lvs负载均衡
文章目录
一、什么是lvs
? LVS(Linux Virtual Server)即Linux虚拟服务器,是由章文嵩博士主导的开源负载均衡项目,目前LVS已经被集成到Linux内核模块中。该项目在Linux内核中实现了基于IP的数据请求负载均衡调度方案,其体系结构如图1所示,终端互联网用户从外部访问公司的外部负载均衡服务器,终端用户的Web请求会发送给LVS调度器,调度器根据自己预设的算法决定将该请求发送给后端的某台Web服务器,比如,轮询算法可以将外部的请求平均分发给后端的所有服务器,终端用户访问LVS调度器虽然会被转发到后端真实的服务器,但如果真实服务器连接的是相同的存储,提供的服务也是相同的服务,最终用户不管是访问哪台真实服务器,得到的服务内容都是一样的,整个集群对用户而言都是透明的。最后根据LVS工作模式的不同,真实服务器会选择不同的方式将用户需要的数据发送到终端用户,LVS工作模式分为NAT模式、TUN模式、以及DR模式。
二、lvs的作用
? LVS主要用于多服务器的负载均衡。它工作在传输层,可以实现高性能,高可用的服务器集群技术。
它廉价,可把许多低性能的服务器组合在一起形成一个超级服务器。
? 它易用,配置非常简单,且有多种负载均衡的方法。它稳定可靠,即使在集群的服务器中某台服务器无法正常工作,也不影响整体效果。
另外可扩展性也非常好。
? 因为lvs工作在传输层,所以相对于其他的负载均衡的解决办法(DNS域名轮流解析、应用层负载的调度、客户端的调度等,它的效率是非常高的)
? LVS的通过控制IP来实现负载均衡。IPVS是其具体的实现模块。
三、lvs三种工作模式
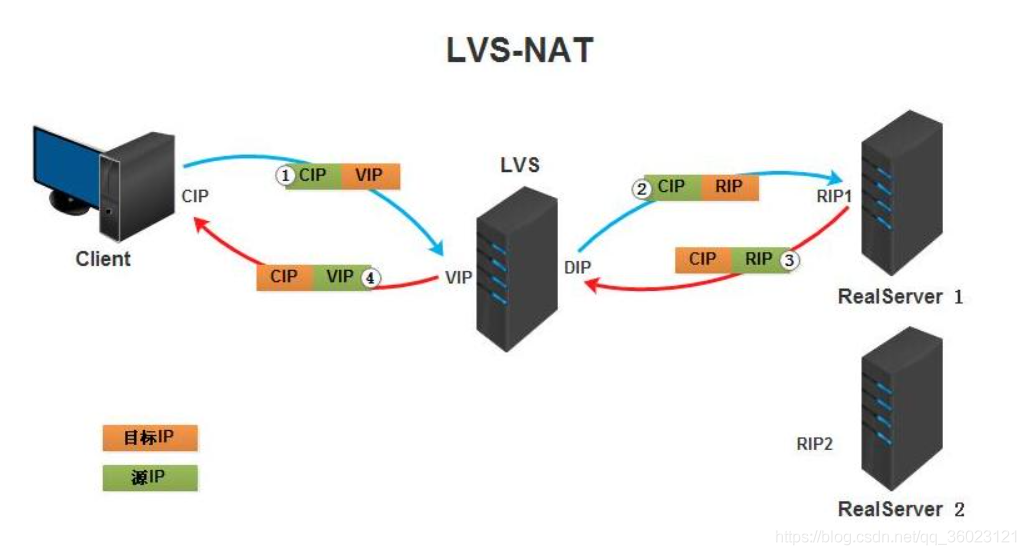
NAT模式
-
NAT(Network Address Translation)即网络地址转换,其作用是通过数据报头的修改,使得位于企业内部的私有IP地址可以访问外网,以及外部用用户可以访问位于公司内部的私有IP主机
-
工作过程:
-
(1):用户通过互联网DNS服务器解析到公司负载均衡设备上的外网地址,相对于真实服务器而言,LVS外网ip又称为vip,用户通过访问vip,即可连接后端的真实服务器,而此时用户对这一切都是不可知的,用户认为自己还在访问真实的后端服务器,也不知道自己访问的vip只是一个调度器。
-
(2):用户将请求发送至调度器上,此时LVS根据算法选择一个后端的真实服务器,将数据请求包转发给真实服务器,并在转发之前LVS会修改数据包中的目标地址以及目标端口,此时修改为真实的服务器ip地址
-
(3):真实的服务器将响应的数据包返回给LVS调度器,调度器在响应数据包后会将源地址和源端口修改为vip及调度器相应端口,修改完成后,由调度器响应数据包发送给终端
-
-
LVS调度器中有一个连接Hash表,该表会记录连接请求及其转发信息,当同一个连接下一个数据包发送给调度器时,该Hash’表可以直接找到之前连接的记录,并根据记录信息选出相同真实服务器及其端口信息。
-
NAT的优点是服务器可以运行在任何支持TCP/IP的操作系统,他只需要在调度器上配置一个ip 服务器组可以用私有的ip地址。
-
NAT的缺点是伸缩能力有限,当服务器节点数目上升到20时,调度器本身有可能成为系统的新瓶 颈,因为请求和响应的报文都需要经过调度器。
TUN模式
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-73C0AdHE-1664455212649)(http://rhuik45mo.hn-bkt.clouddn.com/lvs/3.png)]
-
LVS(NAT)模式的集群环境中,所有数据包的请求的回应的哦欧需要经过调度器处理,但是在TUN模式中,将NAT模式中的问题有所解决。因为数据包的请求包往往远远小于响应数据包的大小。因为响应数据包中有包含客户需要的具体数据所以,TUN的原理就是将请求与响应数据分离。,让调度器仅仅处理数据请求,让真实的服务器响应数据包直接返回给客户。
-
IP(隧道)是一种数据包分装技术,他可以经原始的数据包分装并添加新的包头(内容包括新的源地址及端口、目标地址及端口),从而实现将一个目标为调度器的vip地址的数据包分装,通过隧道转发给真实的后端服务器,通过将客户端发往调度器的原始数据包分装,并在其基础上添加新的数据包头(修改目标地址为调度器选择出来的真实服务的ip地址以及对应端口),lLVS(Tun)模式要求真实的服务器可以与外部网络连接,真实服务器在受到请求数据包后直接给客户端返回响应数据。
-
LVS(Tun)技术对服务器有要求,即所有服务器必须支持"IP Tunneling"或者IP Encapsulation”协议。目前,VS/TUN 的后端服务器主要运行 Linux 操作系统。
DR模式
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-PUhMI4Y6-1664455212651)(http://rhuik45mo.hn-bkt.clouddn.com/lvs/4.png)]
在LVS(TUN)模式中,需要LVS调度器与真实的服务器之间创建隧道连接,这样就会增加服务器的负担。DR模式也叫路由模式,该模式中LVS依然仅承担数据的请求以及根据算法调度出合理的后端服务器,最终由后端真实服务器负责响应数据包发送返回给客户端。与隧道模式不同的是,DR模式要求调度器与后端服务器必须在统一个局域网内u,VIP地址需要在调度器与后端所有服务器之间共享,因为最终的真实服务器会给客户端回应数据包时需要设置源IP为VIP,目标IP为客户端IP,这样客户端访问的时调度器VIP地址,回应的源地址也是VIP,这样客户端是感觉不到后端服务器的存在。由于多台计算机都设置了同样的VIP地址,所以在直接路由模式中要求调度器的VIP是对外可见的,客户端将请求数据包发送到调度器主机,而所有的真实服务器的VIP必须配置在Non-ARP的网络上ARP是一个协议。调度器根据算法在选出真实的服务器后,在不修改数据报文的情况下,将数据帧的MAC地址修改为选出的真实的MAC地址,通过交换机将该数据帧发给真实的服务器。
四、LVS的10种调度算法
-
静态算法:
-
1.轮询调度:
轮询调度(Round Robin 简称’RR’)算法就是按依次循环的方式将请求调度到不同的服务器上,该算法最大的特点就是实现简单。轮询算法假设所有的服务器处理请求的能力都一样的,调度器会将所有的请求平均分配给每个真实服务器。
-
2.加权轮询调度:
加权轮询(Weight Round Robin 简称’WRR’)算法主要是对轮询算法的一种优化与补充,LVS会考虑每台服务器的性能,并给每台服务器添加一个权值,如果服务器A的权值为1,服务器B的权值为2,则调度器调度到服务器B的请求会是服务器A的两倍。权值越高的服务器,处理的请求越多。
-
3.源地址散列调度:
源地址散列调度(Source Hashing 简称’SH’)算法先根据请求的源IP地址,作为散列键(Hash Key)从静态分配的散列表找出对应的服务器,若该服务器是可用的且并未超载,将请求发送到该服务器,否则返回空。它采用的散列函数与目标地址散列调度算法的相同,它的算法流程与目标地址散列调度算法的基本相似。
-
4.目标地址散列调度:
目标地址散列调度(Destination Hashing 简称’DH’)算法先根据请求的目标IP地址,作为散列键(Hash Key)从静态分配的散列表找出对应的服务器,若该服务器是可用的且并未超载,将请求发送到该服务器,否则返回空。
-
-
动态调度算法:
- 1.最少链接调度:
最小连接调度(Least Connections 简称’LC’)算法是把新的连接请求分配到当前连接数最小的服务器。最小连接调度是一种动态的调度算法,它通过服务器当前活跃的连接数来估计服务器的情况。调度器需要记录各个服务器已建立连接的数目,当一个请求被调度到某台服务器,其连接数加1;当连接中断或者超时,其连接数减1。
(集群系统的真实服务器具有相近的系统性能,采用最小连接调度算法可以比较好地均衡负载。) - 2.加权最少链接调度:
加权最少连接(Weight Least Connections 简称’WLC’)算法是最小连接调度的超集,各个服务器相应的权值表示其处理性能。服务器的缺省权值为1,系统管理员可以动态地设置服务器的权值。加权最小连接调度在调度新连接时尽可能使服务器的已建立连接数和其权值成比例。调度器可以自动问询真实服务器的负载情况,并动态地调整其权值。 - 3.最少期望延迟:
最少期望延迟(Shortest Expected Delay 简称’SED’)算法基于WLC算法。举个例子吧,ABC三台服务器的权重分别为1、2、3 。那么如果使用WLC算法的话一个新请求进入时它可能会分给ABC中的任意一个。使用SED算法后会进行一个运算
A:(1+1)/1=2 B:(1+2)/2=3/2 C:(1+3)/3=4/3 就把请求交给得出运算结果最小的服务器。 - 4.基于局部性的最少连接调度算法:
基于局部性的最少连接调度算法(Locality-Based Least Connections with Replication 简称’LBLCR’)算法也是针对目标IP地址的负载均衡,目前主要用于Cache集群系统,它与LBLC算法不同之处是它要维护从一个目标IP地址到一组服务器的映射,而LBLC算法维护从一个目标IP地址到一台服务器的映射。按’最小连接’原则从该服务器组中选出一一台服务器,若服务器没有超载,将请求发送到该服务器;若服务器超载,则按’最小连接’原则从整个集群中选出一台服务器,将该服务器加入到这个服务器组中,将请求发送到该服务器。同时,当该服务器组有一段时间没有被修改,将最忙的服务器从服务器组中删除,以降低复制的程度。 - 5.复杂的基于局部性最少的连接算法:
复杂的基于局部性最少的连接算法(Locality-Based Least Connections with Replication 简称’LBLCR’)算法也是针对目标IP地址的负载均衡,目前主要用于Cache集群系统,它与LBLC算法不同之处是它要维护从一个目标IP地址到一组服务器的映射,而LBLC算法维护从一个目标IP地址到一台服务器的映射。按’最小连接’原则从该服务器组中选出一一台服务器,若服务器没有超载,将请求发送到该服务器;若服务器超载,则按’最小连接’原则从整个集群中选出一台服务器,将该服务器加入到这个服务器组中,将请求发送到该服务器。同时,当该服务器组有一段时间没有被修改,将最忙的服务器从服务器组中删除,以降低复制的程度。 - 6.永不排队 nq
无需队列,如果有realserver的连接数为0就直接分配过去
- 1.最少链接调度:
五、LVS-实战:搭建HTTP负载均衡集群
1.搭建搭建lvs-nat模式的http负载集群
环境准备:
| 主机名 | 主机作用 | IP/DIP | VIP | 系统 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DR | LVS服务器(DR) | 192.168.174.170 | 172.25.0.100 | centos8 |
| RS1 | apache服务器1(RS) | 192.168.174.175 | 网关为DR网关 | centos8 |
| RS2 | apache服务器2(RS) | 192.168.174.177 | 网关为DR网关 | centos8 |
| client | 客户端 (用于测试) | 192.168.174.178 | 客户端不需要VIP | centos8 |
| RS1配置: |
//关闭selinux和防火墙
[root@RS1 ~]# sed -ri 's/^(SELINUX=).*/\1disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
[root@RS1 ~]# setenforce 0
[root@RS1 ~]# systemctl disable --now firewalld.service
//配置ip
[root@RS1 ~]# nmcli connection modify ens33 ipv4.addresses 192.168.174.177/24 ipv4.gateway 172.25.250.133 ipv4.dns 8.8.8.8 ipv4.method manual autoconnect yes
[root@RS1 ~]# nmcli connection up ens33
Connection successfully activated (D-Bus active path: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/2)
//配置好yum源,然后安装httpd,然后配置好网站首页
[root@RS1 ~]# dnf -y install httpd
[root@RS1 ~]# echo "RS1" > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@RS1 ~]# systemctl enable --now httpd
RS2配置:
//关闭selinux和防火墙
[root@RS2 ~]# sed -ri 's/^(SELINUX=).*/\1disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
[root@RS2 ~]# setenforce 0
[root@RS2 ~]# systemctl disable --now firewalld.service
//配置ip
[root@RS2 ~]# nmcli connection modify ens33 ipv4.addresses 192.168.202.141/24 ipv4.gateway 172.25.250.133 ipv4.dns 114.114.114.114 ipv4.method manual autoconnect yes
[root@RS2 ~]# nmcli connection up ens33
//配置好yum源,然后安装httpd服务,然后配置好网站首页
[root@RS2 ~]# dnf -y install httpd
[root@RS2 ~]# echo "RS2" > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@RS2 ~]# systemctl enable --now httpd
DR配置
//关闭selinux和防火墙
[root@DR ~]# systemctl disable --now firewalld.service
[root@DR ~]# setenforce 0
[root@DR ~]# sed -ri 's/^(SELINUX=).*/\1disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
//再给DR,添加一块网卡,我这里添加的是仅主机模式网卡,以便区分,网段为:172.25.250.0
//设置网卡ip,172.25.250.133
[root@DR ~]# nmcli connection modify Wired\ connection\ 1 con-name eth1 ipv4.addresses 172.25.250.133/24 ipv4.dns 8.8.8.8 ipv4.method manual autoconnect yes
[root@DR ~]# nmcli connection up eth1
Connection successfully activated (D-Bus active path: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/3)
[root@DR ~]# systemctl restart NetworkManager
[root@DR ~]# ip a |grep eth1
3: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 172.25.250.133/24 brd 172.25.250.255 scope global noprefixroute eth1
//开启转发功能
[root@DR ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
[root@DR ~]# sysctl -p
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
//配置好好两台web服务器后,最后再安装ipvsadm并添加规则
[root@DR ~]# dnf -y install ipvsadm
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -A -t 172.25.250.133:80 -s rr
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 172.25.250.133:80 -r 192.168.174.177:80 -m
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 172.25.250.133:80 -r 192.168.174.178:80 -m
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -Ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 172.25.250.133:80 rr
-> 192.168.174.177:80 Masq 1 0 0
-> 192.168.174.178:80 Masq 1 0 0
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -Sn > /etc/sysconfig/ipvsadm
[root@DR ~]# systemctl restart ipvsadm.service
[root@DR ~]# systemctl enable ipvsadm.service
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/ipvsadm.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/ipvsadm.service.
客户端进行测试,因为选择的是轮询(rr)
[root@client ~]# curl http://172.25.250.133
RS2
[root@client ~]# curl http://172.25.250.133
RS1
[root@client ~]# curl http://172.25.250.133
RS2
[root@client ~]# curl http://172.25.250.133
RS1
2.搭建搭建lvs-dr模式的http负载集群
环境准备:
| 主机名 | 主机作用 | IP/DIP | VIP | 系统 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DR | LVS服务器(DR) | 192.168.174.170 | lo:192.168.174.100 | centos8 |
| RS1 | apache服务器1(RS) | 192.168.174.175 | lo:192.168.174.100 | centos8 |
| RS2 | apache服务器2(RS) | 192.168.174.177 | lo:192.168.174.100 | centos8 |
| client | 客户端 (用于测试) | 192.168.174.178 | 客户端不需要VIP | centos8 |
RS1配置:
//关闭selinux和防火墙
[root@RS1 ~]# sed -ri 's/^(SELINUX=).*/\1disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
[root@RS1 ~]# setenforce 0
[root@RS1 ~]# systemctl disable --now firewalld.service
//RS1上配置内核参数
[root@RS1 ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2
[root@RS1 ~]# sysctl -p
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2
//配置VIP
[root@RS1 ~]# dnf -y install net-tools (先安装ifconfig命令)
[root@RS1 ~]# ifconfig lo 192.168.174.100/32 broadcast 192.168.174.100 netmask 255.255.255.255 up
//永久生效lo网卡配置
[root@RS1 ~]# echo "ifconfig lo 192.168.174.100/32 broadcast 192.168.174.100 netmask 255.255.255.255 up" >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local
[root@RS1 ~]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
//添加路由
[root@RS1 ~]# route add -host 192.168.174.100/32 dev lo
//安装httpd服务,然后配置好网站首页
[root@RS1 ~]# dnf -y install httpd
[root@RS1 ~]# echo "RS1" > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@RS1 ~]# systemctl enable --now httpd
RS2配置:
//关闭selinux和防火墙
[root@RS2 ~]# sed -ri 's/^(SELINUX=).*/\1disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
[root@RS2 ~]# setenforce 0
[root@RS2 ~]# systemctl disable --now firewalld.service
//RS2上配置内核参数
[root@RS2 ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2
[root@RS2 ~]# sysctl -p
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2
//配置VIP
[root@RS2 ~]# dnf -y install net-tools
[root@RS2 ~]# ifconfig lo 192.168.174.100/32 broadcast 192.168.174.100 netmask 255.255.255.255 up
//永久生效lo网卡配置
[root@RS2 ~]# echo "ifconfig lo 192.168.174.100/32 broadcast 192.168.174.100 netmask 255.255.255.255 up" >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local
[root@RS2 ~]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
//添加路由
[root@RS2 ~]# route add -host 192.168.174.100/32 dev lo
//安装httpd服务,然后配置好网站首页
[root@RS2 ~]# dnf -y install httpd
[root@RS2 ~]# echo "RS2" > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@RS2 ~]# systemctl enable --now httpd
DR配置:
//关闭selinux和防火墙
[root@DR ~]# systemctl disable --now firewalld.service
[root@DR ~]# setenforce 0
[root@DR ~]# sed -ri 's/^(SELINUX=).*/\1disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
//配置lo网卡ip
[root@DR ~]# dnf -y install net-tools (先安装ifconfig命令)
[root@DR ~]# ifconfig lo 192.168.174.100/32 broadcast 192.168.174.100 netmask 255.255.255.255 up
[root@DR ~]# ip a |grep lo
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 192.168.174.100/0 brd 192.168.174.100 scope global lo
//永久生效lo网卡配置
[root@DR ~]# echo "ifconfig lo 192.168.174.100/32 broadcast 192.168.174.100 netmask 255.255.255.255 up" >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local
[root@DR ~]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
//配置好好两台web服务器后,最后再安装ipvsadm并添加规则
[root@DR ~]# dnf -y install ipvsadm
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -A -t 192.168.174.100:80 -s rr
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.174.100:80 -r 192.168.174.177:80 -g
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.174.100:80 -r 192.168.174.178:80 -g
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -Ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.168.174.100:80 rr
-> 192.168.174.177:80 Route 1 0 0
-> 192.168.174.178:80 Route 1 0 0
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -Sn > /etc/sysconfig/ipvsadm
[root@DR ~]# systemctl restart ipvsadm.service
[root@DR ~]# systemctl enable ipvsadm.service
客户端进行测试,因为选择的是轮询(rr)
[root@client ~]# curl 192.168.174.100
RS1
[root@client ~]# curl 192.168.174.100
RS2
[root@client ~]# curl 192.168.174.100
RS1
[root@client ~]# curl 192.168.174.100
RS2
3.搭建搭建lvs-tun模式的http负载集群
环境需求:
| 主机名 | 主机作用 | IP/DIP | VIP | 系统 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DR | LVS服务器(DR) | 192.168.174.170 | tunl0:192.168.174.201 | centos8 |
| RS1 | apache服务器1(RS) | 192.168.174.175 | tunl0:192.168.174.201 | centos8 |
| RS2 | apache服务器2(RS) | 192.168.174.177 | tunl0:192.168.174.201 | centos8 |
| client | 客户端 (用于测试) | 192.168.174.178 | 客户端不需要VIP | centos8 |
RS1配置:
//关闭selinux和防火墙
[root@RS1 ~]# sed -ri 's/^(SELINUX=).*/\1disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
[root@RS1 ~]# setenforce 0
[root@RS1 ~]# systemctl disable --now firewalld.service
//启用ipip模块,配置VIP
[root@RS1 ~]# dnf -y install net-tools
[root@RS1 ~]# modprobe ipip
[root@RS1 ~]# ifconfig tunl0 192.168.174.201 broadcast 192.168.174.201 netmask 255.255.255.255
[root@RS1 ~]# echo "ifconfig tunl0 192.168.174.201 broadcast 192.168.174.201 netmask 255.255.255.255" >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local
[root@RS1 ~]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
//修改内核参数
[root@RS1 ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.conf.tunl0.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.tunl0.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.tunl0.rp_filter = 0
net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter = 0
[root@RS1 ~]# sysctl -p
net.ipv4.conf.tunl0.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.tunl0.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.tunl0.rp_filter = 0
net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter = 0
//安装httpd服务,然后配置好网站首页
[root@RS1 ~]# dnf -y install httpd
[root@RS1 ~]# echo "RS1" > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@RS1 ~]# systemctl enable --now httpd
RS2配置:
//关闭selinux和防火墙
[root@RS2 ~]# sed -ri 's/^(SELINUX=).*/\1disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
[root@RS2 ~]# setenforce 0
[root@RS2 ~]# systemctl disable --now firewalld.service
//启用ipip模块,配置VIP
[root@RS1 ~]# dnf -y install net-tools
[root@RS1 ~]# modprobe ipip
[root@RS1 ~]# ifconfig tunl0 192.168.174.201 broadcast 192.168.174.201 netmask 255.255.255.255
[root@RS1 ~]# echo "ifconfig tunl0 192.168.174.201 broadcast 192.168.174.201 netmask 255.255.255.255" >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local
[root@RS1 ~]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
//修改内核参数
[root@RS1 ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.conf.tunl0.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.tunl0.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.tunl0.rp_filter = 0
net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter = 0
[root@RS1 ~]# sysctl -p
net.ipv4.conf.tunl0.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.tunl0.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.tunl0.rp_filter = 0
net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter = 0
//安装httpd服务,然后配置好网站首页
[root@RS1 ~]# dnf -y install httpd
[root@RS1 ~]# echo "RS2" > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@RS1 ~]# systemctl enable --now httpd
DR配置:
//关闭selinux和防火墙
[root@DR ~]# systemctl disable --now firewalld.service
[root@DR ~]# setenforce 0
[root@DR ~]# sed -ri 's/^(SELINUX=).*/\1disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
//修改内核参数,开启IP转发
[root@DR ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
[root@DR ~]# sysctl -p
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
//配置VIP
[root@DR ~]# dnf -y install net-tools
[root@DR ~]# ifconfig tunl0 192.168.174.201 broadcast 192.168.174.201 netmask 255.255.255.255
[root@DR ~]# ip a |grep tunl0
3: tunl0@NONE: <NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1480 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.174.201/32 brd 192.168.174.201 scope global tunl0
//永久生效
[root@DR ~]# echo "ifconfig tunl0 192.168.174.201 broadcast 192.168.174.201 netmask 255.255.255.255" >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local
[root@DR ~]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
//配置好好两台web服务器后,最后再安装ipvsadm并添加规则
[root@DR ~]# dnf -y install ipvsadm
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -A -t 192.168.174.201:80 -s rr
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.174.201:80 -r 192.168.174.177:80 -i
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.174.201:80 -r 192.168.174.178:80 -i
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -Ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.168.174.201:80 rr
-> 192.168.174.177:80 Tunnel 1 0 0
-> 192.168.174.178:80 Tunnel 1 0 0
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -Sn > /etc/sysconfig/ipvsadm
[root@DR ~]# systemctl restart ipvsadm.service
[root@DR ~]# systemctl disable ipvsadm.service
客户端进行测试,因为选择的是轮询(rr)
[root@client ~]# curl http://192.168.174.201
RS2-
[root@client ~]# curl http://192.168.174.201
RS1
[root@client ~]# curl http://192.168.174.201
RS2
[root@client ~]# curl http://192.168.174.201
RS1
4.搭建搭建lvs-dr模式的https负载集群
环境需求:
| 主机名 | 主机作用 | IP/DIP | VIP | 系统 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DR | LVS服务器(DR) | 192.168.174.170 | lo:192.168.174.202 | centos8 |
| RS1 | apache服务器1(RS) | 192.168.174.175 | lo:192.168.174.202 | centos8 |
| RS2 | apache服务器2(RS) | 192.168.174.177 | lo:192.168.174.202 | centos8 |
| client | 客户端 (用于测试) | 192.168.174.178 | 客户端不需要VIP | centos8 |
| RS1配置 |
//关闭selinux和防火墙
[root@RS1 ~]# sed -ri 's/^(SELINUX=).*/\1disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
[root@RS1 ~]# setenforce 0
[root@RS1 ~]# systemctl disable --now firewalld.service
//RS1上配置内核参数
[root@RS1 ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2
[root@RS1 ~]# sysctl -p
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2
//配置VIP
[root@RS1 ~]# dnf -y install net-tools
[root@RS1 ~]# ifconfig lo 192.168.174.202/32 broadcast 192.168.174.202 netmask 255.255.255.255 up
//永久生效lo网卡配置
[root@RS1 ~]# echo "ifconfig lo 192.168.174.202/32 broadcast 192.168.174.202 netmask 255.255.255.255 up" >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local
[root@RS1 ~]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
//添加路由
[root@RS1 ~]# route add -host 192.168.174.202/32 dev lo
//安装httpd服务,然后配置好https网站首页
[root@RS1 ~]# dnf -y install httpd mod_ssl
[root@RS1 ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-base.conf
LoadModule ssl_module modules/mod_ssl.so
[root@RS1 ~]# mkdir /etc/httpd/ssl
[root@RS1 ~]# cd /etc/httpd/ssl
[root@RS1 ssl]# openssl genrsa -out httpd.key 2048
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus (2 primes)
...................................................................................................................................+++++
............+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)
[root@RS1 ssl]# openssl req -new -key httpd.key -out httpd.csr
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:cn
State or Province Name (full name) []:hb
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:wh
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:rt
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:alg
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:www.yy.com
Email Address []:1@2.com
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:
An optional company name []:
[root@RS1 ssl]# openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in httpd.csr -signkey httpd.key -out httpd.crt
Signature ok
subject=C = cn, ST = hb, L = wh, O = rt, OU = alg, CN = www.yy.com, emailAddress = 1@2.com
Getting Private key
[root@RS1 ssl]# ls
httpd.crt httpd.csr httpd.key
[root@RS1 ssl]# vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf
SSLCertificateFile /etc/httpd/ssl/httpd.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/httpd/ssl/httpd.key
[root@RS1 ssl]# echo "RS1" > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@RS1 ssl]# systemctl enable --now httpd
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service.
//检查https是否可用
[root@RS1 ssl]# curl -k https://192.168.174.177
RS1
[root@RS1 ssl]# scp /etc/httpd/ssl/* root@192.168.174.178:/root/
root@192.168.174.178's password:
httpd.crt 100% 1237 2.2MB/s 00:00
httpd.csr 100% 1013 2.2MB/s 00:00
httpd.key 100% 1675 351.6KB/s 00:00
RS2配置:
//关闭selinux和防火墙
[root@RS2 ~]# sed -ri 's/^(SELINUX=).*/\1disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
[root@RS2 ~]# setenforce 0
[root@RS2 ~]# systemctl disable --now firewalld.service
//RS2上配置内核参数
[root@RS2 ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2
[root@RS2 ~]# sysctl -p
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_announce = 2
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2
//配置VIP
[root@RS2 ~]# dnf -y install net-tools
[root@RS2 ~]# ifconfig lo 192.168.174.202/32 broadcast 192.168.174.202 netmask 255.255.255.255 up
//永久生效lo网卡配置
[root@RS2 ~]# echo "ifconfig lo 192.168.174.202/32 broadcast 192.168.174.202 netmask 255.255.255.255 up" >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local
[root@RS2 ~]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
//添加路由
[root@RS2 ~]# route add -host 192.168.174.202/32 dev lo
//安装httpd服务,然后配置好https网站首页
[root@RS2 ~]# dnf -y install httpd mod_ssl
[root@RS2 ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-base.conf
LoadModule ssl_module modules/mod_ssl.so
[root@RS2 ~]# mkdir /etc/httpd/ssl
[root@RS2 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg httpd.csr ks-post.log ks-pre.log
httpd.crt httpd.key ks-post-nochroot.log original-ks.cfg
[root@RS2 ~]# mv httpd.* /etc/httpd/ssl/
[root@RS2 ~]# ls /etc/httpd/ssl/
httpd.crt httpd.csr httpd.key
[root@RS2 ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf
SSLCertificateFile /etc/httpd/ssl/httpd.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/httpd/ssl/httpd.key
[root@RS2 ~]# echo "RS2" > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@RS2 ~]# systemctl enable --now httpd
//检查https是否可用
[root@RS2 ~]# curl -k https://192.168.174.178
RS2
DR配置:
//关闭selinux和防火墙
[root@DR ~]# systemctl disable --now firewalld.service
[root@DR ~]# setenforce 0
[root@DR ~]# sed -ri 's/^(SELINUX=).*/\1disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
//配置lo网卡ip
[root@DR ~]# dnf -y install net-tools
[root@DR ~]# ifconfig lo 192.168.174.202/32 broadcast 192.168.174.202 netmas
k 255.255.255.255 up
[root@DR ~]# ip a |grep lo
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 192.168.174.202/0 brd 192.168.174.202 scope global lo
//永久生效lo网卡配置
[root@DR ~]# echo "ifconfig lo 192.168.174.202/32 broadcast 192.168.174.202 netmask 255.255.255.255 up" >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local
[root@DR ~]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
//配置好好两台web服务器后,最后再安装ipvsadm并添加规则
[root@DR ~]# dnf -y install ipvsadm
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -A -t 192.168.174.202:443 -s rr
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.174.202:443 -r 192.168.174.177:443 -g
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.174.202:443 -r 192.168.174.178:443 -g
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -Ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.168.174.202:443 rr
-> 192.168.174.177:443 Route 1 0 0
-> 192.168.174.178:443 Route 1 0 0
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -Sn > /etc/sysconfig/ipvsadm
[root@DR ~]# systemctl restart ipvsadm.service
[root@DR ~]# systemctl enable ipvsadm.service
客户端进行测试,因为选择的是轮询(rr)
[root@client ~]# curl -k https://192.168.174.202
RS2
[root@client ~]# curl -k https://192.168.174.202
RS1
[root@client ~]# curl -k https://192.168.174.202
RS2
[root@client ~]# curl -k https://192.168.174.202
RS1
RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.168.174.202:443 rr
-> 192.168.174.177:443 Route 1 0 0
-> 192.168.174.178:443 Route 1 0 0
[root@DR ~]# ipvsadm -Sn > /etc/sysconfig/ipvsadm
[root@DR ~]# systemctl restart ipvsadm.service
[root@DR ~]# systemctl enable ipvsadm.service
客户端进行测试,因为选择的是轮询(rr)
[root@client ~]# curl -k https://192.168.174.202
RS2
[root@client ~]# curl -k https://192.168.174.202
RS1
[root@client ~]# curl -k https://192.168.174.202
RS2
[root@client ~]# curl -k https://192.168.174.202
RS1