Augmenting Attack Graphs to Represent Data Link and Network Layer Vulnerabilities
一、摘要
Mulval 是一款常用的网络安全分析工具,使用漏洞扫描程序来扫描网络漏洞,之后再生成攻击图进行安全分析。传统的Mulval没有将考虑网络层错误配置带来的影响,本文将针对这一部分展开,介绍针对网络错误配置的自定义规则相关内容。
二、ARP(地址解析协议)
ARP协议是根据IP地址获取物理地址的一个TCP/IP协议,主机发送消息时将包含目标ip地址的ARP请求广播到局域网络的所有主机,并接受返回消息,以此确定目标的物理地址。
举例说明:两台主机AB之间通信,当A要和B通信,第一步需要根据主机A上的路由表内容,确定B的ip地址,然后A在自己的本地ARP缓存中检查主机B的匹配MAC地址;第二步,如果主机A在ARP中没有找到映射,他将发送ARP请求帧广播到本地网络上的所有主机。源主机A的ip地址和MAC地址都在ARP请求中。本地网络中的每台主机都接到ARP请求并检查是否和自己的IP匹配,如果发现不匹配,它将会丢弃该请求;第三步,主机B确定ARP请求中的ip地址和自己的ip地址匹配,则将主机A的ip地址和mac地址映射添加到本地ARP缓存中;第四步,主机B将包含其MAC地址的ARP消息回复给主机A;第五步,主机A收到ARP回复消息的时候,会更新ARP缓存表。
结合上述过程,不难理解ARP欺骗,也就是说当主机A发送ARP广播帧的时候,攻击者C代替B回复,假称他就是B,而A不会取验证回复消息的真伪,在接下来的通信中,它就会将攻击者C误以为成B。从而实现了ARP欺骗的目的。
三、Mulval结合ARP进行自定义规则
下面给出一个ARP欺骗的场景:
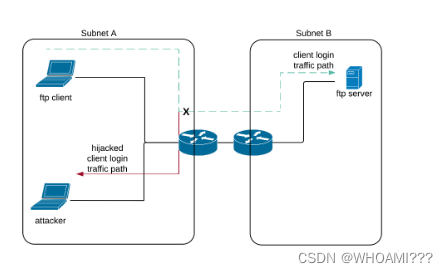
在这个场景中,位于子网A的ftp的客户端准备和位于子网B的服务器端通信,攻击者也位于子网A, 子网A中的所有结点都使用ARP协议获取MAC地址,攻击者可以利用ARP中漏洞欺骗位于子网A中的网关。同时,攻击者可以利用FTP漏洞捕获用户登录的明文信息,进而登录到FTP服务器执行任意代码。
结合上述内容,可以针对ARP欺骗生成如下自定义规则:
/** primitives **/
gateway(_host).
flowExists(_src, _dst, _protocol, _port, _user).
/** interaction rules **/
netAccess(H2, _protocol, _port) :
gateway(H1),
advances(H1, H2),
netAccess(H1, _protocol, _port),
hacl(H1, H2, _protocol, _port).
principalCompromised(Victim) :
hasAccount(Victim, RemoteHost, User),
/* Arp spoof works only if the victim and attacker are in the same subnet*/
attackerLocated(Subnet),
hacl(Subnet, H, _anyProtocol, _anyPort),
/* Victim is using standard arp for address resolution*/
networkServiceInfo(H, arpd, _protocol, _port, _),
/* The standard arpd protocol is vulnerable to spoofing */
vulExists(H, arpSpoofVuln, arpd, remoteExploit, arpSpoof),
/* The User has an account on a login service on the remote host */
logInService(RemoteHost, Protocol, Port),
/* There is an active connection from the host to the remote machine */
flowExists(H, RemoteHost, Protocol, Port, User).
logInService(H, Protocol, Port) :
networkServiceInfo(H, ftpd, Protocol, Port, _).
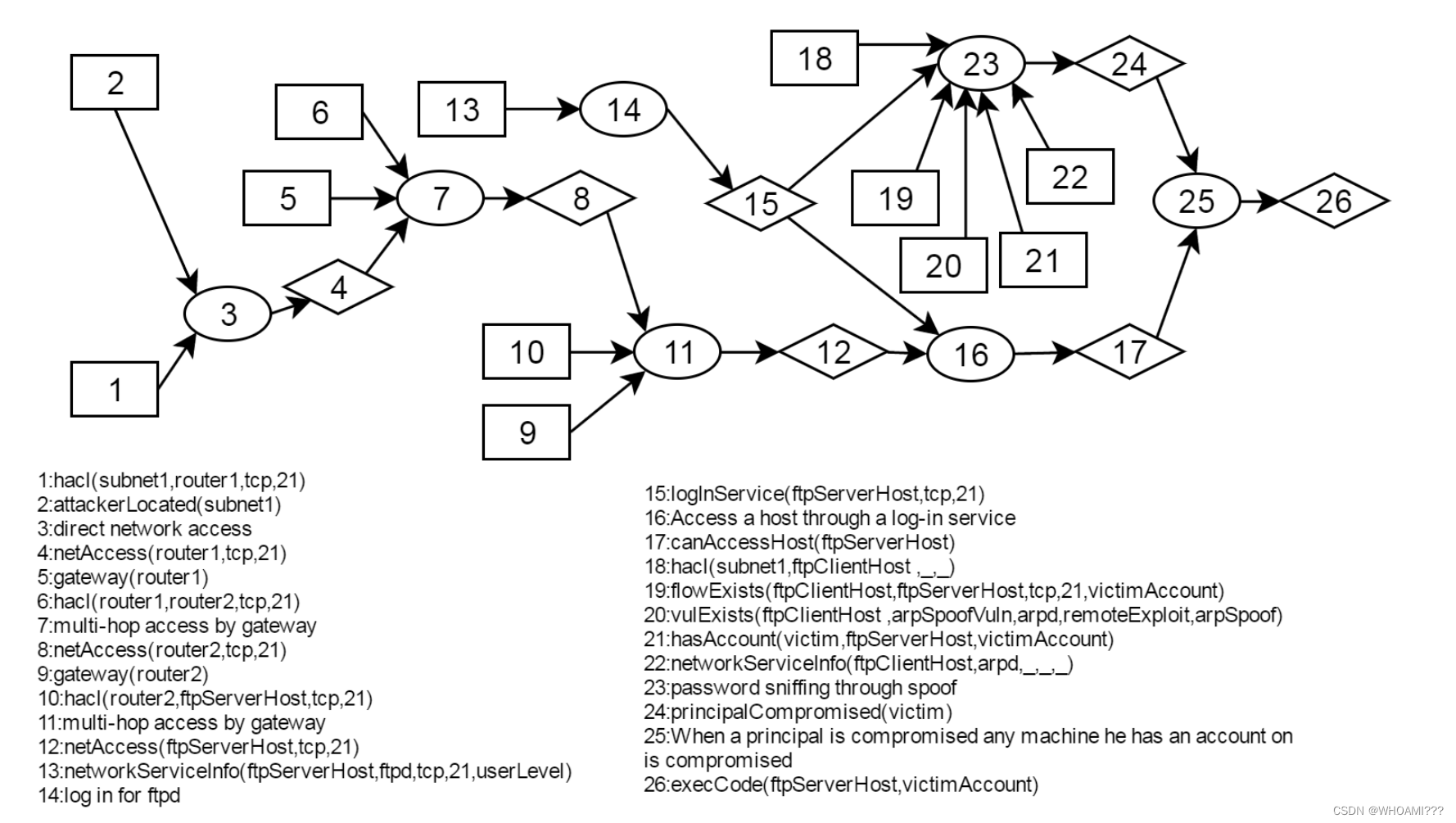
结合自定义规则,可以生成输入文件:
/* attacker specification */
attackerLocated(subnetA).
attackGoal(execCode(ftpServerHost,victimAccount)).
/* topology */
hacl(subnetA, ftpClientHost,_,_).
hacl(subnetA, router1,_,_).
hacl(router1, router2,_, _).
hacl(router2, ftpServerHost, tcp , 21).
/* cross-subnet comms through routers */
gateway(router1).
gateway(router2).
/* client */
networkServiceInfo(ftpClientHost, arpd,_,_,_).
vulExists(ftpClientHost, arpSpoofVuln, arpd).
vulProperty(arpSpoofVuln, remoteExploit, arpSpoof).
/* ftp server */
networkServiceInfo(ftpServerHost, ftpd, tcp, 21, userLevel).
hasAccount(victim, ftpServerHost, victimAccount).
networkServiceInfo(ftpServerHost, arpd, _,_,_).
/* comms */
flowExists(ftpClientHost, ftpServerHost, tcp, 21, victimAccount).
得到攻击图如下:
另外攻击者可以不在目标网络中就完成劫持,需要在上述自定义规则中补充:
principalCompromised(Victim) :
/* The victim has a user account on the remote host */
hasAccount(Victim, RemoteHost, User),
/* nrlolsr is being used */
networkServiceInfo(H, nrlolsr, olsr, _no_port, _user),
/* nrlolsr is misconfigured allowing traffic hijacking */
vulExists(H, nrlolsrVul, nrlolsr, remoteExploit, nrlolsrHijack),
/* The User has an account on a login service on the remote host */
logInService(RemoteHost, Protocol, Port),
/* There is an active connection from the host to the remote machine */
flowExists(H, RemoteHost, Protocol, Port, User).