比较早的调度策略:基于优先级的时间片调度等,这些策略影响调度的因素单一,效果不佳;CFS 基于优先级和负载调度策略,效果较优。
linux 4.19 中定义了6中调度策略算法;
kernel-4.19/include/uapi/linux/sched.h
kernel-4.19/include/linux/sched.h
/*
?* Scheduling policies
?*/
#define SCHED_NORMAL?? ??? ?0
#define SCHED_FIFO?? ??? ?1
#define SCHED_RR?? ??? ?2
#define SCHED_BATCH?? ??? ?3
/* SCHED_ISO: reserved but not implemented yet */
#define SCHED_IDLE?? ??? ?5
#define SCHED_DEADLINE?? ??? ?6
struct task_struct {
?? ?int?? ??? ??? ??? ?prio;
?? ?int?? ??? ??? ??? ?static_prio;
?? ?int?? ??? ??? ??? ?normal_prio;
?? ?unsigned int?? ??? ??? ?rt_priority;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? .policy?? ??? ?= SCHED_NORMAL,
?? ?const struct sched_class?? ?*sched_class;
?? ?struct sched_entity?? ??? ?se;
?? ?struct sched_rt_entity?? ??? ?rt;
}
struct sched_class {
?? ?const struct sched_class *next;
#ifdef CONFIG_UCLAMP_TASK
?? ?int uclamp_enabled;
#endif
?? ?void (*enqueue_task) (struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int flags);
?? ?void (*dequeue_task) (struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int flags);
}
CFS 调度类
kernel-4.19/kernel/sched/fair.c
11957/*
11958 * All the scheduling class methods:
11959 */
11960const struct sched_class fair_sched_class = {
11961?? ?.next?? ??? ??? ?= &idle_sched_class,
11962?? ?.enqueue_task?? ??? ?= enqueue_task_fair,
11963?? ?.dequeue_task?? ??? ?= dequeue_task_fair,
?
}
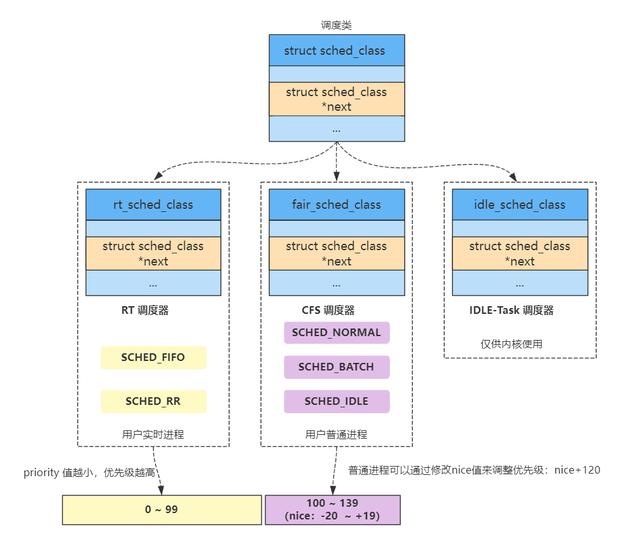
调度类通过next 指针链接,优先级? stop_sched_class >?dl_sched_class >?rt_sched_class>fair_sched_class>idle_sched_class>null ,用户空间通过sched_set/getScheduler 获取和设置
SCHED_NORMAL、SCHED_BATCH?????属于cfs??
SCHED_FIFO、SCHED_RR?????属于rt
1821#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
1822#define sched_class_highest (&stop_sched_class)
1823#else
1824#define sched_class_highest (&dl_sched_class)
1825#endif
1826#define for_each_class(class) \
1827 ? for (class = sched_class_highest; class; class = class->next)
任务优先级
struct task_struct {
?? ?int?? ??? ??? ??? ?prio;
?? ?int?? ??? ??? ??? ?static_prio;
?? ?int?? ??? ??? ??? ?normal_prio;
?? ?unsigned int?? ??? ??? ?rt_priority;
}
内核使用 0~139 表示进程优先级,0~99 rt 优先级,100~139给普通进程使用;另外用户空间优先级 nice -20~19??映射到普通进程优先级 100~139。
static_prio 是进程启动时分配的,内核使用,NICE_TO_PRIO() 可以将nice 和 内核优先级转换,用户可以通过nice 或sched_setscheduler 来改变。
rt_priority 实时进程优先级。
normal_prio 是基于static_prio 和 调度策略计算出来的,创建进程时会继承父进程。对应普通进程static_prio 和normal_prio 相等,对于实时进程会根据rt_priority 重新计算normal_prio(effective_prio()函数实现)
prio 对应动态优先级,有时需要暂时提供进程优先级。
调度实体权重
不同的调度类对应不同的调度实体,对应load_weight 对应调度权重。
struct task_struct {
struct sched_entity?? ??? ?se;
?struct sched_rt_entity?? ??? ?rt;
}
484struct sched_entity {
485?? ?/* For load-balancing: */
486?? ?struct load_weight?? ??? ?load;
487?? ?unsigned long?? ??? ??? ?runnable_weight;
488?? ?struct rb_node?? ??? ??? ?run_node;
489?? ?struct list_head?? ??? ?group_node;
490?? ?unsigned int?? ??? ??? ?on_rq;
}
360struct load_weight {
361?? ?unsigned long?? ??? ??? ?weight;
362?? ?u32?? ??? ??? ??? ?inv_weight;
363};
364
kernel-4.19/kernel/sched/core.c
8383/*
8384 * Nice levels are multiplicative, with a gentle 10% change for every
8385 * nice level changed. I.e. when a CPU-bound task goes from nice 0 to
8386 * nice 1, it will get ~10% less CPU time than another CPU-bound task
8387 * that remained on nice 0.
8388 *
8389 * The "10% effect" is relative and cumulative: from _any_ nice level,
8390 * if you go up 1 level, it's -10% CPU usage, if you go down 1 level
8391 * it's +10% CPU usage. (to achieve that we use a multiplier of 1.25.
8392 * If a task goes up by ~10% and another task goes down by ~10% then
8393 * the relative distance between them is ~25%.)
8394 */
8395const int sched_prio_to_weight[40] = {
8396 /* -20 */ ? ? 88761, ? ? 71755, ? ? 56483, ? ? 46273, ? ? 36291,
8397 /* -15 */ ? ? 29154, ? ? 23254, ? ? 18705, ? ? 14949, ? ? 11916,
8398 /* -10 */ ? ? ?9548, ? ? ?7620, ? ? ?6100, ? ? ?4904, ? ? ?3906,
8399 /* ?-5 */ ? ? ?3121, ? ? ?2501, ? ? ?1991, ? ? ?1586, ? ? ?1277,
8400 /* ? 0 */ ? ? ?1024, ? ? ? 820, ? ? ? 655, ? ? ? 526, ? ? ? 423,
8401 /* ? 5 */ ? ? ? 335, ? ? ? 272, ? ? ? 215, ? ? ? 172, ? ? ? 137,
8402 /* ?10 */ ? ? ? 110, ? ? ? ?87, ? ? ? ?70, ? ? ? ?56, ? ? ? ?45,
8403 /* ?15 */ ? ? ? ?36, ? ? ? ?29, ? ? ? ?23, ? ? ? ?18, ? ? ? ?15,
8404};
8405
8406/*
8407 * Inverse (2^32/x) values of the sched_prio_to_weight[] array, precalculated.
8408 *
8409 * In cases where the weight does not change often, we can use the
8410 * precalculated inverse to speed up arithmetics by turning divisions
8411 * into multiplications:
8412 */
8413const u32 sched_prio_to_wmult[40] = {
8414 /* -20 */ ? ? 48388, ? ? 59856, ? ? 76040, ? ? 92818, ? ?118348,
8415 /* -15 */ ? ?147320, ? ?184698, ? ?229616, ? ?287308, ? ?360437,
8416 /* -10 */ ? ?449829, ? ?563644, ? ?704093, ? ?875809, ? 1099582,
8417 /* ?-5 */ ? 1376151, ? 1717300, ? 2157191, ? 2708050, ? 3363326,
8418 /* ? 0 */ ? 4194304, ? 5237765, ? 6557202, ? 8165337, ?10153587,
8419 /* ? 5 */ ?12820798, ?15790321, ?19976592, ?24970740, ?31350126,
8420 /* ?10 */ ?39045157, ?49367440, ?61356676, ?76695844, ?95443717,
8421 /* ?15 */ 119304647, 148102320, 186737708, 238609294, 286331153,
8422};
sched_prio_to_weight? 里面将 用户空间nice 优先级 -20~19 对应cpu 执行时间权重映射,nice =0 对应 1024 ,nice 每差一个优先级,cpu 时间就相应相差 10% ;nice 对应权重约以1.25 比例增加。
A进程nice 0(权重1024),B进程nice0(权重1024),则A 、B的CPU时间,1024/(1024+1024) = 50%
A进程nice 0(权重1024),B进程nice1(权重820),则B的CPU时间,820/(1024+820) = 45%,A 的cpu 时间 55%
这里变化一个nice 优先级,CPU时间 就相差 10%?
sched_prio_to_wmult[n] = (1/sched_prio_to_weight[n]) <<32?
718static void set_load_weight(struct task_struct *p, bool update_load)
719{
720?? ?int prio = p->static_prio - MAX_RT_PRIO;
721?? ?struct load_weight *load = &p->se.load;
722
723?? ?/*
724?? ? * SCHED_IDLE tasks get minimal weight:
725?? ? */
726?? ?if (idle_policy(p->policy)) {
727?? ??? ?load->weight = scale_load(WEIGHT_IDLEPRIO);
728?? ??? ?load->inv_weight = WMULT_IDLEPRIO;
729?? ??? ?p->se.runnable_weight = load->weight;
730?? ??? ?return;
731?? ?}
732
733?? ?/*
734?? ? * SCHED_OTHER tasks have to update their load when changing their
735?? ? * weight
736?? ? */
737?? ?if (update_load && p->sched_class == &fair_sched_class) {
738?? ??? ?reweight_task(p, prio);
739?? ?} else {
740?? ??? ?load->weight = scale_load(sched_prio_to_weight[prio]);
741?? ??? ?load->inv_weight = sched_prio_to_wmult[prio];
742?? ??? ?p->se.runnable_weight = load->weight;
743?? ?}
744}