcpConnection对象
// __shared_ptr().swap(*this)
item.second.reset();
// 销毁连接
tmp_conn->getLoop()->runInLoop(std::bind(&TcpConnection::connectDestroyed, tmp_conn));
}
}
//设置底层subloop的个数
void TcpServer::setThreadNum(int numThreads)
{
threadPool_->setThreadNum(numThreads);
}
//开启服务器监听 loop.loop()
void TcpServer::start(){
// 防止一个TcpServer对象被start多次,只有第一次调用start才能进入if
if (started_++ == 0){
threadPool_->start(threadInitCallback_);//启动底层的loop线程池
loop_->runInLoop(std::bind(&Acceptor::listen, acceptor_.get())); // 这就是TCP编程直接调用listen了
}
}
// 一条新连接到来,根据轮询算法选择一个subloop并唤醒,把和客户端通信的connfd封装成Channel分发给subloop
// TcpServer要把newConnection设置给Acceptor,让Acceptor对象去调用,工作在mainLoop
// connfd是用于和客户端通信的fd,peerAddr封装了客户端的ip port
void TcpServer::newConnection(int connfd, const InetAddress& peerAddr){
// 轮询算法获取一个subloop指针
EventLoop* ioLoop = threadPool_->getNextLoop();
char buff[64];
snprintf(buff, sizeof(buff), "-%s#%d", ipPort_.c_str(), nextConnId_);
++nextConnId_;
// newConnection的名称
std::string connName = name_ + buff;
LOG_INFO("TcpServer::newConnection [%s] - new connection [%s] from %s \n", name_.c_str(), connName.c_str(), peerAddr.toIpPort().c_str());
// 通过sockfd获取其绑定的本机ip和port
sockaddr_in local;
memset(&local, 0, sizeof(local));
socklen_t addr_len = sizeof(local);
// getsockname通过connfd拿到本地的sockaddr地址信息写入local
if(::getsockname(connfd, (sockaddr*)&local, &addr_len) < 0){
LOG_ERROR("sockets::getLocalAddr \n");
}
InetAddress localAddr(local);
// 将connnfd封装成TcpConnection,TcpConnection有一个Channel的成员变量,这里就相当于把一个TcpConnection对象放入了一个subloop
TcpConnectionPtr conn(new TcpConnection(ioLoop, connName, connfd, localAddr, peerAddr));
// 将新的TcpConnectionPtr存入TcpServer::connections_
connections_[connName] = conn;
// 下面的回调都是用户设置给TcpServer的,然后TcpServer => TcpConnection => Channel,Channel会把自己封装的fd和events注册到Poller,发生事件时Poller调用Channel的handleEvent方法处理
// 就比如这个messageCallback_,用户把on_message(messageCallback_)传给TcpServer,TcpServer会调用TcpConnection::setMessageCallback,那么TcpConnection的成员messageCallback_就保存了on_message
// TcpConnection会把handleRead设置到Channel的readCallBack_,而handleRead就包括了TcpConnection::messageCallback_(on_message)
conn->setConnectionCallback(connectionCallback_);
conn->setMessageCallback(messageCallback_);
conn->setWriteCompleteCallback_(writeCompleteCallback_);
// 设置了如何关闭连接的回调 conn->shutDown()
conn->setCloseCallback(std::bind(&TcpServer::removeConnection, this, std::placeholders::_1));
// 只要有一个客户端连接,就会直接调用TcpConnection::connectEstablished
ioLoop->runInLoop(std::bind(&TcpConnection::connectEstablished, conn));
}
// 连接已断开,从ConnectionMap里面移除
void TcpServer::removeConnection(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn){
loop_->runInLoop(std::bind(&TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop, this, conn));
}
// 从事件循环中删除连接
void TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn){
LOG_INFO("TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop [%s] - connection %s\n", name_.c_str(), conn->name().c_str());
connections_.erase(conn->name());
EventLoop* ioLoop = conn->getLoop();
ioLoop->queueInLoop(std::bind(&TcpConnection::connectDestroyed, conn));
}
