文章目录
测试1(测试简单的宏展开)
ubuntu上
如:
test.c
#define KY_GET_CURRENT_TIME (time)
int main(){
KY_GET_CURRENT_TIME(NULL);
return 0;
}
预处理:
[root@ubuntu /arnold_test/20220509_compile_preprocessing_test]3# gcc -E test.c
# 1 "test.c"
# 1 "<built-in>"
# 1 "<command-line>"
# 1 "/usr/include/stdc-predef.h" 1 3 4
# 1 "<command-line>" 2
# 1 "test.c"
int main(){
(time)(NULL);
return 0;
}
或:
[root@ubuntu /arnold_test/20220509_compile_preprocessing_test]4# gcc -E test.c -o test.i
[root@ubuntu /arnold_test/20220509_compile_preprocessing_test]5#
[root@ubuntu /arnold_test/20220509_compile_preprocessing_test]5#
[root@ubuntu /arnold_test/20220509_compile_preprocessing_test]5# cat test.i
# 1 "test.c"
# 1 "<built-in>"
# 1 "<command-line>"
# 1 "/usr/include/stdc-predef.h" 1 3 4
# 1 "<command-line>" 2
# 1 "test.c"
int main(){
(time)(NULL);
return 0;
}
[root@ubuntu /arnold_test/20220509_compile_preprocessing_test]6#
测试2(测试简单的宏替换)
ubuntu上
#define KY_print printf
int main(){
KY_print("I miss u\n");
return 0;
}
预处理:
[root@ubuntu /arnold_test/20220509_compile_preprocessing_test]8# gcc -E test.c
# 1 "test.c"
# 1 "<built-in>"
# 1 "<command-line>"
# 1 "/usr/include/stdc-predef.h" 1 3 4
# 1 "<command-line>" 2
# 1 "test.c"
int main(){
printf("I miss u\n");
return 0;
}
来看两个花括号测试(花括号能隔离环境)
ubuntu上
测试1
#pragma warning(disable : 4996)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
int a = 1;
{
int a = 2;
printf("%d\n", a); //2
}
printf("%d\n", a); //1
return 0;
}
ubuntu上
测试2
#pragma warning(disable : 4996)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
int a = 1;
{
a = 2;
printf("%d\n", a); //2
}
printf("%d\n", a); //2
return 0;
}
测试宏函数(visual studio vc 无法使用复合语句表达式 ({}))
ubuntu上
//#pragma warning(disable : 4996)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define PLUS \
({int a = 1;\
int b =2;\
(a+b);})
int main() {
printf("%u\n", PLUS);
return 0;
}
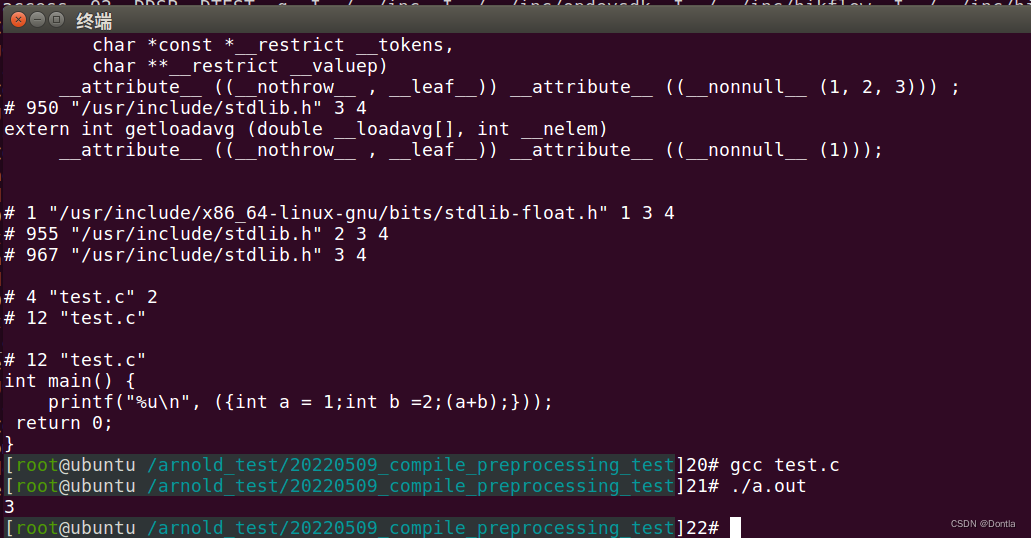
vs上代码检查就报错了,啥情况呢?
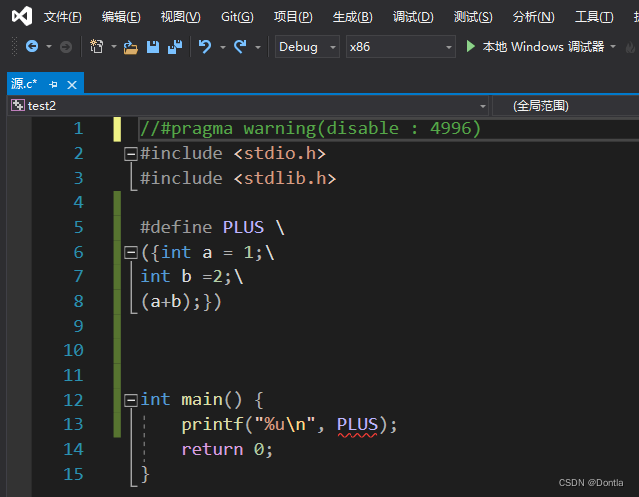
C语言复合语句表达式 ({}) (只适用于gnu)
上面的语法其实是gnu的复合语句表达式
语法规则
1、?对圆括号在外边,?对?括号在??。
2、复合语句可以有函数调?、变量赋值
3、最后?条语句必须以分号结尾。
4、最后?条语句的值,将作为整个表达式的值
5、如果你在?括号?的最后?句?的是没有返回值的语句,则整个表达式的返回类型为 void,即没有合法的返回值
参考文章:C语言的复合语句表达式
示例1(在复合表达式中定义函数,调用函数,判断语句,以最后一个语句的值作为返回)
//#pragma warning(disable : 4996)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
int a = ({
int foo()
{
return 10;
}
int y =foo();
int z;
if(y > 0)
z = y;
else
z =-y;
z;
});
printf("%d\n", a);
return 0;
}
同样,猜测({})也能隔绝环境,没测试哈。。。
