XHCI注册过程和设备接入识别
- 2. XHCI host设备初始化
- 2 `xhci_pci_init`
- 2. `xhci_init_driver`
- 3. `pci_register_driver`
- 4. 设备接入和识别过程
- 4.1 函数调用流程
- 4.2 关键函数介绍
- 4.2.1 port_event
- 4.2.1.1 hub_port_connect_change
- 4.2.1.1.1 hub_port_connect
- 4.2.1.1.1 hub_port_init
- 4.2.1.1.2 `usb_new_device`
- 4.2.1.1.2.1 枚举设备:usb_enumerate_device
- 4.2.1.1.2.2 获取配置信息:usb_get_configuration
- 4.2.1.1.2.3 解析配置信息:usb_parse_configuration
- 4.2.1.1.2.4 解析接口信息:usb_parse_interface
- 4.2.1.1.2.5 解析端点:usb_parse_endpoint
- 4.2.1.1.3 输出主机控制器信息:announce_device
- 4.2.1.1.4 `device_add`
- 4.2.1.1.4.1 `bus_probe_device`
- 4.2.1.1.4.2 `device_initial_probe`
- 4.2.1.1.4.3 `__device_attach`
- 4.2.1.1.4.4 `bus_for_each_drv`
- 4.2.1.1.4.5 `__device_attach_driver`
- 4.2.1.1.4.6 `driver_match_device()`
- 4.2.1.1.4.7 `usb_new_device()`--`usb_device_match()`调用流程
- 4.2.1.1.4.8 usb_bus_type 中的 usb_device_match
- 4.2.1.1.4.9 usb_probe_device
- 4.2.1.1.4.10 generic_probe
- 4.2.1.1.4.11 usb_set_configuration
- 4.2.1.1.4.12 usb_bus_type 中的 usb_device_match
- 参考
- 这里选择PCI方式的xHCI, 即挂接在PCI总线的xHCI设备PCI-xHCI,另外对于龙芯平台,所有的USB均是通过PCI总线连接到7A桥片上后通过桥片进行控制的。
- 对于PCI-xHCI而言,既然是PCI设备,那么就需要注册PCI驱动。
- 这里我们不讨论PCI相关的代码。
2. XHCI host设备初始化
总体流程图
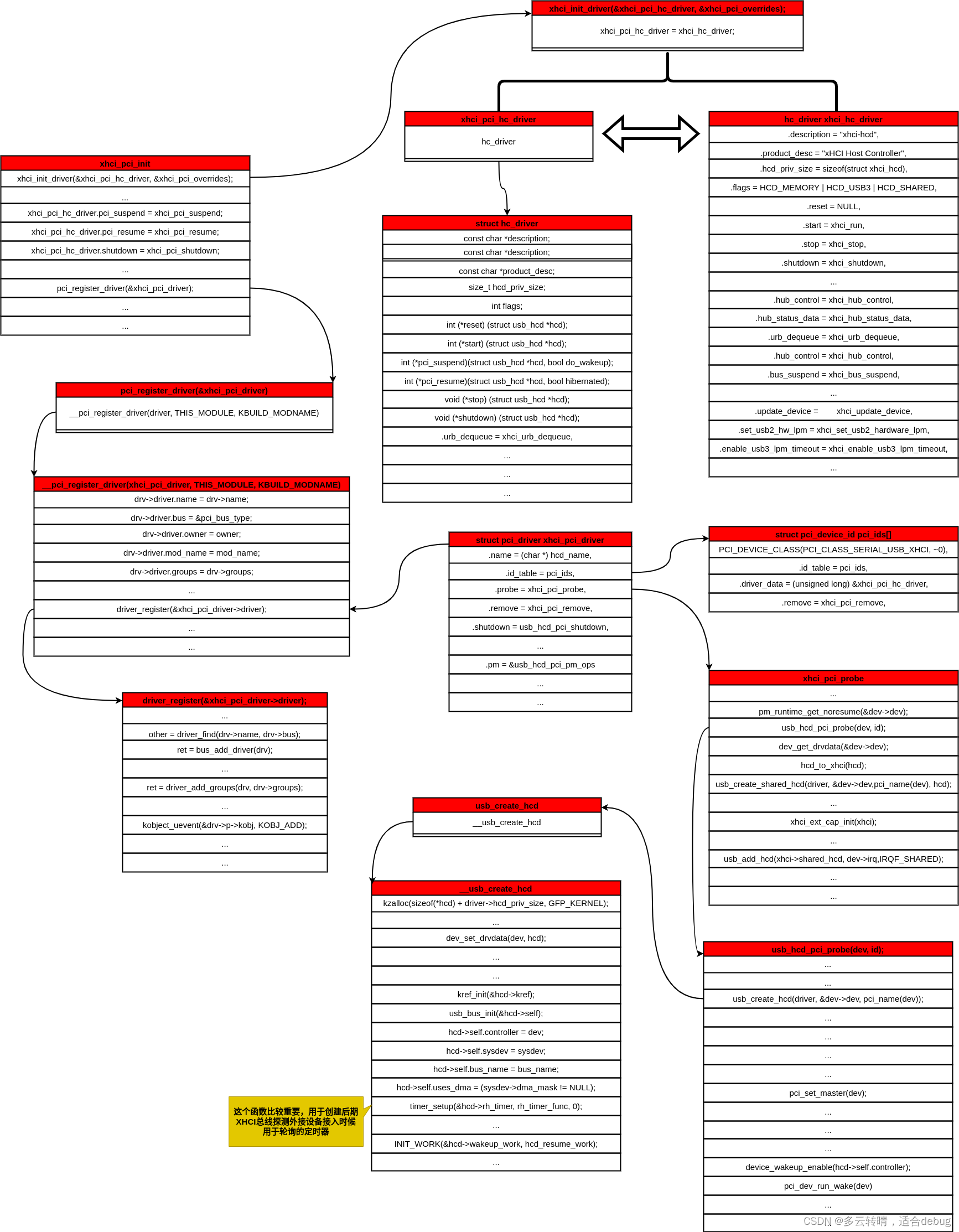
2 xhci_pci_init
位于文件drivers/usb/host/xhci-pci.c中
static int __init xhci_pci_init(void)
{
xhci_init_driver(&xhci_pci_hc_driver, &xhci_pci_overrides);
#ifdef CONFIG_PM
xhci_pci_hc_driver.pci_suspend = xhci_pci_suspend;
xhci_pci_hc_driver.pci_resume = xhci_pci_resume;
xhci_pci_hc_driver.shutdown = xhci_pci_shutdown;
#endif
return pci_register_driver(&xhci_pci_driver);
}
module_init(xhci_pci_init);
xhci_pci_init函数主要是初始化 xhci_pci_hc_driver ,注册 xhci_pci_driver。
2. xhci_init_driver
drivers/usb/host/xhci.c
结合xhci_pci_init() 函数中的xhci_init_driver(&xhci_pci_hc_driver, &xhci_pci_overrides);可知xhci_init_driver的作用为:初始化全局变量 xhci_pci_hc_driver 为 xhci_hc_driver。
两者都是struct hc_driver类型,xhci_pci_hc_driver在drivers/usb/host/xhci-pci.c中定义,是真正起作用的xHCI驱动,但它在定义的时候没有进行任何成员的初始化:
static struct hc_driver __read_mostly xhci_pci_hc_driver;
2.1 struct hc_driver
struct hc_driver {
const char *description; /* "ehci-hcd" etc */
const char *product_desc; /* product/vendor string */
size_t hcd_priv_size; /* size of private data */
/* irq handler */
irqreturn_t (*irq) (struct usb_hcd *hcd);
int flags;
...
/* called to init HCD and root hub */
int (*reset) (struct usb_hcd *hcd);
int (*start) (struct usb_hcd *hcd);
/* NOTE: these suspend/resume calls relate to the HC as
* a whole, not just the root hub; they're for PCI bus glue.
*/
/* called after suspending the hub, before entering D3 etc */
int (*pci_suspend)(struct usb_hcd *hcd, bool do_wakeup);
/* called after entering D0 (etc), before resuming the hub */
int (*pci_resume)(struct usb_hcd *hcd, bool hibernated);
/* cleanly make HCD stop writing memory and doing I/O */
void (*stop) (struct usb_hcd *hcd);
/* shutdown HCD */
void (*shutdown) (struct usb_hcd *hcd);
/* return current frame number */
int (*get_frame_number) (struct usb_hcd *hcd);
/* manage i/o requests, device state */
int (*urb_enqueue)(struct usb_hcd *hcd,
struct urb *urb, gfp_t mem_flags);
int (*urb_dequeue)(struct usb_hcd *hcd,
struct urb *urb, int status);
/*
* (optional) these hooks allow an HCD to override the default DMA
* mapping and unmapping routines. In general, they shouldn't be
* necessary unless the host controller has special DMA requirements,
* such as alignment contraints. If these are not specified, the
* general usb_hcd_(un)?map_urb_for_dma functions will be used instead
* (and it may be a good idea to call these functions in your HCD
* implementation)
*/
int (*map_urb_for_dma)(struct usb_hcd *hcd, struct urb *urb,
gfp_t mem_flags);
void (*unmap_urb_for_dma)(struct usb_hcd *hcd, struct urb *urb);
/* hw synch, freeing endpoint resources that urb_dequeue can't */
void (*endpoint_disable)(struct usb_hcd *hcd,
struct usb_host_endpoint *ep);
/* (optional) reset any endpoint state such as sequence number
and current window */
void (*endpoint_reset)(struct usb_hcd *hcd,
struct usb_host_endpoint *ep);
/* root hub support */
int (*hub_status_data) (struct usb_hcd *hcd, char *buf);
int (*hub_control) (struct usb_hcd *hcd,
u16 typeReq, u16 wValue, u16 wIndex,
char *buf, u16 wLength);
int (*bus_suspend)(struct usb_hcd *);
int (*bus_resume)(struct usb_hcd *);
int (*start_port_reset)(struct usb_hcd *, unsigned port_num);
unsigned long (*get_resuming_ports)(struct usb_hcd *);
/* force handover of high-speed port to full-speed companion */
void (*relinquish_port)(struct usb_hcd *, int);
/* has a port been handed over to a companion? */
int (*port_handed_over)(struct usb_hcd *, int);
/* CLEAR_TT_BUFFER completion callback */
void (*clear_tt_buffer_complete)(struct usb_hcd *,
struct usb_host_endpoint *);
/* xHCI specific functions */
/* Called by usb_alloc_dev to alloc HC device structures */
int (*alloc_dev)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *);
/* Called by usb_disconnect to free HC device structures */
void (*free_dev)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *);
/* Change a group of bulk endpoints to support multiple stream IDs */
int (*alloc_streams)(struct usb_hcd *hcd, struct usb_device *udev,
struct usb_host_endpoint **eps, unsigned int num_eps,
unsigned int num_streams, gfp_t mem_flags);
/* Reverts a group of bulk endpoints back to not using stream IDs.
* Can fail if we run out of memory.
*/
int (*free_streams)(struct usb_hcd *hcd, struct usb_device *udev,
struct usb_host_endpoint **eps, unsigned int num_eps,
gfp_t mem_flags);
/* Bandwidth computation functions */
/* Note that add_endpoint() can only be called once per endpoint before
* check_bandwidth() or reset_bandwidth() must be called.
* drop_endpoint() can only be called once per endpoint also.
* A call to xhci_drop_endpoint() followed by a call to
* xhci_add_endpoint() will add the endpoint to the schedule with
* possibly new parameters denoted by a different endpoint descriptor
* in usb_host_endpoint. A call to xhci_add_endpoint() followed by a
* call to xhci_drop_endpoint() is not allowed.
*/
/* Allocate endpoint resources and add them to a new schedule */
int (*add_endpoint)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *,
struct usb_host_endpoint *);
/* Drop an endpoint from a new schedule */
int (*drop_endpoint)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *,
struct usb_host_endpoint *);
/* Check that a new hardware configuration, set using
* endpoint_enable and endpoint_disable, does not exceed bus
* bandwidth. This must be called before any set configuration
* or set interface requests are sent to the device.
*/
int (*check_bandwidth)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *);
/* Reset the device schedule to the last known good schedule,
* which was set from a previous successful call to
* check_bandwidth(). This reverts any add_endpoint() and
* drop_endpoint() calls since that last successful call.
* Used for when a check_bandwidth() call fails due to resource
* or bandwidth constraints.
*/
void (*reset_bandwidth)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *);
/* Returns the hardware-chosen device address */
int (*address_device)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *udev);
/* prepares the hardware to send commands to the device */
int (*enable_device)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *udev);
/* Notifies the HCD after a hub descriptor is fetched.
* Will block.
*/
int (*update_hub_device)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *hdev,
struct usb_tt *tt, gfp_t mem_flags);
int (*reset_device)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *);
/* Notifies the HCD after a device is connected and its
* address is set
*/
int (*update_device)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *);
int (*set_usb2_hw_lpm)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *, int);
/* USB 3.0 Link Power Management */
/* Returns the USB3 hub-encoded value for the U1/U2 timeout. */
int (*enable_usb3_lpm_timeout)(struct usb_hcd *,
struct usb_device *, enum usb3_link_state state);
/* The xHCI host controller can still fail the command to
* disable the LPM timeouts, so this can return an error code.
*/
int (*disable_usb3_lpm_timeout)(struct usb_hcd *,
struct usb_device *, enum usb3_link_state state);
int (*find_raw_port_number)(struct usb_hcd *, int);
/* Call for power on/off the port if necessary */
int (*port_power)(struct usb_hcd *hcd, int portnum, bool enable);
};
2.2 static const struct hc_driver xhci_hc_driver
static const struct hc_driver xhci_hc_driver = {
.description = "xhci-hcd",
.product_desc = "xHCI Host Controller",
.hcd_priv_size = sizeof(struct xhci_hcd),
/*
* generic hardware linkage
*/
.irq = xhci_irq,
.flags = HCD_MEMORY | HCD_USB3 | HCD_SHARED,
/*
* basic lifecycle operations
*/
.reset = NULL, /* set in xhci_init_driver() */
.start = xhci_run,
.stop = xhci_stop,
.shutdown = xhci_shutdown,
/*
* managing i/o requests and associated device resources
*/
.urb_enqueue = xhci_urb_enqueue,
.urb_dequeue = xhci_urb_dequeue,
.alloc_dev = xhci_alloc_dev,
.free_dev = xhci_free_dev,
.alloc_streams = xhci_alloc_streams,
.free_streams = xhci_free_streams,
.add_endpoint = xhci_add_endpoint,
.drop_endpoint = xhci_drop_endpoint,
.endpoint_reset = xhci_endpoint_reset,
.check_bandwidth = xhci_check_bandwidth,
.reset_bandwidth = xhci_reset_bandwidth,
.address_device = xhci_address_device,
.enable_device = xhci_enable_device,
.update_hub_device = xhci_update_hub_device,
.reset_device = xhci_discover_or_reset_device,
/*
* scheduling support
*/
.get_frame_number = xhci_get_frame,
/*
* root hub support
*/
.hub_control = xhci_hub_control,
.hub_status_data = xhci_hub_status_data,
.bus_suspend = xhci_bus_suspend,
.bus_resume = xhci_bus_resume,
.get_resuming_ports = xhci_get_resuming_ports,
/*
* call back when device connected and addressed
*/
.update_device = xhci_update_device,
.set_usb2_hw_lpm = xhci_set_usb2_hardware_lpm,
.enable_usb3_lpm_timeout = xhci_enable_usb3_lpm_timeout,
.disable_usb3_lpm_timeout = xhci_disable_usb3_lpm_timeout,
.find_raw_port_number = xhci_find_raw_port_number,
};
2.3 xhci_init_driver
void xhci_init_driver(struct hc_driver *drv,
const struct xhci_driver_overrides *over)
{
BUG_ON(!over);
/* Copy the generic table to drv then apply the overrides */
*drv = xhci_hc_driver;
if (over) {
drv->hcd_priv_size += over->extra_priv_size;
if (over->reset)
drv->reset = over->reset;
if (over->start)
drv->start = over->start;
}
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(xhci_init_driver);
xhci_init_driver函数将xhci_hc_driver的值赋给xhci_pci_hc_driver后,前者也就退下了舞台。
3. pci_register_driver
xhci_pci_init调用pci_register_driver,将xhci_pci_driver注册为PCI设备驱动。
#define pci_register_driver(driver) \
__pci_register_driver(driver, THIS_MODULE, KBUILD_MODNAME)
drivers/pci/pci-driver.c
/**
* __pci_register_driver - register a new pci driver
* @drv: the driver structure to register
* @owner: owner module of drv
* @mod_name: module name string
*
* Adds the driver structure to the list of registered drivers.
* Returns a negative value on error, otherwise 0.
* If no error occurred, the driver remains registered even if
* no device was claimed during registration.
*/
int __pci_register_driver(struct pci_driver *drv, struct module *owner,
const char *mod_name)
{
/* initialize common driver fields */
drv->driver.name = drv->name;
drv->driver.bus = &pci_bus_type;
drv->driver.owner = owner;
drv->driver.mod_name = mod_name;
drv->driver.groups = drv->groups;
...
/* register with core */
return driver_register(&drv->driver);//**此时注册的drv->name:xhci_hcd, mod_name:xhci_pci**
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__pci_register_driver);
xhci_pci_driver是xHCI控制器作为PCI设备对应的驱动,符合PCI设备驱动的标准类型struct pci_driver,在drivers/usb/host/xhci-pci.c中静态定义并初始化:
/* pci driver glue; this is a "new style" PCI driver module */
static struct pci_driver xhci_pci_driver = {
.name = (char *) hcd_name,
.id_table = pci_ids,
.probe = xhci_pci_probe,
.remove = xhci_pci_remove,
/* suspend and resume implemented later */
.shutdown = usb_hcd_pci_shutdown,
#ifdef CONFIG_PM
.driver = {
.pm = &usb_hcd_pci_pm_ops
},
#endif
};
其中有两个成员需要重点关注,一个是id_table,一个是probe。id_table包含了驱动支持的PCI设备类型,PCI总线就是靠它判断驱动和设备能否配对。这里的id_table成员设置为pci_ids,它也是静态定义的全局变量:
/* PCI driver selection metadata; PCI hotplugging uses this */
static const struct pci_device_id pci_ids[] = { {
/* handle any USB 3.0 xHCI controller */
PCI_DEVICE_CLASS(PCI_CLASS_SERIAL_USB_XHCI, ~0),
.driver_data = (unsigned long) &xhci_pci_hc_driver,
},
{ /* end: all zeroes */ }
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(pci, pci_ids);
注意pci_ids中唯一一个元素的driver_data成员指向刚才在xhci_pci_init中完成初始化的xhci_pci_hc_driver变量,这就将作为PCI设备驱动的xhci_pci_driver和作为USB主机控制器设备驱动xhci_pci_hc_driver联系了起来。
注意:
很多教程中说的是:当pci_register_driver调用完成后,xhci_pci_driver就被加入了PCI总线的驱动列表,xhci_pci_probe在注册时候也会被调用,当总线检测到与之匹配的设备,即xHCI控制器的时候,会调用驱动的probe成员函数,而xhci_pci_driver.probe在初始化时被设置为xhci_pci_probe函数。
但是后期通过在龙芯平台上验证并非这样的流程,当pci_register_driver调用完成后,xhci_pci_driver就被加入了PCI总线的驱动列表,xhci_pci_probe在注册时候也会被调用,这个流程是正确的,但是匹配新接入的设备的时候调用xhci_pci_probe函数是错误的,龙芯平台并没有走着一条调用流程,而是另外一个流程,下面会详细介绍。
4. 设备接入和识别过程
USB接入识别大致过程:
当识别出有USB设备插入后,linux内的USB总线驱动程序发出命令至该设备,与设备对话,并询问设备信息(描述符),设备收到请求后,回复设备描述符给总线驱动程序。且总线驱动程序会为该设备分配一个地址,如上地址为2,当后期访问某个USB设备时,均会通过这个地址编号,当新接入的USB设备被第一次访问时,以地址0来访问。当USB总线驱动程序识别出设备后,会为其找到该USB设备驱动程序,如键盘,鼠标,U盘。
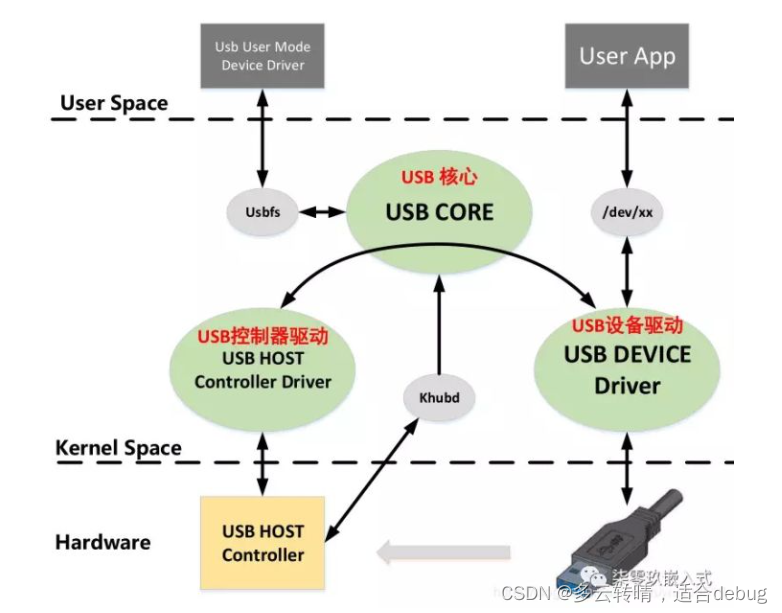
主要包含三个部分:USB控制器驱动,USB核心,USB设备驱动。如上图khubd是USB守护进程,当USB设备插入的时候,守护进程监测到,USB主机控制器就会产生一个hub_irq中断,控制器调用hub的探测函数,来解析设备信息。
4.1 函数调用流程
定时轮询方式,当定时时间到了运行定时器程时指定的定时器rh_timer的function函数rh_timer_func。
整体函数调用如下:
->rh_timer_func
->usb_hcd_poll_rh_status //hcd.c
->hcd->driver->hub_status_data(hcd, buffer)
->usb_hcd_unlink_urb_from_ep(hcd, urb);
->usb_hcd_giveback_urb(hcd, urb, 0)
->usb_giveback_urb_bh(); //tasklet_hi_schedule(&bh->bh);
->__usb_hcd_giveback_urb(urb);
->urb->complete(urb); //hub_irq
->hub_irq //hub.c usb_fill_int_urb(hub->urb, hdev, pipe, *hub->buffer, maxp, hub_irq,----拔出时候有提示
->kick_hub_wq(hub);
->hub_event //INIT_WORK(&hub->events, hub_event);
->port_event(hub, i);
->hub_port_connect_change
->hub_port_connect
->hub_port_init
->usb_new_device(udev);
->usb_enumerate_device(udev);//开始枚举
->device_add(&udev->dev);//枚举完毕后加载设备驱动
Note:
使用定时器查询的主要原因是USB通信过程均为主从结构,USB主机发起通信请求,设备进行数据回复,USB设备不具备主动向主机通信的能力,即USB没有中断USB控制器的能力,所以当USB设备接入之后,获取USB输入的信息是无法通过中断方式来获取,只能通过定时器定时轮训获取。当USB设备未插入时,定时器rh_timer会停止,直到USB插入之后,再次开启定时查询USB设备输入的信息。
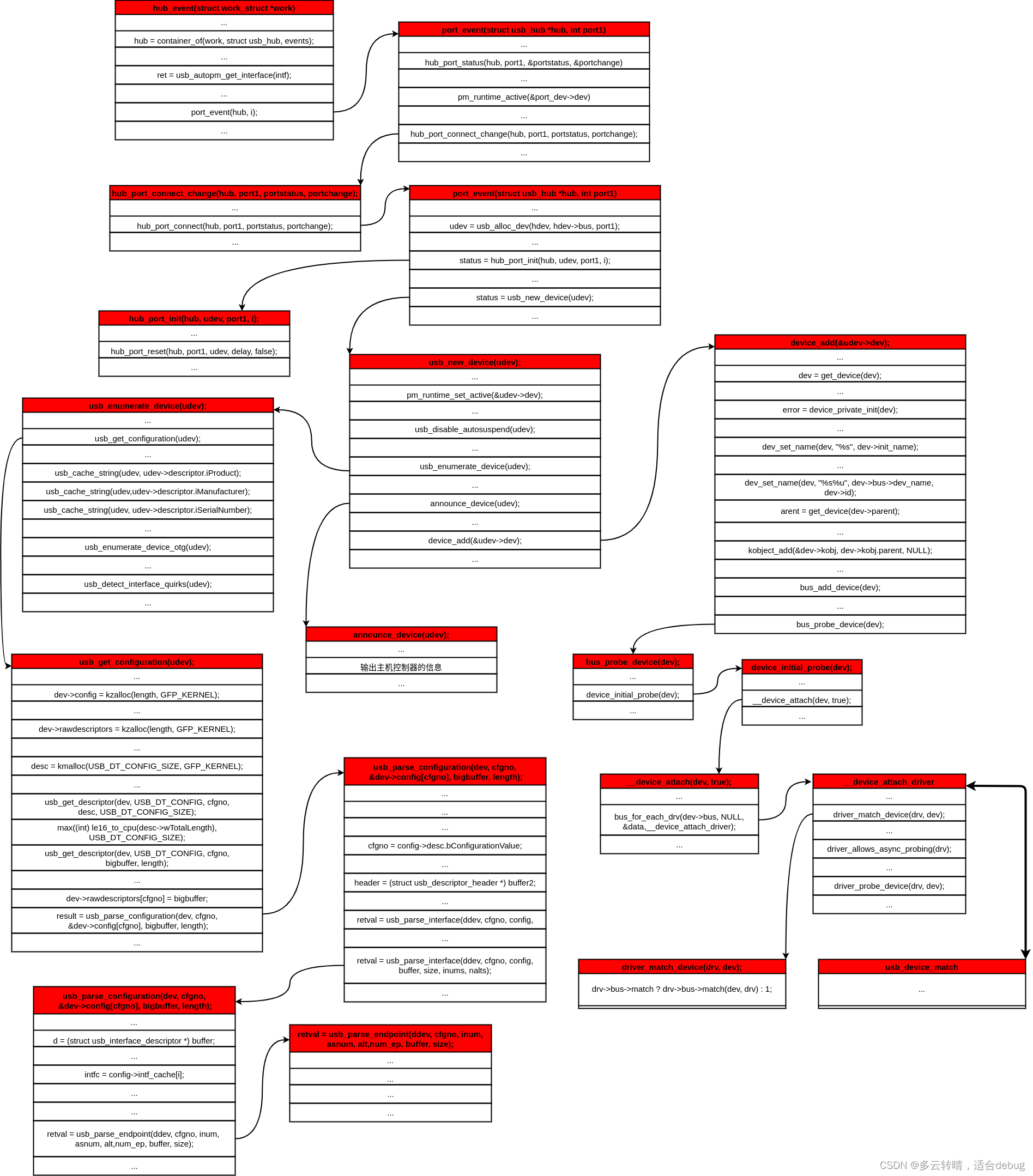
4.2 关键函数介绍
4.2.1 port_event
static void port_event(struct usb_hub *hub, int port1)
__must_hold(&port_dev->status_lock)
{
int connect_change;
struct usb_port *port_dev = hub->ports[port1 - 1];
struct usb_device *udev = port_dev->child;
struct usb_device *hdev = hub->hdev;
u16 portstatus, portchange;
connect_change = test_bit(port1, hub->change_bits);
clear_bit(port1, hub->event_bits);
clear_bit(port1, hub->wakeup_bits);
if (hub_port_status(hub, port1, &portstatus, &portchange) < 0)
return;
...
if (!pm_runtime_active(&port_dev->dev))
return;
if (hub_handle_remote_wakeup(hub, port1, portstatus, portchange))
...
if (hub_port_warm_reset_required(hub, port1, portstatus)) {
...
}
if (connect_change)
hub_port_connect_change(hub, port1, portstatus, portchange);
}
4.2.1.1 hub_port_connect_change
函数位于:./drivers/usb/core/hub.c
/* Handle physical or logical connection change events.
* This routine is called when:
* a port connection-change occurs;
* a port enable-change occurs (often caused by EMI);
* usb_reset_and_verify_device() encounters changed descriptors (as from
* a firmware download)
* caller already locked the hub
*/
static void hub_port_connect_change(struct usb_hub *hub, int port1,
u16 portstatus, u16 portchange)
__must_hold(&port_dev->status_lock)
{
struct usb_port *port_dev = hub->ports[port1 - 1];
struct usb_device *udev = port_dev->child;
int status = -ENODEV;
...
clear_bit(port1, hub->change_bits);
...
hub_port_connect(hub, port1, portstatus, portchange);
...
}
4.2.1.1.1 hub_port_connect
static void hub_port_connect(struct usb_hub *hub, int port1, u16 portstatus,
u16 portchange)
{
int status = -ENODEV;
int i;
unsigned unit_load;
struct usb_device *hdev = hub->hdev;
struct usb_hcd *hcd = bus_to_hcd(hdev->bus);
struct usb_port *port_dev = hub->ports[port1 - 1];
struct usb_device *udev = port_dev->child;
static int unreliable_port = -1;
...
status = 0;
for (i = 0; i < SET_CONFIG_TRIES; i++) {
udev = usb_alloc_dev(hdev, hdev->bus, port1);
...
...
status = hub_port_init(hub, udev, port1, i);
usb_unlock_port(port_dev);
...
...
/* Run it through the hoops (find a driver, etc) */
if (!status) {
status = usb_new_device(udev);
...
}
...
status = hub_power_remaining(hub);
...
}
4.2.1.1.1 hub_port_init
/* Reset device, (re)assign address, get device descriptor.
* Device connection must be stable, no more debouncing needed.
* Returns device in USB_STATE_ADDRESS, except on error.
*
* If this is called for an already-existing device (as part of
* usb_reset_and_verify_device), the caller must own the device lock and
* the port lock. For a newly detected device that is not accessible
* through any global pointers, it's not necessary to lock the device,
* but it is still necessary to lock the port.
*/
static int
hub_port_init(struct usb_hub *hub, struct usb_device *udev, int port1,
int retry_counter)
{
struct usb_device *hdev = hub->hdev;
struct usb_hcd *hcd = bus_to_hcd(hdev->bus);
struct usb_port *port_dev = hub->ports[port1 - 1];
int retries, operations, retval, i;
unsigned delay = HUB_SHORT_RESET_TIME;
enum usb_device_speed oldspeed = udev->speed;
const char *speed;
int devnum = udev->devnum;
const char *driver_name;
...
/* Reset the device; full speed may morph to high speed */
/* FIXME a USB 2.0 device may morph into SuperSpeed on reset. */
retval = hub_port_reset(hub, port1, udev, delay, false);
...
...
...
}
4.2.1.1.2 usb_new_device
再后续时创建了一个新的usb设备,使用位于drivers/usb/core/hub.c中的usb_new_device函数
流程图
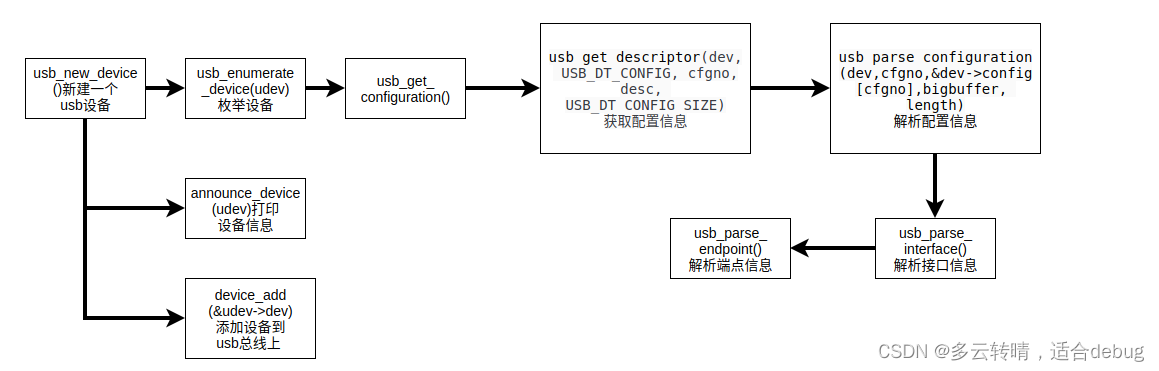
int usb_new_device(struct usb_device *udev)
{
int err;
...
/* Tell the runtime-PM framework the device is active */
pm_runtime_set_active(&udev->dev);
pm_runtime_get_noresume(&udev->dev);
pm_runtime_use_autosuspend(&udev->dev);
pm_runtime_enable(&udev->dev);
/* By default, forbid autosuspend for all devices. It will be
* allowed for hubs during binding.
*/
usb_disable_autosuspend(udev);
//枚举设备
err = usb_enumerate_device(udev); /* Read descriptors */
if (err < 0)
goto fail;
...
/* export the usbdev device-node for libusb */
udev->dev.devt = MKDEV(USB_DEVICE_MAJOR,
(((udev->bus->busnum-1) * 128) + (udev->devnum-1)));//设备号
/* Tell the world! */
announce_device(udev);//输出主机控制器信息
...
/* Register the device. The device driver is responsible
* for configuring the device and invoking the add-device
* notifier chain (used by usbfs and possibly others).
*/
err = device_add(&udev->dev);
...
...
}
这里主要分析设备枚举,是这里最核心的一个地方!!!
4.2.1.1.2.1 枚举设备:usb_enumerate_device
static int usb_enumerate_device(struct usb_device *udev)
{
int err;
if (udev->config == NULL) {
err = usb_get_configuration(udev); //获取配置信息
...
}
/* read the standard strings and cache them if present */
udev->product = usb_cache_string(udev, udev->descriptor.iProduct);//获取产品号
udev->manufacturer = usb_cache_string(udev,
udev->descriptor.iManufacturer);//制造商
udev->serial = usb_cache_string(udev, udev->descriptor.iSerialNumber);//序列号
err = usb_enumerate_device_otg(udev);
...
usb_detect_interface_quirks(udev);
return 0;
}
4.2.1.1.2.2 获取配置信息:usb_get_configuration
int usb_get_configuration(struct usb_device *dev)
{
struct device *ddev = &dev->dev;
int ncfg = dev->descriptor.bNumConfigurations; //usb配置个数
int result = 0;
unsigned int cfgno, length;
unsigned char *bigbuffer;
struct usb_config_descriptor *desc;
cfgno = 0;
result = -ENOMEM;
...
length = ncfg * sizeof(struct usb_host_config);
dev->config = kzalloc(length, GFP_KERNEL); //分配一个设备下的ncfg个config配置结构体
...
length = ncfg * sizeof(char *);
dev->rawdescriptors = kzalloc(length, GFP_KERNEL); //分配ncfg个char指针
...
desc = kmalloc(USB_DT_CONFIG_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL);
...
result = 0;
for (; cfgno < ncfg; cfgno++) {
/* We grab just the first descriptor so we know how long
* the whole configuration is */
result = usb_get_descriptor(dev, USB_DT_CONFIG, cfgno,
desc, USB_DT_CONFIG_SIZE); //由于无法知道配置的长度,这里使用一个小技巧,先读取配置USB_DT_CONFIG_SIZE个字节,从该长度内部可以获取配置下的接口长度,所以这里会读取两次,这是第一次!!!
...
length = max((int) le16_to_cpu(desc->wTotalLength), //获取当前配置的的总长度
USB_DT_CONFIG_SIZE);
/* Now that we know the length, get the whole thing */
bigbuffer = kmalloc(length, GFP_KERNEL);
...
//获取配置的所有长度信息,这里是第二次读取!!!
result = usb_get_descriptor(dev, USB_DT_CONFIG, cfgno,
bigbuffer, length);
...
dev->rawdescriptors[cfgno] = bigbuffer; //每一个指针指向一个配置
...
//解析配置信息
result = usb_parse_configuration(dev, cfgno,
&dev->config[cfgno], bigbuffer, length);
...
}
...
}
4.2.1.1.2.3 解析配置信息:usb_parse_configuration
static int usb_parse_configuration(struct usb_device *dev, int cfgidx,
struct usb_host_config *config, unsigned char *buffer, int size)
{
struct device *ddev = &dev->dev;
unsigned char *buffer0 = buffer;
int cfgno;
int nintf, nintf_orig;
int i, j, n;
struct usb_interface_cache *intfc;
unsigned char *buffer2;
int size2;
struct usb_descriptor_header *header;
int len, retval;
u8 inums[USB_MAXINTERFACES], nalts[USB_MAXINTERFACES];
unsigned iad_num = 0;
memcpy(&config->desc, buffer, USB_DT_CONFIG_SIZE); //拷贝当前配置信息到config->desc
...
cfgno = config->desc.bConfigurationValue; //当前配置编号值
//这里偏移buffer的目的是啥???不过下面又开始计算配置下的接口了!!!
//上面是以前的疑问,现在明白了,buffer += config->desc.bLength 表示跳过配置的内容,直接跳转到接口
buffer += config->desc.bLength; //偏移到接口
size -= config->desc.bLength; //减去配置的长度
nintf = nintf_orig = config->desc.bNumInterfaces; //接口个数
...
/* Go through the descriptors, checking their length and counting the
* number of altsettings for each interface */
n = 0;
for ((buffer2 = buffer, size2 = size); //遍历接口
size2 > 0;
(buffer2 += header->bLength, size2 -= header->bLength)) {
if (size2 < sizeof(struct usb_descriptor_header)) {
...
}
header = (struct usb_descriptor_header *) buffer2; //这里先获取描述符接口的长度和描述符的类型(这里类型为接口)两个字段
...
if (header->bDescriptorType == USB_DT_INTERFACE) { //是接口
...
d = (struct usb_interface_descriptor *) header; //上面通过两个字段确定了为接口,这里直接转换为接口描述符 struct usb_interface_descriptor
...
inum = d->bInterfaceNumber; //获取接口的编号
...
if (inum >= nintf_orig) //当前接口编号是否大于总得接口个数
...
/* Have we already encountered this interface?
* Count its altsettings */
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (inums[i] == inum) //确定之前是否已经统计了该接口
break;
}
if (i < n) { //
if (nalts[i] < 255)
++nalts[i]; //对当前接口编号相同的进行统计(初始化为1,在else if语句中)
} else if (n < USB_MAXINTERFACES) {
inums[n] = inum; //记录当前接口的编号到inums数组中
nalts[n] = 1; //初始化当前接口值为1
++n;
}
}
...
} /* for ((buffer2 = buffer, size2 = size); ...) */
size = buffer2 - buffer; //size=一个配置中所有接口描述符的长度
config->desc.wTotalLength = cpu_to_le16(buffer2 - buffer0); //config->desc.wTotalLength = 一个配置和接口描述符的总长度
...
/* Check for missing interface numbers */
for (i = 0; i < nintf; ++i) { //由于inums数组中存储的是随机接口编号,所以这里通过从小到大的顺序检测是否正常,否则输出调试警告
...
}
/* Allocate the usb_interface_caches and altsetting arrays */
for (i = 0; i < nintf; ++i) { //遍历接口
...
//sizeof(*intfc): 接口缓存的长度
//sizeof(struct usb_host_interface) * j: 表示一个主机控制的长度*接口个数
len = sizeof(*intfc) + sizeof(struct usb_host_interface) * j;
//表示一个接口的缓存(包括接口轮流, 因为存在多个相同的接口编号)
config->intf_cache[i] = intfc = kzalloc(len, GFP_KERNEL);
...
}
...
config->extra = buffer; //处理设备中要求的接口个数,之外的接口数据
i = find_next_descriptor(buffer, size, USB_DT_INTERFACE,
USB_DT_INTERFACE, &n);
...
/* Parse all the interface/altsetting descriptors */
while (size > 0) {
//解析接口数据
retval = usb_parse_interface(ddev, cfgno, config,
buffer, size, inums, nalts);
...
}
...
return 0;
}
4.2.1.1.2.4 解析接口信息:usb_parse_interface
static int usb_parse_interface(struct device *ddev, int cfgno,
struct usb_host_config *config, unsigned char *buffer, int size,
u8 inums[], u8 nalts[])
{
unsigned char *buffer0 = buffer;
struct usb_interface_descriptor *d;
int inum, asnum;
struct usb_interface_cache *intfc;
struct usb_host_interface *alt;
int i, n;
int len, retval;
int num_ep, num_ep_orig;
d = (struct usb_interface_descriptor *) buffer; //获取接口描述符信息
...
...
...
inum = d->bInterfaceNumber; //接口编号
for (i = 0; i < config->desc.bNumInterfaces; ++i) { //根据设备中获取的接口总数,遍历接口,匹配与当前inum接口编号相等的
if (inums[i] == inum) {
intfc = config->intf_cache[i]; //获取接口缓存信息
break;
}
}
...
memcpy(&alt->desc, d, USB_DT_INTERFACE_SIZE); //拷贝一个接口描述符
...
/* Allocate space for the right(?) number of endpoints */
num_ep = num_ep_orig = alt->desc.bNumEndpoints; //获取接口的端点个数
alt->desc.bNumEndpoints = 0; /* Use as a counter */
...
if (num_ep > 0) {
/* Can't allocate 0 bytes */
len = sizeof(struct usb_host_endpoint) * num_ep; //分配端点个数的空间
...
...
}
...
while (size > 0) {
...
//解析端点
retval = usb_parse_endpoint(ddev, cfgno, inum, asnum, alt,
num_ep, buffer, size);
...
}
...
}
4.2.1.1.2.5 解析端点:usb_parse_endpoint
static int usb_parse_endpoint(struct device *ddev, int cfgno, int inum,
int asnum, struct usb_host_interface *ifp, int num_ep,
unsigned char *buffer, int size)
{
unsigned char *buffer0 = buffer;
struct usb_endpoint_descriptor *d;
struct usb_host_endpoint *endpoint;
int n, i, j, retval;
d = (struct usb_endpoint_descriptor *) buffer; //获取端点描述符
buffer += d->bLength;
size -= d->bLength;
if (d->bLength >= USB_DT_ENDPOINT_AUDIO_SIZE)
n = USB_DT_ENDPOINT_AUDIO_SIZE;
else if (d->bLength >= USB_DT_ENDPOINT_SIZE)
n = USB_DT_ENDPOINT_SIZE;
else {
dev_warn(ddev, "config %d interface %d altsetting %d has an "
"invalid endpoint descriptor of length %d, skipping\n",
cfgno, inum, asnum, d->bLength);
goto skip_to_next_endpoint_or_interface_descriptor;
}
i = d->bEndpointAddress & ~USB_ENDPOINT_DIR_MASK;
if (i >= 16 || i == 0) {
dev_warn(ddev, "config %d interface %d altsetting %d has an "
"invalid endpoint with address 0x%X, skipping\n",
cfgno, inum, asnum, d->bEndpointAddress);
goto skip_to_next_endpoint_or_interface_descriptor;
}
/* Only store as many endpoints as we have room for */
if (ifp->desc.bNumEndpoints >= num_ep)
goto skip_to_next_endpoint_or_interface_descriptor;
endpoint = &ifp->endpoint[ifp->desc.bNumEndpoints];
++ifp->desc.bNumEndpoints;
memcpy(&endpoint->desc, d, n);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&endpoint->urb_list);
/* Fix up bInterval values outside the legal range. Use 32 ms if no
* proper value can be guessed. */
//根据不同速率的usb,计算时间
i = 0; /* i = min, j = max, n = default */
j = 255;
if (usb_endpoint_xfer_int(d)) {
i = 1;
switch (to_usb_device(ddev)->speed) {
case USB_SPEED_SUPER:
case USB_SPEED_HIGH:
/* Many device manufacturers are using full-speed
* bInterval values in high-speed interrupt endpoint
* descriptors. Try to fix those and fall back to a
* 32 ms default value otherwise. */
n = fls(d->bInterval*8);
if (n == 0)
n = 9; /* 32 ms = 2^(9-1) uframes */
j = 16;
break;
default: /* USB_SPEED_FULL or _LOW */
/* For low-speed, 10 ms is the official minimum.
* But some "overclocked" devices might want faster
* polling so we'll allow it. */
n = 32;
break;
}
} else if (usb_endpoint_xfer_isoc(d)) {
i = 1;
j = 16;
switch (to_usb_device(ddev)->speed) {
case USB_SPEED_HIGH:
n = 9; /* 32 ms = 2^(9-1) uframes */
break;
default: /* USB_SPEED_FULL */
n = 6; /* 32 ms = 2^(6-1) frames */
break;
}
}
if (d->bInterval < i || d->bInterval > j) {
dev_warn(ddev, "config %d interface %d altsetting %d "
"endpoint 0x%X has an invalid bInterval %d, "
"changing to %d\n",
cfgno, inum, asnum,
d->bEndpointAddress, d->bInterval, n);
endpoint->desc.bInterval = n;
}
/* Some buggy low-speed devices have Bulk endpoints, which is
* explicitly forbidden by the USB spec. In an attempt to make
* them usable, we will try treating them as Interrupt endpoints.
*/
if (to_usb_device(ddev)->speed == USB_SPEED_LOW &&
usb_endpoint_xfer_bulk(d)) {
dev_warn(ddev, "config %d interface %d altsetting %d "
"endpoint 0x%X is Bulk; changing to Interrupt\n",
cfgno, inum, asnum, d->bEndpointAddress);
endpoint->desc.bmAttributes = USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_INT;
endpoint->desc.bInterval = 1;
if (usb_endpoint_maxp(&endpoint->desc) > 8)
endpoint->desc.wMaxPacketSize = cpu_to_le16(8); //低速设备端点字节为8个
}
/*
* Some buggy high speed devices have bulk endpoints using
* maxpacket sizes larger than 64 under full-speed mode.
* Full speed HCDs may not
* be able to handle that particular bug, so let's modify
* the maxpacket size to make it work.
*/
if (to_usb_device(ddev)->speed == USB_SPEED_FULL
&& usb_endpoint_xfer_bulk(d)) {
if (usb_endpoint_maxp(&endpoint->desc) > 64)
endpoint->desc.wMaxPacketSize = cpu_to_le16(64); //全速设备端点字节为64个
}
/*
* Some buggy high speed devices have bulk endpoints using
* maxpacket sizes other than 512. High speed HCDs may not
* be able to handle that particular bug, so let's warn...
*/
if (to_usb_device(ddev)->speed == USB_SPEED_HIGH
&& usb_endpoint_xfer_bulk(d)) {
unsigned maxp;
maxp = usb_endpoint_maxp(&endpoint->desc) & 0x07ff; //高速设备端点字节数。。。
if (maxp != 512)
dev_warn(ddev, "config %d interface %d altsetting %d "
"bulk endpoint 0x%X has invalid maxpacket %d\n",
cfgno, inum, asnum, d->bEndpointAddress,
maxp);
}
/* Parse a possible SuperSpeed endpoint companion descriptor */
if (to_usb_device(ddev)->speed == USB_SPEED_SUPER)
usb_parse_ss_endpoint_companion(ddev, cfgno,
inum, asnum, endpoint, buffer, size);
/* Skip over any Class Specific or Vendor Specific descriptors;
* find the next endpoint or interface descriptor */
endpoint->extra = buffer;
i = find_next_descriptor(buffer, size, USB_DT_ENDPOINT,
USB_DT_INTERFACE, &n);
endpoint->extralen = i;
retval = buffer - buffer0 + i;
if (n > 0)
dev_dbg(ddev, "skipped %d descriptor%s after %s\n",
n, plural(n), "endpoint");
return retval;
skip_to_next_endpoint_or_interface_descriptor:
i = find_next_descriptor(buffer, size, USB_DT_ENDPOINT,
USB_DT_INTERFACE, NULL);
return buffer - buffer0 + i;
}
端点部分主要工作是,根据不同速率的usb,传输不同的字节数,以及主机查询端点的间隔时间。至此分析完了枚举一个usb主机控制器的过程:设备–>N个配置–>N个接口–>N个端点,最后通过如下函数输出控制器的功能信息:
4.2.1.1.3 输出主机控制器信息:announce_device
static void announce_device(struct usb_device *udev)
{
dev_info(&udev->dev, "New USB device found, idVendor=%04x, idProduct=%04x\n",
le16_to_cpu(udev->descriptor.idVendor),
le16_to_cpu(udev->descriptor.idProduct));
dev_info(&udev->dev,
"New USB device strings: Mfr=%d, Product=%d, SerialNumber=%d\n",
udev->descriptor.iManufacturer,
udev->descriptor.iProduct,
udev->descriptor.iSerialNumber);
show_string(udev, "Product", udev->product);
show_string(udev, "Manufacturer", udev->manufacturer);
show_string(udev, "SerialNumber", udev->serial);
}
系统启动时输出上述信息:
usb usb1: New USB device found, idVendor=..., idProduct=...
usb usb1: New USB device strings: Mfr=n, Product=n, SerialNumber=n
usb usb1: Product: ...
usb usb1: Manufacturer: ...
usb usb1: SerialNumber: ...
总结
本文开始通过platform总线完成xhci设备和驱动的匹配调用探测函数xhci_pci_probe(),然后在函数usb_add_hcd内部完成主机控制器的寄存器资源分配,然后注册一个hcd主机控制器(包括是否使用DMA池),然后增加主机控制器到usb总线上,然后注册一个根hub,期间包括最重要的部分,即设备枚举,在枚举的过程,先获取设备,通过设备获取接口,因接口长度未定,所以分两次读取接口信息,即第一次读取固定长度的接口信息,第二次根据第一次的描述符信息里的长度再读取整个接口信息,最后根据接口信息解析端点,最后将该主机控制器的根hub注册到usb总线上。
4.2.1.1.4 device_add
drivers/bash/core.c
int device_add(struct device *dev)
{
struct device *parent;
struct kobject *kobj;
struct class_interface *class_intf;
int error = -EINVAL;
struct kobject *glue_dir = NULL;
dev = get_device(dev);//增加该设备的引用计数
...
if (!dev->p) {
error = device_private_init(dev);//初始化设备的私有成员
...
}
...
if (dev->init_name) {
dev_set_name(dev, "%s", dev->init_name);//初始化设备内部的kobject的名字
...
}
/* subsystems can specify simple device enumeration */
if (!dev_name(dev) && dev->bus && dev->bus->dev_name)
dev_set_name(dev, "%s%u", dev->bus->dev_name, dev->id);//使用bus以及设备id来初始化设备内部kobject名字
if (!dev_name(dev)) {//获得设备的名字
...
}
...
parent = get_device(dev->parent);//增加设备父设备并增加父设备引用计数
kobj = get_device_parent(dev, parent);
...
if (kobj)
dev->kobj.parent = kobj;//在kobject层实现设备父子关系
...
error = kobject_add(&dev->kobj, dev->kobj.parent, NULL);//将设备加入到kobject模型中,创建sys相关目录
...
error = device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_uevent);//创建sys目录下设备的uevent属性文件,通过它可以查看设备的uevent事件
...
error = device_add_attrs(dev);//创建sys目录下设备的设备号属性,即major和minor
...
error = bus_add_device(dev);//将设备加入到管理它的bus总线的设备连表上
...
error = dpm_sysfs_add(dev);//电源管理相关
...
if (MAJOR(dev->devt)) {
error = device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_dev);//创建sys目录下设备的设备号属性,即major和minor
...
...
}
...
if (dev->bus)
blocking_notifier_call_chain(&dev->bus->p->bus_notifier,
BUS_NOTIFY_ADD_DEVICE, dev);//通知注册监听该总线的设备,有新设备加入
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);//产生一个内核uevent事件,该事件可以被内核以及应用层捕获,属于linux设备模型中热插拔机制
bus_probe_device(dev);//------------开始寻找设备所对应的驱动------------
if (parent)
klist_add_tail(&dev->p->knode_parent,
&parent->p->klist_children);//建立设备与总线间的父子关系
if (dev->class) {//如果设备的属于某个设备类,比如Mass storage,HID等等
mutex_lock(&dev->class->p->mutex);
/* tie the class to the device */
klist_add_tail(&dev->knode_class,
&dev->class->p->klist_devices);//将设备挂接在其设备类上面
/* notify any interfaces that the device is here */
list_for_each_entry(class_intf,
&dev->class->p->interfaces, node)
if (class_intf->add_dev)
class_intf->add_dev(dev, class_intf);//通知有新设备加入
mutex_unlock(&dev->class->p->mutex);
}
...
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(device_add);
device_add函数会出发总线的通知链发送通知,最终会调用总线的match方法。usb设备和驱动一旦match,则会调用驱动的drvwrap.driver.probe方法:
?* 若是设备则通过driver.c的usb_register_device_driver函数调用usb_probe_device方法
?* 若是接口则通过driver.c的usb_register_driver函数调用usb_probe_interface方法
?* 假设是U盘接入,则调用mass_storage驱动的probe,并在probe中使用usb_alloc_urb分配urb,最后usb_submit_urb提交urb。
4.2.1.1.4.1 bus_probe_device
开始寻找设备所对应的驱动
/**
* bus_probe_device - probe drivers for a new device
* @dev: device to probe
*
* - Automatically probe for a driver if the bus allows it.
*/
//为设备找到一个驱动
void bus_probe_device(struct device *dev)
{
struct bus_type *bus = dev->bus;//获得设备的隶属的总线,该值在设备初始化时设置
struct subsys_interface *sif;
if (!bus)
return;
if (bus->p->drivers_autoprobe)
device_initial_probe(dev);//-------尝试为该设备找一个driver-------
mutex_lock(&bus->p->mutex);
list_for_each_entry(sif, &bus->p->interfaces, node)
if (sif->add_dev)
sif->add_dev(dev, sif);
mutex_unlock(&bus->p->mutex);
}
4.2.1.1.4.2 device_initial_probe
void device_initial_probe(struct device *dev)
{
__device_attach(dev, true);
}
通过device_add就注册到了USB 总线klist_devices中, 然后调用到driver_match_device()和driver_probe_device()函数
4.2.1.1.4.3 __device_attach
static int __device_attach(struct device *dev, bool allow_async)
{
int ret = 0;
...
if (dev->driver) {
if (device_is_bound(dev)) {
...
}
ret = device_bind_driver(dev);
...
} else {
struct device_attach_data data = {
.dev = dev,
.check_async = allow_async,
.want_async = false,
};
if (dev->parent)
pm_runtime_get_sync(dev->parent);
ret = bus_for_each_drv(dev->bus, NULL, &data,
__device_attach_driver);
...
}
...
}
4.2.1.1.4.4 bus_for_each_drv
从总线上已注册的所有驱动中找出匹配的驱动程序: bus_for_each_drv
int bus_for_each_drv(struct bus_type *bus, struct device_driver *start,
void *data, int (*fn)(struct device_driver *, void *))
{
struct klist_iter i;
struct device_driver *drv;
int error = 0;
if (!bus)
return -EINVAL;
klist_iter_init_node(&bus->p->klist_drivers, &i,
start ? &start->p->knode_bus : NULL);
while ((drv = next_driver(&i)) && !error)
error = fn(drv, data);
klist_iter_exit(&i);
return error;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(bus_for_each_drv);
4.2.1.1.4.5 __device_attach_driver
static int __device_attach_driver(struct device_driver *drv, void *_data)
{
struct device_attach_data *data = _data;
struct device *dev = data->dev;
bool async_allowed;
int ret;
ret = driver_match_device(drv, dev);
...
async_allowed = driver_allows_async_probing(drv);
...
return driver_probe_device(drv, dev);
}
4.2.1.1.4.6 driver_match_device()
static inline int driver_match_device(struct device_driver *drv, struct device *dev)
{
return drv->bus->match ? drv->bus->match(dev, drv) : 1;//调用match函数,如果没用则默认返回1 -->usb_device_match(dev, drv)
}
4.2.1.1.4.7 usb_new_device()–usb_device_match()调用流程
usb_new_device() --> device_add() --> bus_probe_device(dev)-->device_initial_probe(dev)-->__device_attach(dev, true)-->bus_for_each_drv(...)-->__device_attach_driver(...)--> usb_device_match(dev, drv)
根据以上分析会调用usb_device_match(…)来匹配驱动。
因为driver_match_device(struct device_driver *drv, struct device *dev)函数中 device_driver类型的*drv中的bus是 bus_type类型,而bus_type结构体中的match函数是usb_device_match函数。
4.2.1.1.4.8 usb_bus_type 中的 usb_device_match
static int usb_device_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
/* devices and interfaces are handled separately */
//return container_of(drv, struct usbdrv_wrap, driver)->for_devices
if (is_usb_device(dev)) { //是否是usb设备
/* interface drivers never match devices */
//return container_of(drv, struct usbdrv_wrap, driver)->for_devices
if (!is_usb_device_driver(drv))
...
} else if (is_usb_interface(dev)) { //是否是usb接口
struct usb_interface *intf;
struct usb_driver *usb_drv;
const struct usb_device_id *id;
/* device drivers never match interfaces */
if (is_usb_device_driver(drv))
...
intf = to_usb_interface(dev);
usb_drv = to_usb_driver(drv);
id = usb_match_id(intf, usb_drv->id_table);
...
id = usb_match_dynamic_id(intf, usb_drv);
...
}
...
}
在usb_device_match函数内部是usb设备或接口将执行不同的操作,我们在usb_register()函数注册时并未绑定类型,所以这里直接返回0,也就不会执行相应的probe探测函数了。
由于在usb_alloc_dev函数中dev->dev.type = &usb_device_type;然后又会判断for_devices,在usb_init中的usb_register_device_driver(&usb_generic_driver, THIS_MODULE)中
new_udriver->drvwrap.for_devices = 1;
new_udriver->drvwrap.driver.name = new_udriver->name;
new_udriver->drvwrap.driver.bus = &usb_bus_type;
new_udriver->drvwrap.driver.probe = usb_probe_device;
new_udriver->drvwrap.driver.remove = usb_unbind_device;
new_udriver->drvwrap.driver.owner = owner;
所以满足条件驱动的probe函数为usb_probe_device(),其最后会调用到usb_generic_driver 中的 probe函数generic_probe()
4.2.1.1.4.9 usb_probe_device
./drivers/usb/core/driver.c
static int usb_probe_device(struct device *dev)
{
//udriver = usb_generic_driver;
struct usb_device_driver *udriver = to_usb_device_driver(dev->driver);
struct usb_device *udev = to_usb_device(dev);
error = udriver->probe(udev);
}
4.2.1.1.4.10 generic_probe
static int generic_probe(struct usb_device *udev)
{
int err, c;
/* Choose and set the configuration. This registers the interfaces
* with the driver core and lets interface drivers bind to them.
*/
//获取coniguration
if (udev->authorized == 0)
dev_err(&udev->dev, "Device is not authorized for usage\n");
else {
c = usb_choose_configuration(udev);
...
}
/* USB device state == configured ... usable */
usb_notify_add_device(udev);
return 0;
}
4.2.1.1.4.11 usb_set_configuration
intf->dev.type = &usb_if_device_type 将在usb_set_configuration()内部初始化
int usb_set_configuration(struct usb_device *dev, int configuration)
{
int i, ret;
struct usb_host_config *cp = NULL;
struct usb_interface **new_interfaces = NULL;
struct usb_hcd *hcd = bus_to_hcd(dev->bus);
int n, nintf;
...
...
/* Wake up the device so we can send it the Set-Config request */
ret = usb_autoresume_device(dev);
if (ret)
goto free_interfaces;
...
/* Get rid of pending async Set-Config requests for this device */
cancel_async_set_config(dev);
...
mutex_lock(hcd->bandwidth_mutex);
...
ret = usb_hcd_alloc_bandwidth(dev, cp, NULL, NULL);
...
for (i = 0; i < nintf; ++i) {
struct usb_interface_cache *intfc;
struct usb_interface *intf;
struct usb_host_interface *alt;
u8 ifnum;
cp->interface[i] = intf = new_interfaces[i];
intfc = cp->intf_cache[i];
intf->altsetting = intfc->altsetting;
intf->num_altsetting = intfc->num_altsetting;
intf->authorized = !!HCD_INTF_AUTHORIZED(hcd);
kref_get(&intfc->ref);
alt = usb_altnum_to_altsetting(intf, 0);
...
device_enable_async_suspend(&intf->dev);
ret = device_add(&intf->dev);
...
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(usb_set_configuration);
我们直接看usb_set_configuration函数. 从传参能够可以知道HUB有1个configuration, 至少1个interface.所以最后调到device_add()中. 然后调到usb_device_match中,然后调用is_usb_interface()和usb_match_id(), 而此时满足条件的驱动只有usb_probe_interface().
4.2.1.1.4.12 usb_bus_type 中的 usb_device_match
static int usb_device_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
/* devices and interfaces are handled separately */
if (is_usb_device(dev)) { //是否是usb设备
/* interface drivers never match devices */
if (!is_usb_device_driver(drv))
return 0;
/* TODO: Add real matching code */
return 1;
} else if (is_usb_interface(dev)) { //是否是usb接口
struct usb_interface *intf;
struct usb_driver *usb_drv;
const struct usb_device_id *id;
/* device drivers never match interfaces */
if (is_usb_device_driver(drv))
...
intf = to_usb_interface(dev);
usb_drv = to_usb_driver(drv);
id = usb_match_id(intf, usb_drv->id_table);
...
id = usb_match_dynamic_id(intf, usb_drv);
...
}
return 0;
}
在usb_device_match函数内部是usb设备或接口将执行不同的操作,我们在usb_register()函数注册时并未绑定类型,所以这里直接返回0,也就不会执行相应的probe探测函数了。
