一、虚拟机
1、虚拟机概述
虚拟机运行在计算机上的一款软件程序,模拟计算机硬件功能为其他软件程序提供一个独立的计算机环境。
2、虚拟机产品
1)Vmware
VMware Workstation (寄居)
VMware vSphere (原生)
2)微软
Virtual PC
Virtual Server
Hyper-V
3)RedHat
KVM
RHEV
4)Oracle
VM VirtualBox
虚拟机运行模式
1)寄居架构
作为应用软件安装在操作系统上 ,可以在此应用软件上安装多个操作系统
2)原生架构
虚拟机软件直接安装在计算机硬件上
虚拟机本身就是一个操作系统
二、 TCP/IP协议
1、TCP/IP通信协议是目前最完整、最被广泛支持的通信协议,它可以让不同网络架构、不同操作系统的计算机之间通信,是Internet的标准通信协议
IP地址介绍:
1、作用:用来标识一个节点的网络地址
2、组成:网络位+主机位 两部分组成
3、长度:32个二进制位,
4、表示:以4个十进制数来表示,之间用 . 隔开,又称点分十进制。
3、 IP地址分类:
A 1 ~ 127 网+主+主+主
B 128 ~ 191 网+网+主+主
C 192 ~ 223 网+网+网+主
D 224 ~ 239 组播(多播)
E 240 ~ 254 科研
5、子网掩码
作用:区分IP地址的网络位和主机位
长度:32个二进制位
特点:子网掩码不能单独存在,它必须结合IP地址一起使用
默认子网掩码:
A 类 255.0.0.0 (1网3主)
B类 255.255.0.0 (2网2主)
C 类 255.255.255.0 (3网1主)
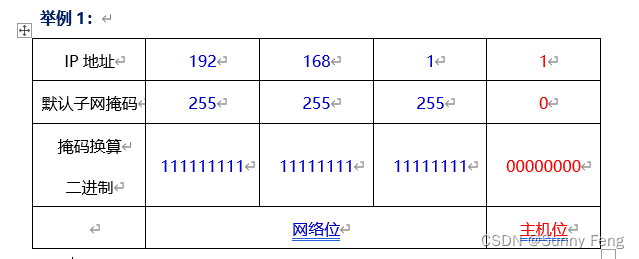
注:
1)IP地址由网络位和主机位两部分组成
2)C类IP地址的默认子网掩码是 255.255.255.0
3)十进制255换算成二进制是 11111111
4)对应IP地址的网络部分用1表示,对应IP地址主机部分用0表示
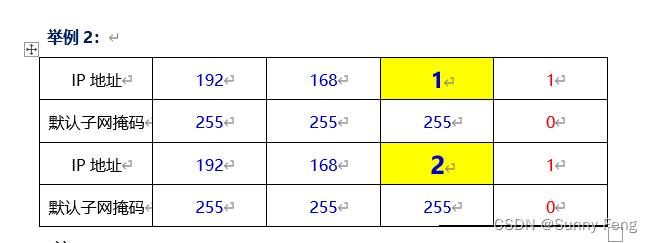
注:
1)根据上图:192.168.1.1 和192.168.2.1 不属于同一个网段
6、公有IP地址和私有IP地址
公有地址,也可称为公网地址,通过它直接访问因特网,它是广域网范畴内的。
私有地址,也可称为专网地址,专门为组织机构内部使用,它是局域网范畴内的,
私有地址范围:
A类 10.0.0.1 ~ 10.255.255.255
B类 172.16.0.1 ~ 172.31.255.254
C类 192.168.0.1 ~ 192.168.255.254
1、A、B、C 类IP地址的网络范围分别是多少?
A类,1.0.0.0~127.0.0.0 ==》子网掩码 255.0.0.0
B类,128.0.0.0~191.255.0.0 ==》子网掩码 255.255.0.0
C类,192.0.0.0~223.255.255.0 ==》子网掩码 255.255.255.0
2、子网掩码的作用是什么?
子网掩码:用于确定IP地址的网络位、主机位,当一台计算机访问其他IP地址时,通过比较本机与目标主机的网络位来决定是否需要找网关(若网络位相同则不需要)。
3、预留给企业私用的IP地址包括哪些?
私有地址包括:
在A类地址中预留出 10.0.0.1 ~ 10.255.255.254;
在B类地址中预留出 172.16.0.1 ~ 172.31.255.254;
在C类地址中预留出 192.168.0.1 ~ 192.168.255.254
4、默认网关的作用是什么?
网关指的是从一个网络连接另一个网络的“关口”,通常是一台路由器,或者防火墙/接入服务器的地址。对于计算机来说,当没有明确的路由条目指出如何到达一个目标地址时,一概将数据包转交给默认网关。
三. 命令行视图
用户视图
- <Huawei>
-系统视图 - <Huawei>system-view
-进入系统视图 Enter
system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
进入系统视图,返回用户视图按 Ctrl+Z.
[Huawei] 系统视图状态 - 接口视图
- [Huawei] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 进入端口0/0/1
- [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] 接口视图状态
- interface:接口
- Ethernet:接口类型
- 0/0/1:第一个“0”代表槽位号,第二个“0”代表子卡号,“1”代表接口号
-
协议视图
[Huawei]ospf 1
进入OSPF 1 视图
[Huawei-ospf-1]
OSPF视图状态 -
视图间转换
- Ctrl+Z 返回用户视图按
- quit 可从当前视图退出至上一层视图
- return 直接退回到用户视图
- 快捷键
- Ctrl+Z
- Ctrl+C
- Ctrl+]
- Backspace :退格键
- 小键盘左右方向键
- 命令行帮助
部分帮助:s?
完全帮助: [Huawei]?
命令补全: sy—>Tab键
命令简写: sy—>回车键
- 交换机命令行配置
-
配置主机名称
<Huawei>system-view
进入系统视图
[Huawei]sysname tarena1
设置设备名称tarena1
[tarena1] -
显示VRP版本
[tarena1]display version
显示版本
Huawei Versatile Routing Platform Software
华为通用路由平台软件
VRP ? software, Version 5.110 (S5700 V200R001C00)
VRP(R)软件,版本5.110(S5700 V200R00100) -
查看交换机配置
<tarena1>display current-configuration
显示当前配置
- 配置通过Console口登录设备
-
Password 认证
[tarena1]user-interface console 0
进入console 视图
[tarena1-ui-console0]authentication-mode password
认证模式为password
[tarena1-ui-console0]set authentication password simple huawei123
设置认证密码为简单的 huawei123 -
none 认证
[tarena1]user-interface console0
进入console 视图
[tarena1-ui-console0]authentication-mode none
认证模式为none -
保存命令
<tarena1>save all
保存所有
The current configuration will be written to the device.
当前这个配置将写入这个设备
Are you sure to continue?[Y/N]y
你确定要继续吗?选择(yes或者no)
Info: Please input the file name ( *.cfg, *.zip ) [vrpcfg.zip]:
消息:请输入这个文件的名字 ,保存格式.cfg、zip
Aug 2 2017 09:01:13-08:00 tarena1 %%01CFM/4/SAVE(l)[5]:The user chose Y when deciding whether to save the configuration to the device.
已确认将配置保存到当前配置
Now saving the current configuration to the slot 0.
现将当前配置保存到插槽0
Save the configuration successfully.
这个配置成功保存
-
设置用户连接的超时时间
<Huawei>system-view
[Huawei]user-interface console 0
[Huawei-ui-console0]idle-timeout ?
INTEGER<0-35791> Set the number of minutes before a terminal user times
设置终端用户时间分钟整数范围(0-35791)
out(default: 10minutes)
默认是10分钟
[Huawei-ui-console0]idle-timeout 30
空闲超时时间30分钟 -
恢复出厂设置
<Huawei>reset saved-configuration
复位 保存配置(出厂配置)
Warning: The action will delete the saved configuration in the device.
警告:该操作将删除这个设备上保存的配置
The configuration will be erased to reconfigure. Continue? [Y/N]:y
该配置将被擦除,继续重置配置(yes/no)
Warning: Now clearing the configuration in the device.
警告:现在清楚这个设备配置
<Huawei>reboot
重启设备 -
重启设备
- reboot
四. 路由器
1、路由器转发数据包的依据是路由表
路由表格式:
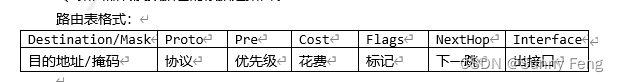
2、原理:
路由器接到数据包,检查数据包的目标IP地址,再在路由表中查找到达目标的路线,并选择最佳路线按照最佳路线转发数据包。
3、开启关闭接口,配置路由器接口IP地址
[Router]interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip address 192.168.1.254 24
[S2]interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2
[S2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]shutdown :关闭接口
[S2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]undo shutdown :开启接口
4、查看路由表命令
<Router>display ip routing-table :查看路由表
5、远程路由器命令
R1(tedu)配置
<Huawei>system-view :进入系统视图
[Huawei]sysname tedu :修改主机名
[tedu]interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0 :进入接口0/0/0
[tedu-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip address 192.168.1.2 24
配置接口IP地址为192.168.1.2 掩码为255.255.255.0
[tedu-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]quit :退回到系统视图
[tedu]user-interface vty 0 4 :进入虚拟终端接口
[tedu-ui-vty0-4]authentication-mode password
设置认证模式为password
Please configure the login password (maximum length 16):123 :密码123
[tedu-ui-vty0-4]user privilege level 15 :用户权限标准为15
R2(NTD)配置 (远程路由器)
<Huawei>system-view :进入系统视图
[Huawei]sysname NTD :修改主机名
[ntd]interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0 :进入接口0/0/0
[ntd-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip address 192.168.1.1 24
配置接口IP地址为192.168.1.1 掩码为255.255.255.0
[ntd-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]return :退回到用户视图
<ntd>telnet 192.168.1.2 :远程tedu(192.168.1.2)
6、Console 口下AAA认证
[tarena1]user-interface console 0
[tarena1-ui-console0]authentication-mode aaa
认证模式为 AAA
[tarena1-ui-console0]quit
返回系统模式
[tarena1]aaa
进入AAA视图
[tarena1-aaa]local-user admin password cipher huawei456
创建本地用户admin 配置登录密码为加密的huawei456
[tarena1-aaa]local-user admin service-type terminal
配置本地用户的接入类型为Console(终端)用户
- telnet 远程—aaa认证模式(路由器)
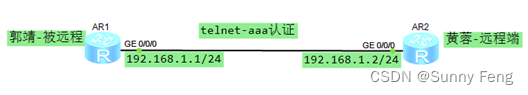
AR1(郭靖)配置
<Huawei>system-view
:进入系统视图
[Huawei]sysname guojing
:修改主机名为guojing
[guojing]interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0
:进入接口0/0/0
[guojing-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip address 192.168.1.1 24
:给接口0/0/0配置IP地址为192.168.1.1 掩码为 24
[guojing-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]quit
:退出,返回系统模式
[guojing]user-interface vty 0 4
:进入虚拟终端(vty)
[guojing-ui-vty0-4]authentication-mode aaa
:设置认证模式为aaa
[guojing-ui-vty0-4]aaa
:进入AAA协议视图
[guojing-aaa]local-user wukong password cipher 123
:设置用户名wukong ,密文密码123
[guojing-aaa]local-user wukong service-type telnet
:设置用户wukong 服务类型为 telnet
[guojing-aaa]local-user wukong privilege level 3
:设置用户wukong 权限标准为3
AR2(黄蓉)配置
<Huawei>system-view
:进入系统视图
[Huawei]sysname huangrong
:修改主机名为guojing
[huangrong]interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0
:进入接口0/0/0
[huangrong-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip address 192.168.1.2 24
:给接口0/0/0配置IP地址为192.168.1.2 掩码为 24
[huangrong-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]return
:退出返回到用户模式
<huangrong>telnet 192.168.1.1
:远程 192.168.1.1(验证)
- telnet 远程—aaa认证模式(交换机)

LSW1(郭靖)配置
<Huawei>system-view
:进入系统视图
[Huawei]sysname guojing
:修改主机名为guojing
[guojing]interface Vlanif 1
:进入虚接口vlanif1
[guojing-Vlanif1]ip address 192.168.1.1 24
:给vlanif1 配置IP地址为192.168.1.1 掩码为 24
[guojing-Vlanif1]quit
:退出,返回系统模式
[guojing]user-interface vty 0 4
:进入虚拟终端(vty)
[guojing-ui-vty0-4]authentication-mode aaa
:设置认证模式为aaa
[guojing-ui-vty0-4]aaa
:进入AAA协议视图
[guojing-aaa]local-user wukong password cipher 123
:设置用户名wukong ,密文密码123
[guojing-aaa]local-user wukong service-type telnet
:设置用户wukong 服务类型为 telnet
[guojing-aaa]local-user wukong privilege level 3
:设置用户wukong 权限标准为3
LSW2(黄蓉)配置
<Huawei>system-view
:进入系统视图
[Huawei]sysname huangrong
:修改主机名为guojing
[huangrong]interface Vlanif 1
:进入虚接口vlanif1
[huangrong -Vlanif1]ip address 192.168.1.2 24
:给vlanif1 配置IP地址为192.168.1.2 掩码为 24
[huangrong -Vlanif1]return
:退出返回到用户模式
<huangrong>telnet 192.168.1.1
:远程 192.168.1.1(验证)
Linux常用命令
1、linux 界面切换:
使用ctrl+alt+F1~6切换到命令行界面;ctrl+alt+F7切换到图形界面
打开终端,输入init 3,回车即可。
init 后数字的含义:
0 - halt (Do NOT set initdefault to this) //停机(不要把initdefault设置为零为0,因为这样会使Linux无法启动)
1 - Single user mode //单用户模式,就像WinXP下的安全模式
2 - Multiuser, without NFS (The same as 3, if you do not have networking) //多用户,但没有NFS
3 - Full multiuser mode //完全多用户模式,标准的运行极,即命令行界面
4 - unused //一般不用,但在一些特殊情况下可以用他来做一些事情
5 - X11 //选择此项,系统在登录时将进入图形化登录界面
6 - reboot (Do NOT set initdefault to this) //重新启动(不要把initdefault设置为6,因为这样会使linux不断重新启动)
(注:以上方法切换后,图形界面完全关闭。如果窗口中有文件未保存,将丢失。用init 5 可以回到图形界面,但原来的进程已死。用startx 则在当前级别3上加载图形界面)
每次启动直接进入命令行界面,则要修改etc/inittab文件,将启动级别由5改为3即可
终端以root身份执行 vi /etc/inittab 打开inittab文件,编辑后保存重启即可
2、在图形化界面,鼠标右击–>打开终端—
调大字体:ctrl+shift+“+ "
缩小字体:ctrl +”-"
3、[root@bogon ~ ]#
用户 主机名 当前位置 管理员
4、[tedu@bogon root ]$
用户 主机名 当前位置 普通用户
5、清空屏幕的快捷键: ctrl +L
6、绝对路径,相对路径
—cd /etc/gss :绝对路径
—cd home/tedu :相对路径
7、pwd :打印工作路径
8、cd :切换路径
9、ls :列表
10、hostname :查看计算机名
11、hostnamectl :查看系统详细信息
12、ls -lh /root :查看/root/下的 详细信息
13、ls -lhd /root :查看 /root这个目录本身的详细信息
14、hostnamectl set-hostname “主机名” :修改主机名
15、 route -n : 查看默认网关
16、ls -lh /boot/vmlinuz-3.10.0-862.el7.x86_64 :查看Linux内核文件
17、cat /etc/passwd :查看passwd 文件内容
18、cat /etc/resolv.conf :查看dns 地址
19、 nmcli device status :列出已连接的网卡
20、nmcli connection show :列出已有的连接
21、nmcli connection modify “ens33” ipv4.method manual ipv4.addresses 192.168.1.1/24
连接 修改 网卡名 手动 地址
ipv4.gateway 192.168.1.254 ipv4.dns 8.8.8.8
网关
22、 nmcli connection modify “ens33” connection.autoconnect yes :自动连接
23、nmcli connection up “ens33” 激活这个连接
24、nmtui 修改IP地址
25、netstat -ano 查看连接情况
26、netstat -an | grep 22 查看22端口的情况
27、ss -ntl | grep 22 查看22端口的情况
ss -lntup | grep java 查看java端口
28、 du -sh 查看文件夹大小/查看原始目录占用空间
29、 tar -xcf 解压文件
30、 ln -s /app/xxx /app 软连接
31、 uptime 查看cpu运行时间
32、 who 查询当前用户
33、 who | wc -l 统计当前用户总数
34、 pgrep httpd 查看进程
35、 pgrep -c . 统计所有进程数
36、 iptraf-ng ip流量监控/查看网卡的流量
37、 uname -----查看内核名字
uname -r ------ 查看内核版本
uname -a ---- 查看内核信息
38、 cat /etc/redhat-release 查看系统版本
cat /proc/version
39、 ps -ef | grep java 查看java进程
40、 find -type f -name “*.xml”| xargs grep ‘127’ 查找有127的文件
41、 sed -i.bak ‘s#127#\d+#g’ ./webapps/manager/META-INF/context.xml
将文件中的127替换成\d
##################################################
常用命令选项
– -l :以长格式显示,显示目录内容的详细属性
– -h :带容量单位
– -d :只列出目录本身(不包含内容)
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /root
[root@localhost ~]# ls -lh /root
[root@localhost ~]# ls -lhd /root
##################################################
? mkdir — Make Directory
– 格式:mkdir [/路径/]目录名…
[root@A ~]# mkdir test01 #当前目录创建
[root@A ~]# ls #查看当前路径下内容
[root@A ~]# mkdir /student #在根目录下创建student目录
[root@A ~]# ls / #查看根目录下内容
[root@A ~]# mkdir /opt/test02 #在/opt目录创建test02目录
[root@A ~]# ls /opt #查看/opt目录内容
##################################################
? touch命令
– 用途:新建空文件
– 格式:touch 文件名…
[root@A ~]# touch /opt/2.txt
[root@A ~]# ls /opt/
##################################################
文本内容操作
? less分屏阅读工具
? 格式:less [选项] 文件名…
– 优势:支持前后翻页
? 基本交互操作
– 按 / 键向后查找(n、N切换)
[root@A /]# less /etc/passwd
按键盘上下键,进行滚动
输入 /a 全文查找a,按n、N切换跳转匹配项
按q退出less模式
##################################################
? head、tail 命令
– 格式:head -n 数字 文件名
tail -n 数字 文件名
[root@A /]# head -3 /etc/passwd
[root@A /]# head -4 /etc/passwd
[root@A /]# head -12 /etc/passwd
[root@A /]# tail -3 /etc/passwd
[root@A /]# tail -10 /etc/passwd #默认显示10行
##################################################
? grep工具
– 用途:输出包含指定字符串的行
– 格式:grep ‘查找条件’ 目标文件
[root@A /]# grep root /etc/passwd
[root@A /]# grep bin /etc/passwd
[root@A /]# grep bash /etc/passwd
##################################################
? 快捷键
– Ctrl + c:废弃当前编辑的命令行,结束正在运行的命令
– Esc + . 或 Alt + . :粘贴上一个命令的参数
[root@A /]# ls /etc/redhat-release
[root@A /]# ls -l Alt + .
[root@A /]# cat Alt + .
[root@A /]# cat -n Alt + .
– Ctrl + l:清空整个屏幕
– Ctrl + u:清空至行首
– Ctrl + w:往回删除一个单词(以空格界定)
Ctrl+shift++ 放大字体
Ctrl± 缩小字体
Ctrl+C 打断输入
Ctrl+L 清屏
Ctrl+shift+T 打开新终端
Tab 补全命令
###############################################
使用通配符
? 针对不确定的文档名称,以特殊字符表示
– *:任意多个任意字符
– ?:单个字符
[root@A ~]# ls /boot/vm* #列出以vm开头的文档
[root@A ~]# ls /etc/*tab #列出以tab结尾的文档
[root@A ~]# ls /dev/tty* #列出以tty开头的文档
[root@A ~]# ls /etc/*.conf #列出以.conf结尾的文档
[root@A ~]# ls /dev/tty? #列出tty后面只能有一个字符的
[root@A ~]# ls /dev/tty?? #列出tty后面只能有两个字符的
列出/etc/下以re开头并且以.conf结尾
[root@A ~]# ls /etc/re*.conf
– [a-z]:多个字符或连续范围中的一个,若无则忽略
– {a,min,xy}:多组不同的字符串,全匹配
[root@A ~]# ls /dev/tty[3-8]
[root@A ~]# ls /dev/tty[1-5]
[root@A ~]# ls /dev/tty{1,3,7,9,12,38,S0}
[root@A ~]# ls /dev/tty{1,3,5,7,9,11,S1}
列出/dev/tty20至/dev/tty30之间所有设备文件?
[root@A ~]# ls /dev/tty2[0-9] /dev/tty30
[root@A ~]# ls /dev/tty{2[0-9],30}
######################################################
? rm — Remove
– 格式:rm [选项]… 文件或目录…
? 常用命令选项
-r:递归删除(含目录) 递归:目录本身以及目录下所有
-f:强制删除
[root@A ~]# rm -rf /opt/1.txt /opt/nsd01
[root@A ~]# ls /opt/
test
[root@A ~]# rm -rf /opt/test/
[root@A ~]# ls /opt/
##################################################
? 移动
mv 移动/改名
[root@A ~]# mv /opt/1.txt /opt/ntd01
[root@A ~]# ls /opt/
##################################################
重命名:路径不变的移动
[root@A ~]# mv /opt/ntd01 /opt/student
[root@A ~]# ls /opt/
[root@A ~]# mv /opt/student/ /opt/ntd
[root@A ~]# ls /opt/
##################################################
cp 复制
? cp — Copy
– 格式:cp [选项]… 原文件… 目标路径
? 常用命令选项
– -r:递归,复制目录时必须有此选项
– -P: 保持被复制文件的原属性不变
[root@A ~]# cp -r /boot/ /opt/
[root@A ~]# ls /opt/
[root@A ~]# ls /opt/boot/
[root@A ~]# cp -r /boot/ /opt/
[root@A ~]# ls /opt/
[root@A ~]# ls /opt/boot/
[root@A ~]# cp -p /etc/passwd /opt/
[root@A ~]# ls –lh /opt/passwd
? 复制可以支持两个以上的参数
永远把最后一个参数作为目标,其他的所有参数都做为源文档
[root@A ~]# cp /etc/fstab /etc/shadow /opt/
? 复制与 “ . ”连用
[root@A ~]# cd /opt
[root@A opt]# cp -r /root . #将/root复制到当前路径下
[root@A ~]# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
[root@A network-scripts]# cp /etc/passwd .
? 复制时可以重新命名,目标路径文件名
[root@A /]# cp /etc/redhat-release /opt/abc
[root@A /]# ls /opt/
[root@A /]# cp -r /mnt/ /opt/haha
[root@A /]# cp -r /mnt/ /opt/test #将/mnt放入/opt命名为test
##################################################
别名的定义:简化复杂的命令
? 查看已设置的别名
– alias [别名名称]
? 定义新的别名
– alias 别名名称= ‘实际执行的命令行’
? 取消已设置的别名
– unalias [别名名称]
[root@A ~]# alias hn=‘hostname’ #定义别名
[root@A ~]# alias #显示当前正在生效的别名
[root@A ~]# hn #执行成功
[root@A ~]# unalias hn #删除别名
[root@A ~]# hn #执行失败
##################################################
使用vim创建/修改文件
? vim文本编辑器
– 格式:vim [[/目录/]文件名]
– 若目标文件不存在,则新建空文件并编辑
– 若目标文件已存在,则打开此文件并编辑
vim模式:命令模式 输入模式(插入模式 编辑模式) 末行模式
[root@A /]# vim /opt/haxi.txt
i 键
命--------------------->输入模式(按Esc 键 回到命令模式)
令
模
式--------------------->末行模式(按Esc 键 回到命令模式)
: 键
末行模式 :wq 保存并退出
末行模式 :q! 强制不保存并退出
? 命令模式的基本操作
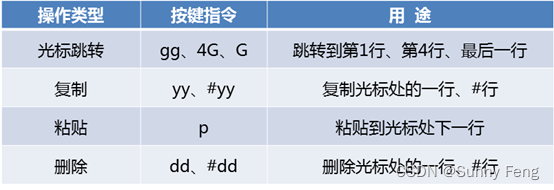
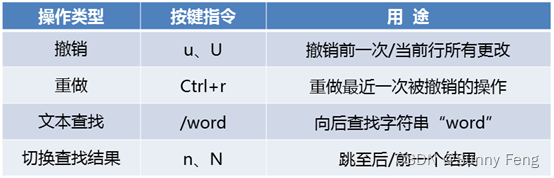
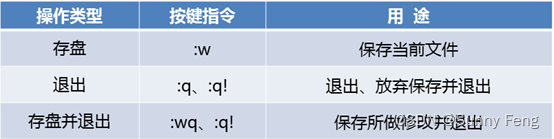
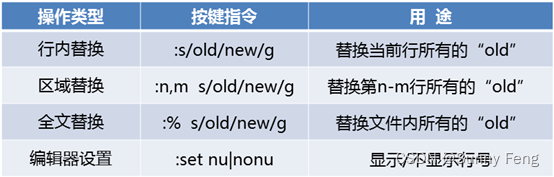
1、基本权限的类别
? 访问方式(权限)
– 读取:允许查看内容-read r
– 写入:允许修改内容-write w
– 可执行:允许运行和切换-execute x
对于文本文件
r: cat less head tail
w:vim
x: cd Shell脚本 可以运行
? 权限适用对象(归属)
– 所有者:拥有此文件/目录的用户-user u
– 所属组:拥有此文件/目录的组-group g
– 其他用户:除所有者、所属组以外的用户-other o
2、查看权限
? 使用 ls -l 命令
– ls -ld 文件或目录…
开头 d 为目录
开头 - 为文本文件
开头 l 为快捷方式
[root@server0 /]# ls -lhd /etc/
d rwx r-x r-x . 134 root root 8.0K 8月 2 02:59 /etc
属主权限 属组权限 其他人权限
[root@server0 /]# ls -lh /etc/passwd
- rw- r-- r-- . 1 root root 2.3K 7月 31 02:59 /etc/passwd
属主权限 属组权限 其他人权限
3、设置基本权限
? 使用 chmod 命令
– chmod [-R] 归属关系±=权限类别 文档…
[-R]:递归设置
(u=用户 g=组 o=其他人)
[root@server0 /]# mkdir /ntd01
:新建目录 ntd01
[root@server0 /]# ls -ld /ntd01
:查看ntd01的详细属性
[root@server0 /]# chmod u-w /ntd01
:给ntd01修改权限 用户去掉写入权限(u-w)
[root@server0 /]# ls -ld /ntd01
:检查结果
[root@server0 /]# chmod u+w /ntd01
:给ntd01修改权限 用户加上写入权限(u-w)
[root@server0 /]# ls -ld /ntd01
:检查结果
[root@server0 /]# chmod o=--- /ntd01
:给ntd01修改权限 去掉其他人的全部权限,读写执行全部为空
[root@server0 /# ls -ld /ntd01
:检查结果
[root@server0 /]# chmod ugo=rwx /ntd01
:给ntd01修改权限 设置用户、组、其他人的权限全部为可读、可写、可执行
[root@server0 /]# ls -ld /ntd01
:检查结果
[root@server0 /]# chmod o-w /ntd01
:给ntd01修改权限 去掉其他人的写入权限
[root@server0 /]# ls -ld /ntd01
:检查结果
[root@server0 /]# chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=--- /ntd01
:给ntd01修改权限 设置用户的权限为读、写、执行、,设置组的权限为读、执行,设置其他人的权限为空
[root@server0 /]# ls -ld /ntd01
:检查结果
[root@server0 /]# mkdir -p /opt/aa/bb/cc/dd
:新建目录 /opt/aa/bb/cc/dd
[root@server0 /# chmod -R o=--- /opt/aa
:递归修改/opt/aa 和aa下面所有目录和文件,其他人的权限都为空
[root@server0 /]# ls -ld /opt/
:检查结果
4、Linux中如何判断用户权限:
1)判断用户的角色 顺序:所有者>所属组>其他人 匹配及停止
2)查看相应权限位置的权限设置
###################################################
Permission denied : 权限不足
command not found: 命令没有找到
目录的 r 权限:能够 ls 浏览此目录内容
目录的 w 权限:能够执行 rm/mv/cp/mkdir/touch/ 等更改目录内容的操作
目录的 x 权限:能够 cd 切换到此目录
以root用户新建/ntddir/目录,在此目录下新建readme.txt文件,并进一步完成下列操作
1)使用户zhoujia能够在此目录下创建子目录 切换用户 su - zhoujia
chmod o+w /ntddir/
2)使用户lisi不能够在此目录下创建子目录
chmod o-w /ntddir/
3)使用户lisi能够修改readme.txt文件
chmod o+w /ntddir/readme.txt
4)调整此目录的权限,使所有用户都不能cd进入此目录
chmod u-x,g-x,o-x /ntddir/
5)为此目录及其下所有文档设置权限 rwxr-x---
chmod -R u=rwx,g=rx,o=--- /ntddir/
5、设置文档归属
? 使用 chown 命令
– chown [-R] 属主 文档…
– chown [-R] :属组 文档…
– chown [-R] 属主:属组 文档…
[-R]:递归设置
[root@server0 /]# mkdir /ntd03
:新建ntd03目录
[root@server0 /]# ls -ld /ntd03
:查看ntd03目录详细属性
[root@server0 /]# useradd guojing
:新建用户guojing
[root@server0 /]# useradd huangrong
:新建用户huangrong
[root@server0 /]# groupadd taohuadao
:新建组taohuadao
[root@server0 /]# chown guojing:taohuadao/ntd03
:将目录ntd03的属主修改为用户guojing ,将属组修改为taohuadao
[root@server0 /]# ls -ld /ntd03
:检查结果
[root@server0 /]# chown huagnrong /ntd03
将目录ntd03的属主修改为用户huangrong
[root@server0 /]# ls -ld /ntd03
:检查结果
[root@server0 /]# chown :guojing /ntd03
将目录ntd03的将属组修改为guojing
[root@server0 /]# ls -ld /ntd03
:检查结果
6、备份与恢复
.zip 压缩包的处理 ——
制作备份:zip -ry 备份文件名.zip 被备份的文档… …
释放备份:
unzip 备份文件名.zip
unzip 备份文件名.zip -d 目标文件夹
[root@server0 /]# zip -ry /opt/abc.zip /boot/
:将/boot/备份至 /opt/下 命名abc.zip包
[root@server0 /]# ls /opt
:检查结果
[root@server0 /]unzip /opt/abc.zip -d /mnt
:将备份至 /opt/下 的abc.zip包解压到 /mnt下
[root@server0 /]ls /mnt
:检查结果
[root@server0 /]#zip -ry /opt/abcd.zip /home/ /etc/passwd /usr/local/
:将/home/ /etc/passwd /usr/local/ 等备份至 /opt/下 命名abcd.zip包
[root@server0 /]# ls /opt/
:检查结果
[root@server0 /]unzip /opt/abcd.zip -d /mnt
:将备份至 /opt/下 的abcd.zip包解压到 /mnt下
[root@server0 /]ls /mnt
:检查结果
1、tar备份与恢复
1)Linux常见的压缩格式及命令工具:
gzip ------> .gz
bzip2 ----> .bz2
xz -------> .xz
2)制作tar包:
tar 选项 /路径/归档及压缩包的名字 /路径/源文档 …
3)制作备份:
tar -zcPf 备份文件名.tar.gz 被备份的文档… …
tar -jcPf 备份文件名.tar.bz2 被备份的文档… …
tar -JcPf 备份文件名.tar.xz 被备份的文档… …
4)释放tar包:
tar 选项 /路径/归档及压缩包的名字 -C /路径/
5)释放备份:
tar -xf 备份文件名.tar.*
tar -xf 备份文件名.tar.* -C 目标文件夹
tar -xPf 备份文件名.tar.*
6).tar包 命令选项
– -C(大写):指定释放的位置
– -c:创建归档
– -x:释放归档
– -f:指定归档文件名称,必须放在所有选项的最后
– -z、调用 .gz、格式的工具进行处理
– -j、调用 …bz2、格式的工具进行处理
– -J、调用 .xz 格式的工具进行处理
– -t:显示归档中的文件清单
[root@A ~]# tar -zcf /opt/test01.tar.gz /home/ /etc/passwd
:将/home/ 和/etc/passwd 打包备份到/opt/下命名 test01.tar.gz文件
[root@A ~]# ls /opt/
:检查结果
[root@A ~]# tar -jcf /opt/abc.tar.bz2 /home/ /etc/passwd
:将/home/ 和/etc/passwd 打包备份到/opt/下命名 abc.tar.bz2文件
[root@A ~]# ls /opt/
:检查结果
[root@A ~]# tar -Jcf /opt/ntd.tar.xz /home/ /etc/passwd
:将/home/ 和/etc/passwd 打包备份到/opt/下命名 ntd.tar.xz文件
[root@A ~]# ls /opt/
:检查结果
7)使用 tar 工具完成以下备份任务:
– 创建一个名为 /root/backup.tar.bz2 的备份文件
– 其中包含 /usr/local 目录中的内容
[root@A ~]# tar -jcf /root/backup.tar.bz2 /usr/local/
:将/usr/local/打包备份到/root/下命名 backup.tar.bz2文件
[root@A ~]# ls /root/
:检查结果
8)释放
[root@A ~]# rm -rf /mnt/*
:删除/mnt/下的所有文件,清空
[root@A ~]# ls /mnt/
:检查删除结果
[root@A ~]# tar -xf /root/backup.tar.bz2 -C /mnt/
:将/root/backup.tar.bz2的tar包文件,解压(释放)到/mnt/目录下
[root@A ~]# ls /mnt/
:检查结果
[root@A ~]# ls /mnt/usr/
:检查结果
9)查看tar包内容``
[root@A ~]# tar -tf /root/backup.tar.bz2
:查看tar包内容
2、挂载与卸载设备
1)挂载、装载的含义:
把指定的设备装到某个Linux目录下,然后通过这个目录就可以访问到设备中的文档数据
2)指定的设备:
光盘 /dev/cdrom、U盘、格式化好的分区、ISO镜像文件……
某个Linux目录(挂载点),用户自己定义,尽量不要用系统默认的那些特殊目录(/boot、/root、/home、/tmp)
3)挂载操作:
– mount 被挂载的设备 挂载点目录
– ls 挂载点目录
4)卸载操作:
–umount 挂载点目录
5)挂载一个存储设备的方式 :
–需要时使用mount命令手动挂载
–配置开机自动挂载
6)实现开机自动挂载XX设备:
[root@A ~]# vim /etc/fstab
/dev/cdrom /mnt/abc iso9660 defaults 0 0
存储设备 挂载点 类型
[root@A ~]# mount -a 【自动挂载所有已配置设备】
7)准备工作:开机自动把CentOS7光盘挂载到 /repo/cos7dvd
–确保Linux主机已经连接CentOS7光盘
–确保挂载点目录已经准备好
[root@A ~]# mkdir -p /repo/cos7dvd 【创建挂载点目录】
[root@A ~]# vim /etc/fstab 【修改开机挂载配置文件】
.. ..
/dev/cdrom /repo/cos7dvd iso9660 defaults 0 0
[root@A ~]#ls /repo/cos7dvd 【挂载点目录下为空】
[root@A ~]# mount -a 【检查并挂载设备//检查开机挂载配置】
[root@A ~]# ls /repo/cos7dvd 【挂载点下可看到光盘文档】
[root@A ~]# reboot 【重启系统】
[root@A ~]# ls /repo/cos7dvd 【再次检查结果】
