内存规整
内存规整是Mel Gormal开发防止内存碎片anti-fragmen pach补丁的第二个部分Avoiding fragmentation with page clustering v27 [LWN.net],主要用于解决当系统长时间运行之后,造成比较碎化内存时,通过内存规整将处于可以移动MOVE的类型内存,重新进行页迁移 整合出较大连续物理内存:
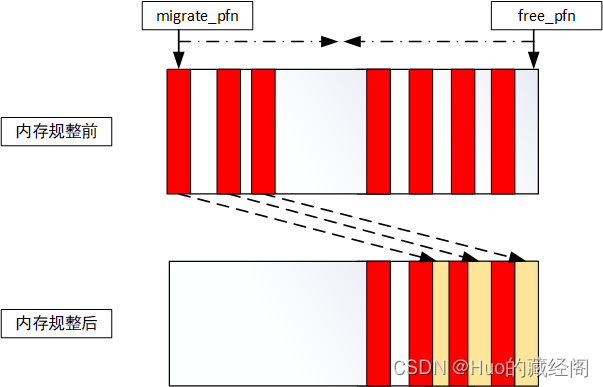
内存规整机制原因比较简单:
- 利用类似快慢指针技巧,当需要对一个zone进行内存规整时,使用migrate_pfn和free_pfn两个遍历;
- migrate_pfn 为从zone 头部开始进行扫描,依次扫描出已经被分配出去但是可以进行页迁移的页面
- free_pfn:为从zone 尾部开始扫描,依次扫描出空闲page。
- 当每次扫描结束后,将migrate_pfn扫描出的可迁移页面 依次迁移到free_pfn 空闲page中。
- 当free_pfn和migrate_pfn 两个遇见相等时说明内存规整完毕。
- 这样规整之后,zone前半部分可以需要迁移的页面被迁移到zone后半部分空闲page中, 这样前半部分会空闲出大块连续物理内存,供下次申请内存使用。
内存规整技术是页迁移技术的一个比较重要的使用场景,帮助系统整理出连续物理内存。
触发时机
内存规整触发时机主要有以下三种:
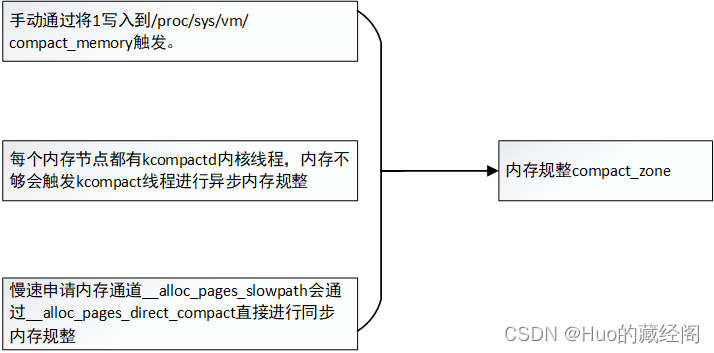
- 通过/proc/sys/vm/compact_memory 由用户根据手动触发,如果是NUMA系统则还可以通过/sys/devices/system/node/node<id>/compact 触发
- kcompatd线程类似与kswapd线程,内存水位不够时,会触发kcompactd线程进行异步内存规整。
- 慢速申请内存通道,说明内存压力过大,__alloc_pages_slowpath会通过__alloc_pages_direct_compact 进行同步内存规整。
相关数据结构
由于内存规整是以zone为单位进行扫描,因此不像kswapd由于pgdata中相关数据,内存规整主要涉及到struct? zone中数据用于记录内存规整的进度:
struct zone {
... ...
#if defined CONFIG_COMPACTION || defined CONFIG_CMA
unsigned long compact_cached_free_pfn; //用于记录从尾部开始扫描的空闲page的位置
unsigned long compact_cached_migrate_pfn[2];//该数组用于控制异步和同步两种memory compact场景所从头部开始扫描的页迁移位置
unsigned long compact_init_migrate_pfn; //内存规整页迁移起始地址
unsigned long compact_init_free_pfn; //内存规整的空闲free起始地址
#endif
} ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
struct compact_control
struct compact_control结构类似与kswapd中的struct scan_control, 该结构主要用于内存规整时内部使用的数据结构,同时还可以控制内存规整起始位置,以及策略等。
struct compact_control {
struct list_head freepages; /* List of free pages to migrate to */
struct list_head migratepages; /* List of pages being migrated */
unsigned int nr_freepages; /* Number of isolated free pages */
unsigned int nr_migratepages; /* Number of pages to migrate */
unsigned long free_pfn; /* isolate_freepages search base */
unsigned long migrate_pfn; /* isolate_migratepages search base */
unsigned long fast_start_pfn; /* a pfn to start linear scan from */
struct zone *zone;
unsigned long total_migrate_scanned;
unsigned long total_free_scanned;
unsigned short fast_search_fail;/* failures to use free list searches */
short search_order; /* order to start a fast search at */
const gfp_t gfp_mask; /* gfp mask of a direct compactor */
int order; /* order a direct compactor needs */
int migratetype; /* migratetype of direct compactor */
const unsigned int alloc_flags; /* alloc flags of a direct compactor */
const int highest_zoneidx; /* zone index of a direct compactor */
enum migrate_mode mode; /* Async or sync migration mode */
bool ignore_skip_hint; /* Scan blocks even if marked skip */
bool no_set_skip_hint; /* Don't mark blocks for skipping */
bool ignore_block_suitable; /* Scan blocks considered unsuitable */
bool direct_compaction; /* False from kcompactd or /proc/... */
bool whole_zone; /* Whole zone should/has been scanned */
bool contended; /* Signal lock or sched contention */
bool rescan; /* Rescanning the same pageblock */
bool alloc_contig; /* alloc_contig_range allocation */
};
主要成员说明:
- struct list_head freepages: 空闲页链表,表明页面要迁移到目的页即空闲页链表,处于该链表中的空闲页,被isolate孤立出来,防止同时被buddy给其他进程使用。
- struct list_head migratepages:所要迁移的页面链表,用于记录本次所需要迁移的页面,处于该链表中的空闲页,被isolate孤立出来,防止页面被swap out到磁盘或者page cache被释放等场景。
- unsigned int nr_freepages: 记录freepages中有多少个空闲页 被isolate孤立出来。
- unsigned int nr_migratepages: 记录migratepages中有多少个页面要进行迁移,并被isolate孤立出来
- unsigned long free_pfn: 从尾部开始扫描的空闲起始页帧号,即本次扫描zone,从尾部开始扫描寻找空闲页的起始位置。
- unsigned long migrate_pfn:本次扫描,从头部往尾部开始扫描的 起始位置,从该位置开始寻找符合要求的页进行迁移。
- unsigned long fast_start_pfn:用于快速线性扫描的起始位置
- struct zone *zone:所要扫描的zone
- unsigned long total_migrate_scanned:已经扫描并做页迁移的页数目
- unsigned long total_free_scanned:已经扫描用用作空闲页 作为页前面目的的数目
- const gfp_t gfp_mask: gfp mask
- short search_order: 扫描是开始的order 即一次性做页迁移的数目
- int order: 扫描时所需要的至少order 页数目。
- int migratetype:页迁移类型
- const int highest_zoneidx: 最高zone,扫描的zone范围‘
- enum migrate_mode mode: 是同步还是异步模式,即是通过kcompact线程进行内存规整,还是通过直接方式进行内存规整
- bool direct_compaction: 如果为false,则是通过kscompact线程 或者??/proc手动触发触发
- bool whole_zone:是否一次性扫描整个zone.
compact_zone()
compact_zone()函数是实施内存规整的核心函数,不管是哪种触发方式最终都会通过compact_zone 规整指定的zone进行内存规整,
调用关系
按照compact_zone触发关系调用关系图如下:
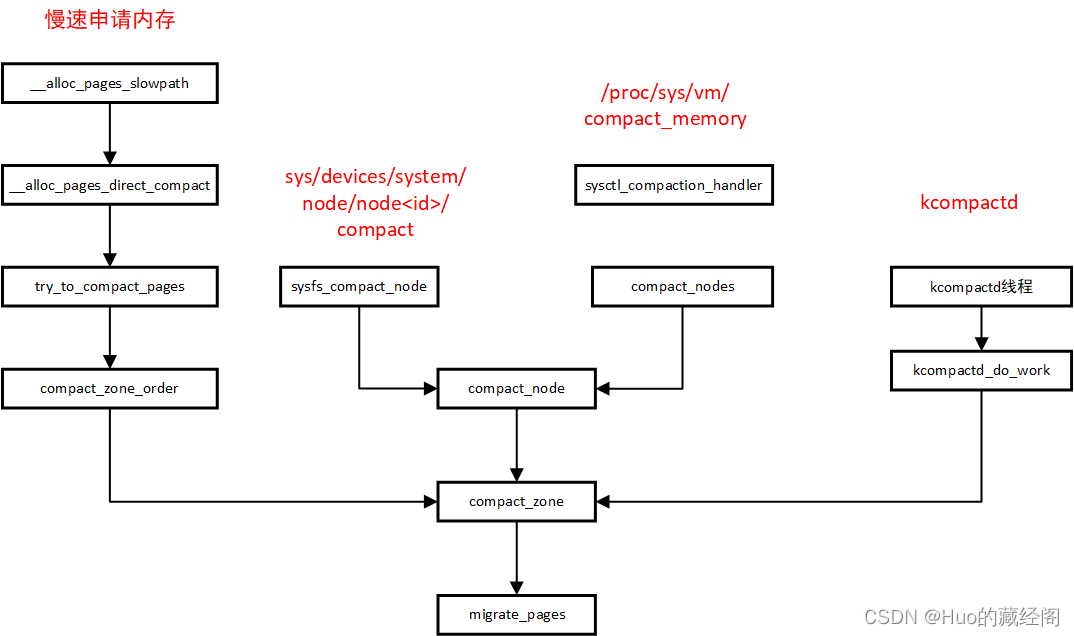
上述四种触发方式,最终都是靠compact_zone实现页迁移功能
compact_zone源码
static enum compact_result
compact_zone(struct compact_control *cc, struct capture_control *capc)
{
enum compact_result ret;
unsigned long start_pfn = cc->zone->zone_start_pfn;
unsigned long end_pfn = zone_end_pfn(cc->zone);
unsigned long last_migrated_pfn;
const bool sync = cc->mode != MIGRATE_ASYNC;
bool update_cached;
/*
* These counters track activities during zone compaction. Initialize
* them before compacting a new zone.
*/
cc->total_migrate_scanned = 0;
cc->total_free_scanned = 0;
cc->nr_migratepages = 0;
cc->nr_freepages = 0;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cc->freepages);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cc->migratepages);
cc->migratetype = gfp_migratetype(cc->gfp_mask);
ret = compaction_suitable(cc->zone, cc->order, cc->alloc_flags,
cc->highest_zoneidx);
/* Compaction is likely to fail */
if (ret == COMPACT_SUCCESS || ret == COMPACT_SKIPPED)
return ret;
/* huh, compaction_suitable is returning something unexpected */
VM_BUG_ON(ret != COMPACT_CONTINUE);
/*
* Clear pageblock skip if there were failures recently and compaction
* is about to be retried after being deferred.
*/
if (compaction_restarting(cc->zone, cc->order))
__reset_isolation_suitable(cc->zone);
/*
* Setup to move all movable pages to the end of the zone. Used cached
* information on where the scanners should start (unless we explicitly
* want to compact the whole zone), but check that it is initialised
* by ensuring the values are within zone boundaries.
*/
cc->fast_start_pfn = 0;
if (cc->whole_zone) {
cc->migrate_pfn = start_pfn;
cc->free_pfn = pageblock_start_pfn(end_pfn - 1);
} else {
cc->migrate_pfn = cc->zone->compact_cached_migrate_pfn[sync];
cc->free_pfn = cc->zone->compact_cached_free_pfn;
if (cc->free_pfn < start_pfn || cc->free_pfn >= end_pfn) {
cc->free_pfn = pageblock_start_pfn(end_pfn - 1);
cc->zone->compact_cached_free_pfn = cc->free_pfn;
}
if (cc->migrate_pfn < start_pfn || cc->migrate_pfn >= end_pfn) {
cc->migrate_pfn = start_pfn;
cc->zone->compact_cached_migrate_pfn[0] = cc->migrate_pfn;
cc->zone->compact_cached_migrate_pfn[1] = cc->migrate_pfn;
}
if (cc->migrate_pfn <= cc->zone->compact_init_migrate_pfn)
cc->whole_zone = true;
}
last_migrated_pfn = 0;
/*
* Migrate has separate cached PFNs for ASYNC and SYNC* migration on
* the basis that some migrations will fail in ASYNC mode. However,
* if the cached PFNs match and pageblocks are skipped due to having
* no isolation candidates, then the sync state does not matter.
* Until a pageblock with isolation candidates is found, keep the
* cached PFNs in sync to avoid revisiting the same blocks.
*/
update_cached = !sync &&
cc->zone->compact_cached_migrate_pfn[0] == cc->zone->compact_cached_migrate_pfn[1];
trace_mm_compaction_begin(start_pfn, cc->migrate_pfn,
cc->free_pfn, end_pfn, sync);
migrate_prep_local();
while ((ret = compact_finished(cc)) == COMPACT_CONTINUE) {
int err;
unsigned long start_pfn = cc->migrate_pfn;
/*
* Avoid multiple rescans which can happen if a page cannot be
* isolated (dirty/writeback in async mode) or if the migrated
* pages are being allocated before the pageblock is cleared.
* The first rescan will capture the entire pageblock for
* migration. If it fails, it'll be marked skip and scanning
* will proceed as normal.
*/
cc->rescan = false;
if (pageblock_start_pfn(last_migrated_pfn) ==
pageblock_start_pfn(start_pfn)) {
cc->rescan = true;
}
switch (isolate_migratepages(cc)) {
case ISOLATE_ABORT:
ret = COMPACT_CONTENDED;
putback_movable_pages(&cc->migratepages);
cc->nr_migratepages = 0;
goto out;
case ISOLATE_NONE:
if (update_cached) {
cc->zone->compact_cached_migrate_pfn[1] =
cc->zone->compact_cached_migrate_pfn[0];
}
/*
* We haven't isolated and migrated anything, but
* there might still be unflushed migrations from
* previous cc->order aligned block.
*/
goto check_drain;
case ISOLATE_SUCCESS:
update_cached = false;
last_migrated_pfn = start_pfn;
;
}
err = migrate_pages(&cc->migratepages, compaction_alloc,
compaction_free, (unsigned long)cc, cc->mode,
MR_COMPACTION);
trace_mm_compaction_migratepages(cc->nr_migratepages, err,
&cc->migratepages);
/* All pages were either migrated or will be released */
cc->nr_migratepages = 0;
if (err) {
putback_movable_pages(&cc->migratepages);
/*
* migrate_pages() may return -ENOMEM when scanners meet
* and we want compact_finished() to detect it
*/
if (err == -ENOMEM && !compact_scanners_met(cc)) {
ret = COMPACT_CONTENDED;
goto out;
}
/*
* We failed to migrate at least one page in the current
* order-aligned block, so skip the rest of it.
*/
if (cc->direct_compaction &&
(cc->mode == MIGRATE_ASYNC)) {
cc->migrate_pfn = block_end_pfn(
cc->migrate_pfn - 1, cc->order);
/* Draining pcplists is useless in this case */
last_migrated_pfn = 0;
}
}
check_drain:
/*
* Has the migration scanner moved away from the previous
* cc->order aligned block where we migrated from? If yes,
* flush the pages that were freed, so that they can merge and
* compact_finished() can detect immediately if allocation
* would succeed.
*/
if (cc->order > 0 && last_migrated_pfn) {
unsigned long current_block_start =
block_start_pfn(cc->migrate_pfn, cc->order);
if (last_migrated_pfn < current_block_start) {
lru_add_drain_cpu_zone(cc->zone);
/* No more flushing until we migrate again */
last_migrated_pfn = 0;
}
}
/* Stop if a page has been captured */
if (capc && capc->page) {
ret = COMPACT_SUCCESS;
break;
}
}
out:
/*
* Release free pages and update where the free scanner should restart,
* so we don't leave any returned pages behind in the next attempt.
*/
if (cc->nr_freepages > 0) {
unsigned long free_pfn = release_freepages(&cc->freepages);
cc->nr_freepages = 0;
VM_BUG_ON(free_pfn == 0);
/* The cached pfn is always the first in a pageblock */
free_pfn = pageblock_start_pfn(free_pfn);
/*
* Only go back, not forward. The cached pfn might have been
* already reset to zone end in compact_finished()
*/
if (free_pfn > cc->zone->compact_cached_free_pfn)
cc->zone->compact_cached_free_pfn = free_pfn;
}
count_compact_events(COMPACTMIGRATE_SCANNED, cc->total_migrate_scanned);
count_compact_events(COMPACTFREE_SCANNED, cc->total_free_scanned);
trace_mm_compaction_end(start_pfn, cc->migrate_pfn,
cc->free_pfn, end_pfn, sync, ret);
return ret;
}
compact_zone流程
该函数整理处理思路相对比较清晰:
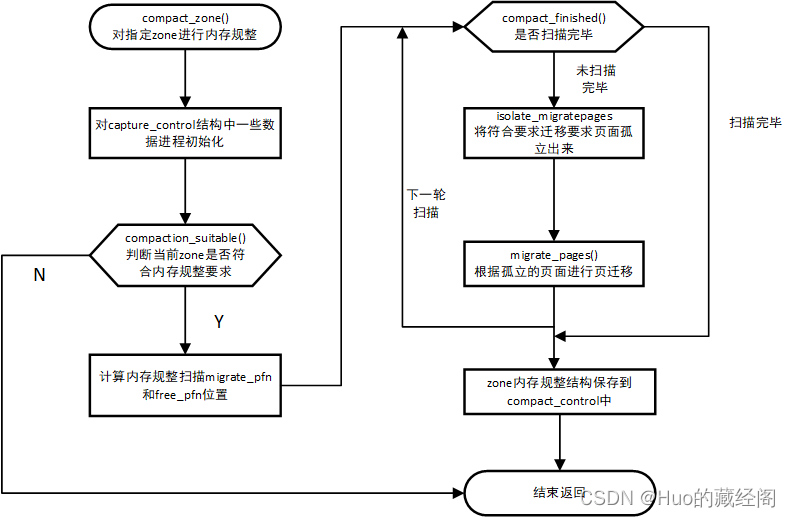
- ?按照指定的zone进行内存规整
- 对compact_control结构中的一些值进行初始化
- compaction_suitable:根据实际内存水位情况判断是否有必要做内存规整,因为内存规整操作比较耗时,如果空闲内存处于较高情况,则没有必要触发内存规整,最终是通过__compaction_suitable实现对内存水位判断
- compact_finished: 用于处理当前zone是否扫描完毕,zone扫描时使用了处理上的技巧。内存规整时分别从zone头部扫描migrate_pfn和从zone尾部扫描free_pfn, 当migrate_pfn与free_pfn相遇时,则认为扫描完毕。最终是调用__compact_finished函数
- isolate_migratepages: 将扫描出的要迁移的页进行孤立isolate,防止在迁移过程中,该页面被释放 或者swap out等,也是做页迁移之前必须准备工作,可以详见《linux那些事之页迁移(page migratiom)》
- migrate_pages:将孤立出来的页面进行页迁移。
- 当zone扫描内存规整完毕之后,需要free_pfn 等信息保存到zone中 用于记录本次扫描位置,空闲页等信息,以便用于下一次内存规整时使用。
- compact_result 为内存规整结果
??????????????关键几个函数
__compaction_suitable
__compaction_suitable用于判断当前zone是否可以做内存规整:
/*
* compaction_suitable: Is this suitable to run compaction on this zone now?
* Returns
* COMPACT_SKIPPED - If there are too few free pages for compaction
* COMPACT_SUCCESS - If the allocation would succeed without compaction
* COMPACT_CONTINUE - If compaction should run now
*/
static enum compact_result __compaction_suitable(struct zone *zone, int order,
unsigned int alloc_flags,
int highest_zoneidx,
unsigned long wmark_target)
{
unsigned long watermark;
if (is_via_compact_memory(order))
return COMPACT_CONTINUE;
watermark = wmark_pages(zone, alloc_flags & ALLOC_WMARK_MASK);
/*
* If watermarks for high-order allocation are already met, there
* should be no need for compaction at all.
*/
if (zone_watermark_ok(zone, order, watermark, highest_zoneidx,
alloc_flags))
return COMPACT_SUCCESS;
/*
* Watermarks for order-0 must be met for compaction to be able to
* isolate free pages for migration targets. This means that the
* watermark and alloc_flags have to match, or be more pessimistic than
* the check in __isolate_free_page(). We don't use the direct
* compactor's alloc_flags, as they are not relevant for freepage
* isolation. We however do use the direct compactor's highest_zoneidx
* to skip over zones where lowmem reserves would prevent allocation
* even if compaction succeeds.
* For costly orders, we require low watermark instead of min for
* compaction to proceed to increase its chances.
* ALLOC_CMA is used, as pages in CMA pageblocks are considered
* suitable migration targets
*/
watermark = (order > PAGE_ALLOC_COSTLY_ORDER) ?
low_wmark_pages(zone) : min_wmark_pages(zone);
watermark += compact_gap(order);
if (!__zone_watermark_ok(zone, 0, watermark, highest_zoneidx,
ALLOC_CMA, wmark_target))
return COMPACT_SKIPPED;
return COMPACT_CONTINUE;
}
主要有以下几种情况:
- is_via_compact_memory: 是否通过/proc/sys/vm/compact_memory 手动强制进行内存规整,如果强制内存规整,则直接返回COMPACT_CONTINUE,继续后续步骤进行内存规整
- zone_watermark_ok: 当作内存water mark满足order,则没有必要做内存规整,能够申请oder 内存成功,返回COMPACT_SUCCESS
- 当内存不满足时,则查看是否可以通过内存压缩满足内存申请,如果能够通过内存规整满足,则返回COMPACT_SUCCESS进行内存规整,如果判断出当前内存不能够通过内存压缩满足分配要求,则说明内存碎片化不严重,没有必要进行内存压缩发跳过此次内存规整操作,返回?COMPACT_SKIPPED。
compact_result
compact_result为此次内存规整之后的结果:
/* Return values for compact_zone() and try_to_compact_pages() */
/* When adding new states, please adjust include/trace/events/compaction.h */
enum compact_result {
/* For more detailed tracepoint output - internal to compaction */
COMPACT_NOT_SUITABLE_ZONE,
/*
* compaction didn't start as it was not possible or direct reclaim
* was more suitable
*/
COMPACT_SKIPPED,
/* compaction didn't start as it was deferred due to past failures */
COMPACT_DEFERRED,
/* compaction not active last round */
COMPACT_INACTIVE = COMPACT_DEFERRED,
/* For more detailed tracepoint output - internal to compaction */
COMPACT_NO_SUITABLE_PAGE,
/* compaction should continue to another pageblock */
COMPACT_CONTINUE,
/*
* The full zone was compacted scanned but wasn't successfull to compact
* suitable pages.
*/
COMPACT_COMPLETE,
/*
* direct compaction has scanned part of the zone but wasn't successfull
* to compact suitable pages.
*/
COMPACT_PARTIAL_SKIPPED,
/* compaction terminated prematurely due to lock contentions */
COMPACT_CONTENDED,
/*
* direct compaction terminated after concluding that the allocation
* should now succeed
*/
COMPACT_SUCCESS,
};
- ?COMPACT_NOT_SUITABLE_ZONE:该zone不适合做内存规整
- COMPACT_SKIPPED:内存规整要求不满足,跳过该zone
- COMPACT_DEFERRED:由于之前的一些错误导致内存规整退出
- COMPACT_INACTIVE:上次内存规整未激活
- COMPACT_NO_SUITABLE_PAGE:没有合适的物理页做内存规整
- COMPACT_CONTINUE:下一个页面块pageblock继续做内存规整
- COMPACT_COMPLETE:zone都以及做内存规整扫描完毕,但是没有合适页面做内存规整
- COMPACT_PARTIAL_SKIPPED:直接内存规整已经扫描了部分zone页面,但是仍然没有合适页面做内存规整
- COMPACT_CONTENDED:由于某些锁竞争导致内存规整退出
- COMPACT_SUCCESS:当前zone内存规整满足页面分配要求,可以退出
__compact_finished
__compact_finished用于判断当前内存压缩扫描是否完成:
static enum compact_result __compact_finished(struct compact_control *cc)
{
unsigned int order;
const int migratetype = cc->migratetype;
int ret;
/* Compaction run completes if the migrate and free scanner meet */
if (compact_scanners_met(cc)) {
/* Let the next compaction start anew. */
reset_cached_positions(cc->zone);
/*
* Mark that the PG_migrate_skip information should be cleared
* by kswapd when it goes to sleep. kcompactd does not set the
* flag itself as the decision to be clear should be directly
* based on an allocation request.
*/
if (cc->direct_compaction)
cc->zone->compact_blockskip_flush = true;
if (cc->whole_zone)
return COMPACT_COMPLETE;
else
return COMPACT_PARTIAL_SKIPPED;
}
if (is_via_compact_memory(cc->order))
return COMPACT_CONTINUE;
/*
* Always finish scanning a pageblock to reduce the possibility of
* fallbacks in the future. This is particularly important when
* migration source is unmovable/reclaimable but it's not worth
* special casing.
*/
if (!IS_ALIGNED(cc->migrate_pfn, pageblock_nr_pages))
return COMPACT_CONTINUE;
/* Direct compactor: Is a suitable page free? */
ret = COMPACT_NO_SUITABLE_PAGE;
for (order = cc->order; order < MAX_ORDER; order++) {
struct free_area *area = &cc->zone->free_area[order];
bool can_steal;
/* Job done if page is free of the right migratetype */
if (!free_area_empty(area, migratetype))
return COMPACT_SUCCESS;
#ifdef CONFIG_CMA
/* MIGRATE_MOVABLE can fallback on MIGRATE_CMA */
if (migratetype == MIGRATE_MOVABLE &&
!free_area_empty(area, MIGRATE_CMA))
return COMPACT_SUCCESS;
#endif
/*
* Job done if allocation would steal freepages from
* other migratetype buddy lists.
*/
if (find_suitable_fallback(area, order, migratetype,
true, &can_steal) != -1) {
/* movable pages are OK in any pageblock */
if (migratetype == MIGRATE_MOVABLE)
return COMPACT_SUCCESS;
/*
* We are stealing for a non-movable allocation. Make
* sure we finish compacting the current pageblock
* first so it is as free as possible and we won't
* have to steal another one soon. This only applies
* to sync compaction, as async compaction operates
* on pageblocks of the same migratetype.
*/
if (cc->mode == MIGRATE_ASYNC ||
IS_ALIGNED(cc->migrate_pfn,
pageblock_nr_pages)) {
return COMPACT_SUCCESS;
}
ret = COMPACT_CONTINUE;
break;
}
}
if (cc->contended || fatal_signal_pending(current))
ret = COMPACT_CONTENDED;
return ret;
}
- compact_scanners_met: cc->free_pfn和cc->migrate_pfn是否相遇,如果说明已经扫描完毕,返回true
- compact_scanners_met 返回true,如果cc->whole_zone为true说明需要扫描整个zone,并且已经扫描完毕了,返回COMPACT_COMPLETE。如果ccf->whole_zone为false,说明不需要扫描整个zone,但是此时已经扫描完整个zone,说明扫描完整个zone还没有满足后续内存分配要求,返回COMPACT_PARTIAL_SKIPPED。
- compact_scanners_met 返回false, is_via_compact_memory()为ture说明是/proc/sys/vm/compact_memory手动触发,需要继续扫描zone下一个pageblock,返回COMPACT_CONTINUE。
- 如果cc->migrate_pfn 不是pageblock对齐,则需要继续扫描
- 接下来一个比较长的循环出来,主要是需要判断后续扫描是否还有空闲page 用来做迁移目的页,如果有则可以继续做迁移,如果没有则返回COMPACT_NO_SUITABLE_PAGE
isolate_migratepages
isolate_migratepages函数处理比较长,整体处理思路就是继续扫描,将扫描出合适的物理页做迁移,并将需要做迁移的页孤立出来,加入到cc->migratepages中:
static isolate_migrate_t isolate_migratepages(struct compact_control *cc)
{
unsigned long block_start_pfn;
unsigned long block_end_pfn;
unsigned long low_pfn;
struct page *page;
const isolate_mode_t isolate_mode =
(sysctl_compact_unevictable_allowed ? ISOLATE_UNEVICTABLE : 0) |
(cc->mode != MIGRATE_SYNC ? ISOLATE_ASYNC_MIGRATE : 0);
bool fast_find_block;
//通过快速通道找到所要迁移扫描的起始pfn
low_pfn = fast_find_migrateblock(cc);
//计算出扫描结束page pfn,要求按照pageblock对齐
block_start_pfn = pageblock_start_pfn(low_pfn);
if (block_start_pfn < cc->zone->zone_start_pfn)
block_start_pfn = cc->zone->zone_start_pfn;
//快速找到的pfn是否成功
fast_find_block = low_pfn != cc->migrate_pfn && !cc->fast_search_fail;
/* Only scan within a pageblock boundary */
block_end_pfn = pageblock_end_pfn(low_pfn);
//对low_pfn起始的pageblock内物理页面做扫描,将合适的做迁移的页面孤立出来
for (; block_end_pfn <= cc->free_pfn;
fast_find_block = false,
low_pfn = block_end_pfn,
block_start_pfn = block_end_pfn,
block_end_pfn += pageblock_nr_pages) {
//如果长时间循环,需要进行放权,给其他进程得到调度机会
if (!(low_pfn % (SWAP_CLUSTER_MAX * pageblock_nr_pages)))
cond_resched();
//检查是否在同一个pageblock内
page = pageblock_pfn_to_page(block_start_pfn,
block_end_pfn, cc->zone);
if (!page)
continue;
//如果最近孤立页面失败,则不进行再次尝试,仅仅做检查
if (IS_ALIGNED(low_pfn, pageblock_nr_pages) &&
!fast_find_block && !isolation_suitable(cc, page))
continue;
//如果是异步规整,则仅规整move页面且非huge page
if (!suitable_migration_source(cc, page)) {
update_cached_migrate(cc, block_end_pfn);
continue;
}
/* Perform the isolation */
//将[low_pfn,block_end_pfn)中的符合内存规整要求的页面孤立出来,将孤立出来的页面加入到cc->migratepages中
low_pfn = isolate_migratepages_block(cc, low_pfn,
block_end_pfn, isolate_mode);
if (!low_pfn)
return ISOLATE_ABORT;
//孤立页面成功或者失败都不在继续
break;
}
//记录下次重新扫描的做页迁移的起始pfn
cc->migrate_pfn = low_pfn;
return cc->nr_migratepages ? ISOLATE_SUCCESS : ISOLATE_NONE;
}
migrate_pages
将上述合适做页迁移的页面,且已经孤立到cc->migratepages中页面做页迁移:
err = migrate_pages(&cc->migratepages, compaction_alloc,
compaction_free, (unsigned long)cc, cc->mode,MR_COMPACTION)关于页迁移详细信息可以参考《linux那些事之页迁移(page migratiom)》
