Linux 电源管理 - Linux regulator framework
前言
Regulator 翻译为 “调节器,稳压器”,分为 voltage regulator(电压调节器)和 current regulator(电流调节器),指可以自动维持恒定电压(或电流)的装置。一般电源管理芯片(Power Management IC)中会包含一个甚至多个regulator。
Regulator 通常的作用是给电子设备供电。大多数 regulator 可以启用(enable) 和禁用(disable) 其输出,同时也可以控制其输出电压(voltage) 和电流(current)。
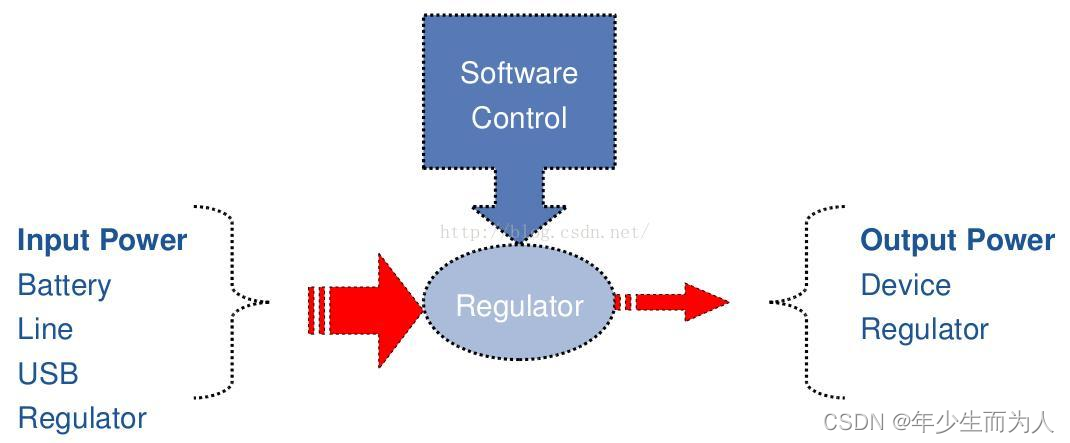
从上图可以看出,input power会经过 regulator 转化为output power,regulator会做如下的约束:
- Voltage control: 输入5V输出1.8V
- Current limiting: 电流的输出最大为20MA
- Power switch: 可以控制电压enable/disable
一、Linux regulator framework 概述
1、简介
Linux Regulator Framework 设计出主要是提供一个标准的内核接口来控制电压和电流调节器。目的是允许系统动态控制 regulator power 输出以节省能源延长电池寿命。这适用于voltage regulator和current regulator(其中电压和电流都是可控的)。
2、相关专业术语
-
Regulator
如上所述,regulator 用于向其他设备提供电源,可以 enable/disable 其输出,有些可以控制输出 voltage 和 current;Input Voltage -> Regulator -> Output Voltage
-
PMIC
Power Management IC,一个电源管理芯片可包含多个regulator; -
Consumer
表示一个 regulator 使用者,regulator 是电源的提供者,而 consumer 则是电源的消费者,一个 regulator 可供多个 consumer 使用;Consumer 可以分为两类:
Static:consumer does not change its supply voltage or
current limit. It only needs to enable or disable its
power supply. Its supply voltage is set by the hardware,
bootloader, firmware or kernel board initialisation code.Dynamic: consumer needs to change its supply voltage or
current limit to meet operation demands. -
Power Domain
电源域,Consumer 被提供输入电源可以由 the output power of a regulator,switch 或 another power domain,如下 one regulators & three power domains:
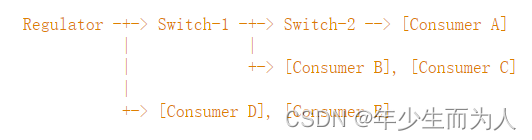
- Domain 1: Switch-1, Consumers D & E.
- Domain 2: Switch-2, Consumers B & C.
- Domain 3: Consumer A.“supplies” relationship:
Domain-1 --> Domain-2 --> Domain-3. -
Constraints
表示regulator的约束,而针对regulator约束也包含三个层次:
Regulator Level: 这属于regulator相关的约束信息,可通过regulator的datasheet中获取该regulator的约束信息;
Power Domain Level:这属于该regulator下不同电源域的约束信息,这些约束信息时regulator自身约束信息的子集(如regulator的电压输出约束为1v-3.5v;而domain1的约束信息为2v-3v;domain2的约束信息为2.5v等);
Consumer Level:可动态设置该consumer所需的输入电压或电流约束等。
3、Framework 组成部分
Linux Regulator Framework 的设计主要分为如下四个部分:
[ 具体内容见下方 ]
- Consumer driver interface:
- Regulator driver interface
- Machine interface
- Userspace ABI
参考 See Documentation/power/regulator/overview.rst
二、Linux regulator framework 驱动分析
1、Machine
Regulator Machine 驱动接口用于特定于板级的初始化代码,可以理解为 regulator 在板级的硬件配置,使用 regulator_init_data 结构体代表 regulator 板级的配置,位于 /include/linux/regulator/machine.h ,详细如下:
描述参考 See Documentation/power/regulator/machine.rst
struct regulator_init_data {
/* Parent regulator,用于级联 regulator 使用 */
const char *supply_regulator; /* or NULL for system supply */
/* 此 regulator 约束,比如输出电压范围,输出电流范围等 */
struct regulation_constraints constraints;
/* 此 regulator 提供的 consume 的个数,也就是控制外设的个数 */
int num_consumer_supplies;
/* 此结构确定 regulator 和 consumer 之间的联系 */
struct regulator_consumer_supply *consumer_supplies;
/* optional regulator machine specific init */
/* regulator 注册时候的回调函数 */
int (*regulator_init)(void *driver_data);
/* regulator_init 回调函数的参数 */
void *driver_data; /* core does not touch this */
};
对于 regulator 板级配置的约束,定义在 regulator_constraints 结构体中,位于 /include/linux/regulator/machine.h ,详细如下:
struct regulation_constraints {
/* 该约束的名字,用于显示目的 */
const char *name;
/* voltage output range (inclusive) - for voltage control */
/* 最小/大的输出电压 */
int min_uV;
int max_uV;
/* consumer看到的电源和实际电源之间的偏移值,用于电源补偿 */
int uV_offset;
/* current output range (inclusive) - for current control */
/* 最小/大的输出电流 */
int min_uA;
int max_uA;
/* 最大输入电流 */
int ilim_uA;
/* used for changing voltage in steps */
/* 最大可能的电压步进变化 */
int max_uV_step;
/* valid regulator operating modes for this machine */
/*
* 该regulator支持的操作模式
* #define REGULATOR_MODE_FAST 0x1 //快速改变模式
* #define REGULATOR_MODE_NORMAL 0x2 //正常模式,大多数驱动都使用这种模式
* #define REGULATOR_MODE_IDLE 0x4 //设备在idle状态,regulator给设备提供服务
* #define REGULATOR_MODE_STANDBY 0x8 //设备在standby状态,regulator给设备提供服务
* /
unsigned int valid_modes_mask;
/* valid operations for regulator on this machine */
/*
* 该regulator支持的操作
* #define REGULATOR_CHANGE_VOLTAGE 0x1 //该regulator可以改变电压
* #define REGULATOR_CHANGE_CURRENT 0x2 //该regulator可以改变电流
* #define REGULATOR_CHANGE_MODE 0x4 //该regulator可以改变 operating modes
* #define REGULATOR_CHANGE_STATUS 0x8 //该regulator可以改变状态,也就是enable/disable power
* #define REGULATOR_CHANGE_DRMS 0x10 //该regulator可以动态改变mode,Dynamic Regulator Mode Switching
* #define REGULATOR_CHANGE_BYPASS 0x20 //该regulator支持bypass mode
* /
unsigned int valid_ops_mask;
/* regulator input voltage - only if supply is another regulator */
int input_uV;
/* regulator suspend states for global PMIC STANDBY/HIBERNATE */
/* 代表该regulator的各种suspend状态 */
struct regulator_state state_disk;
struct regulator_state state_mem;
struct regulator_state state_standby;
suspend_state_t initial_state; /* suspend state to set at init */
/* mode to set on startup */
unsigned int initial_mode;
/* 改变电压到电源稳定后时间。因为硬件原因,改变电源后不能立刻就成功,其中需要有一定的延迟 */
unsigned int ramp_delay;
/* regulator的使能时间 */
unsigned int enable_time;
/* constraint flags */
unsigned always_on:1; /* regulator never off when system is on */
unsigned boot_on:1; /* bootloader/firmware enabled regulator */
unsigned apply_uV:1; /* apply uV constraint if min == max */
unsigned ramp_disable:1; /* disable ramp delay */
};
举例使用:
/*
* Consider the following machine::
* Regulator-1 -+-> Regulator-2 --> [Consumer A @ 1.8 - 2.0V]
* |
* +-> [Consumer B @ 3.3V]
*/
struct regulator_consumer_supply {
const char *dev_name; /* consumer dev_name() */
const char *supply; /* consumer supply - e.g. "vcc" */
};
/* Initialize struct regulator_consumer_supply */
#define REGULATOR_SUPPLY(_name, _dev_name) \
{ \
.supply = _name, \
.dev_name = _dev_name, \
}
/* This maps Regulator-1 to the 'Vcc' supply for Consumer B and maps Regulator-2
to the 'Vcc' supply for Consumer A. */
static struct regulator_consumer_supply regulator1_consumers[] = {
REGULATOR_SUPPLY("Vcc", "consumer B"),
};
static struct regulator_consumer_supply regulator2_consumers[] = {
REGULATOR_SUPPLY("Vcc", "consumer A"),
};
/* Maps the consumer B to its supply regulators */
static struct regulator_init_data regulator1_data = {
.constraints = {
.name = "Regulator-1",
.min_uV = 3300000,
.max_uV = 3300000,
.valid_modes_mask = REGULATOR_MODE_NORMAL,
},
.num_consumer_supplies = ARRAY_SIZE(regulator1_consumers),
.consumer_supplies = regulator1_consumers,
};
/* Maps the consumer A to its supply regulators, Regulator-1 supplies power to Regulator-2 */
static struct regulator_init_data regulator2_data = {
.supply_regulator = "Regulator-1",
.constraints = {
.min_uV = 1800000,
.max_uV = 2000000,
.valid_ops_mask = REGULATOR_CHANGE_VOLTAGE,
.valid_modes_mask = REGULATOR_MODE_NORMAL,
},
.num_consumer_supplies = ARRAY_SIZE(regulator2_consumers),
.consumer_supplies = regulator2_consumers,
};
/* Finally register the regulator devices */
static struct platform_device regulator_devices[] = {
{
.name = "regulator",
.id = DCDC_1,
.dev = {
.platform_data = ®ulator1_data,
},
},
{
.name = "regulator",
.id = DCDC_2,
.dev = {
.platform_data = ®ulator2_data,
},
},
};
/* register regulator 1 device */
platform_device_register(®ulator_devices[0]);
/* register regulator 2 device */
platform_device_register(®ulator_devices[1]);
再如 Linux 内核中 mt6323.dtsi 中使用如下:
/*
* regulator-name对应struct regulation_constraints中的name
* regulator-min-microvolt对应struct regulation_constraints中的min_uV
* regulator-max-microvolt对应struct regulation_constraints中的max_uV
* regulator-ramp-delay对应struct regulation_constraints中的ramp_delay
* regulator-always-on对应struct regulation_constraints中的always_on
* regulator-boot-on对应struct regulation_constraints中的boot_on
*/
mt6323_vproc_reg: buck_vproc{
regulator-name = "vproc";
regulator-min-microvolt = < 700000>;
regulator-max-microvolt = <1350000>;
regulator-ramp-delay = <12500>;
regulator-always-on;
regulator-boot-on;
};
2、Regulator
Regulator 可以理解为 regulator driver,允许 regulator driver 注册到 regulator core framework 中,给 consumer 提供服务。
regulator driver 通过r egulator_register 函数注册 regulator operation 到 regulator core。其中第一个参数 struct regulator_desc 代表静态的regulator 配置,所谓静态就是不再会改变的配置。第二个参数代表 regulator 的动态配置信息。
描述参考 See Documentation/power/regulator/regulator.rst
struct regulator_dev *regulator_register(struct regulator_desc *regulator_desc, const struct regulator_config *config);
void regulator_unregister(struct regulator_dev *rdev);
第一个参数定义在 /include/linux/regulator/driver.h,如下:
struct regulator_desc {
/* regulator 标识的名字 */
const char *name;
/* regulator parent(supply) 标识的名字 */
const char *supply_name;
/* 在 dt 中 regulator 标识的名字 */
const char *of_match;
/* A flag to indicate that the of_match string, if present, should be matched against the node full_name */
bool of_match_full_name;
/* Name of node containing regulator definitions in DT */
const char *regulators_node;
/* Optional callback called only if of_match is present. */
int (*of_parse_cb)(struct device_node *,
const struct regulator_desc *,
struct regulator_config *);
int id; /* regulator 的数字标识符 */
/* 表示regulator是否可以在电压约束范围内连续输出电压 */
unsigned int continuous_voltage_range:1;
/* 通过ops.list_voltage函数获取可用的电压数量 */
unsigned n_voltages;
unsigned int n_current_limits;
const struct regulator_ops *ops; /* regulator的操作函数集合 */
int irq; /* 该regulator的中断号 */
/* 代表当前regulator的类型(voltage or current regulator) */
enum regulator_type type;
struct module *owner;
/* 如果是线性mapp的话,使用最低的selector获取的电压 */
unsigned int min_uV;
/* 每个selector下电压增加step */
unsigned int uV_step;
/* 线性mapp下最小的selector */
unsigned int linear_min_sel;
int fixed_uV; /* 固定电压 */
unsigned int ramp_delay; /* 电压改变之后需要多久时间稳定下来 */
/* 电压的可能范围的常数表 */
const struct linear_range *linear_ranges;
const unsigned int *linear_range_selectors;
/* 电压范围常数表的个数 */
int n_linear_ranges;
const unsigned int *volt_table; /* 电压的mapp表 */
const unsigned int *curr_table; /* 电流的mapp表 */
unsigned int vsel_range_reg;
unsigned int vsel_range_mask;
unsigned int vsel_reg;
unsigned int vsel_mask;
unsigned int vsel_step;
unsigned int csel_reg;
unsigned int csel_mask;
unsigned int apply_reg;
unsigned int apply_bit;
unsigned int enable_reg;
unsigned int enable_mask;
unsigned int enable_val;
unsigned int disable_val;
bool enable_is_inverted;
unsigned int bypass_reg;
unsigned int bypass_mask;
unsigned int bypass_val_on;
unsigned int bypass_val_off;
unsigned int active_discharge_on;
unsigned int active_discharge_off;
unsigned int active_discharge_mask;
unsigned int active_discharge_reg;
unsigned int soft_start_reg;
unsigned int soft_start_mask;
unsigned int soft_start_val_on;
unsigned int pull_down_reg;
unsigned int pull_down_mask;
unsigned int pull_down_val_on;
unsigned int ramp_reg;
unsigned int ramp_mask;
const unsigned int *ramp_delay_table;
unsigned int n_ramp_values;
unsigned int enable_time; /* regulator初始化所需要的时间 */
unsigned int off_on_delay; /* 重新使能regulator的保护时间 */
unsigned int poll_enabled_time;
unsigned int (*of_map_mode)(unsigned int mode);
};
其中 struct regulator_ops 是对此 regulator 硬件操作的封装,其中包含获取电压、设置电压等的成员函数,
struct regulator_ops {
/* enumerate supported voltages */
int (*list_voltage) (struct regulator_dev *, unsigned selector);
/* set regulator voltage */
int (*set_voltage) (struct regulator_dev *, int min_uV, int max_uV,
unsigned *selector);
/* Convert a voltage into a selector */
int (*map_voltage)(struct regulator_dev *, int min_uV, int max_uV);
/* Set the voltage for the regulator using the specified selector */
int (*set_voltage_sel) (struct regulator_dev *, unsigned selector);
/* get regulator voltage */
int (*get_voltage) (struct regulator_dev *);
int (*get_voltage_sel) (struct regulator_dev *);
/* get/set regulator current */
int (*set_current_limit) (struct regulator_dev *,
int min_uA, int max_uA);
int (*get_current_limit) (struct regulator_dev *);
int (*set_input_current_limit) (struct regulator_dev *, int lim_uA);
int (*set_over_current_protection)(struct regulator_dev *, int lim_uA,
int severity, bool enable);
int (*set_over_voltage_protection)(struct regulator_dev *, int lim_uV,
int severity, bool enable);
int (*set_under_voltage_protection)(struct regulator_dev *, int lim_uV,
int severity, bool enable);
int (*set_thermal_protection)(struct regulator_dev *, int lim,
int severity, bool enable);
int (*set_active_discharge)(struct regulator_dev *, bool enable);
/* enable/disable regulator */
int (*enable) (struct regulator_dev *);
int (*disable) (struct regulator_dev *);
/* Return 1 if the regulator is enabled, 0 if not, may also return negative errno */
int (*is_enabled) (struct regulator_dev *);
/* get/set regulator operating mode (defined in consumer.h) */
int (*set_mode) (struct regulator_dev *, unsigned int mode);
unsigned int (*get_mode) (struct regulator_dev *);
/* retrieve current error flags on the regulator */
int (*get_error_flags)(struct regulator_dev *, unsigned int *flags);
/* Time taken to enable or set voltage on the regulator */
int (*enable_time) (struct regulator_dev *);
int (*set_ramp_delay) (struct regulator_dev *, int ramp_delay);
int (*set_voltage_time) (struct regulator_dev *, int old_uV,
int new_uV);
int (*set_voltage_time_sel) (struct regulator_dev *,
unsigned int old_selector,
unsigned int new_selector);
int (*set_soft_start) (struct regulator_dev *);
/* report regulator status ... most other accessors report
* control inputs, this reports results of combining inputs
* from Linux (and other sources) with the actual load.
* returns REGULATOR_STATUS_* or negative errno.
*/
int (*get_status)(struct regulator_dev *);
/* get most efficient regulator operating mode for load */
unsigned int (*get_optimum_mode) (struct regulator_dev *, int input_uV,
int output_uV, int load_uA);
/* set the load on the regulator */
int (*set_load)(struct regulator_dev *, int load_uA);
/* control and report on bypass mode */
int (*set_bypass)(struct regulator_dev *dev, bool enable);
int (*get_bypass)(struct regulator_dev *dev, bool *enable);
/* the operations below are for configuration of regulator state when
* its parent PMIC enters a global STANDBY/HIBERNATE state */
/* set regulator suspend voltage */
int (*set_suspend_voltage) (struct regulator_dev *, int uV);
/* enable/disable regulator in suspend state */
int (*set_suspend_enable) (struct regulator_dev *);
int (*set_suspend_disable) (struct regulator_dev *);
/* set regulator suspend operating mode (defined in consumer.h) */
int (*set_suspend_mode) (struct regulator_dev *, unsigned int mode);
int (*resume)(struct regulator_dev *rdev);
int (*set_pull_down) (struct regulator_dev *);
};
此结构体详细描述可以直接查看 /include/linux/regulator/driver.h。
第二个参数为 struct regulator_config,代表 regulator 的动态配置信息,位于 /include/linux/regulator/driver.h,如下:
struct regulator_config {
/* struct device for the regulator */
struct device *dev;
/* 板级的相关初始化信息,通过解析DT,保存在此 */
const struct regulator_init_data *init_data;
void *driver_data; /* 私有数据 */
struct device_node *of_node; /* dt相关的node */
struct regmap *regmap; /* regulator register map */
struct gpio_desc *ena_gpiod; /* GPIO controlling regulator enable */
};
当调用 regulator_register 函数之后,传入静态和动态参数之后,就会返回一个 regulator_dev 结构(位于 /include/linux/regulator/driver.h)。此结构可以认为是 regulator 设备的一个抽象描述。
/*
* struct regulator_dev
*
* Voltage / Current regulator class device. One for each
* regulator.
*
* This should *not* be used directly by anything except the regulator
* core and notification injection (which should take the mutex and do
* no other direct access).
*/
struct regulator_dev {
const struct regulator_desc *desc;
int exclusive; /* 该regulator是否是唯一的标志 */
/* 代表该regulator的使用计数 */
u32 use_count;
u32 open_count;
u32 bypass_count;
/* lists we belong to */
struct list_head list; /* list of all regulators */
/* lists we own */
struct list_head consumer_list; /* consumers we supply */
struct coupling_desc coupling_desc;
/* 此regulator的通知链,用于给consumer通知event */
struct blocking_notifier_head notifier;
struct ww_mutex mutex; /* consumer lock */
struct task_struct *mutex_owner;
int ref_cnt;
struct module *owner;
struct device dev;
struct regulation_constraints *constraints;
/* 该regulator的supply,级联时候使用 */
struct regulator *supply; /* for tree */
const char *supply_name;
struct regmap *regmap;
/* 该regulator的延迟工作,用于延迟disable regulator */
struct delayed_work disable_work;
void *reg_data; /* regulator_dev data */
struct dentry *debugfs;
struct regulator_enable_gpio *ena_pin;
unsigned int ena_gpio_state:1;
unsigned int is_switch:1;
/* time when this regulator was disabled last time */
ktime_t last_off;
int cached_err;
bool use_cached_err;
spinlock_t err_lock;
};
3、Consumer
Consumer drivers can get and put a regulator (like they can with clocks atm) and get/set voltage, current limit, mode, enable and disable.
详细描述参考 See Documentation/power/regulator/consumer.rst
4、sysfs-class-regulator
regulator core framework 通过sysfs文件系统导出了一些 "voltage/current/opmode" 相关的信息,此将很有帮忙监控设备的功耗使用情况。
详细描述参考 See Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-class-regulator
三、Linux regulator 常见 API
Linux 的 Regulator 子系统提供消费者 (Consumer) API 以便其他的驱动获取、设置、关闭和使能 regulator 等。
1、获取/释放regulator
/* regulator get and put */
struct regulator * regulator_get(struct device *dev,
const char *id);
struct regulator * devm_regulator_get(struct device *dev,
const char *id);
void regulator_put(struct regulator *regulator);
void devm_regulator_put(struct regulator *regulator);
2、Enable and disable regulator
int regulator_enable(regulator);
int regulator_disable(regulator);
int regulator_force_disable(regulator);
3、设置 regulator 的电压,获得 regulator 的电压状态、设置 regulator 的电流,获得 regulator 的电流状态
int regulator_set_voltage(regulator, min_uV, max_uV);
int regulator_get_voltage(regulator);
int regulator_set_current_limit(regulator, min_uA, max_uA);
int regulator_get_current_limit(regulator);
4、regulator的模式设置,间接(通过负载),直接设置
int regulator_set_optimum_mode(struct regulator *regulator, int load_uA);
int regulator_set_mode(struct regulator *regulator, unsigned int mode);
unsigned int regulator_get_mode(struct regulator *regulator);
5、Regulator Driver interface
/* register/unregister regulator */
struct regulator_dev *regulator_register(struct regulator_desc *regulator_desc,
const struct regulator_config *config);
void regulator_unregister(struct regulator_dev *rdev);
/* regulator 事件通知 */
int regulator_notifier_call_chain(struct regulator_dev *rdev,
unsigned long event, void *data);
四、Linux regulator 使用举例
在内核 drivers/regulator/dummy.c文件中构造了一个虚拟的 regulator 可以参考,如下:
drivers/regulator/dummy.c
对于使用可以参考 mt6323 的 regulator 使用,
(1) dts: arch/arm/boot/dts/mt6323.dtsi
(2) driver:drivers/regulator/mt6323-regulator.c
参考链接 - Linux电源管理-Linux regulator framework概述
参考链接 - Linux电源管理-Linux Regulator Framework代码分析
