环境:
Ubuntu:20.04
nginx:1.18
tomcat: 10.0.23.0
虚拟机:
tomcat? ?192.168.111.145:8080
nginx:? ? ?192.168.111.144:80
反向代理:
目的:
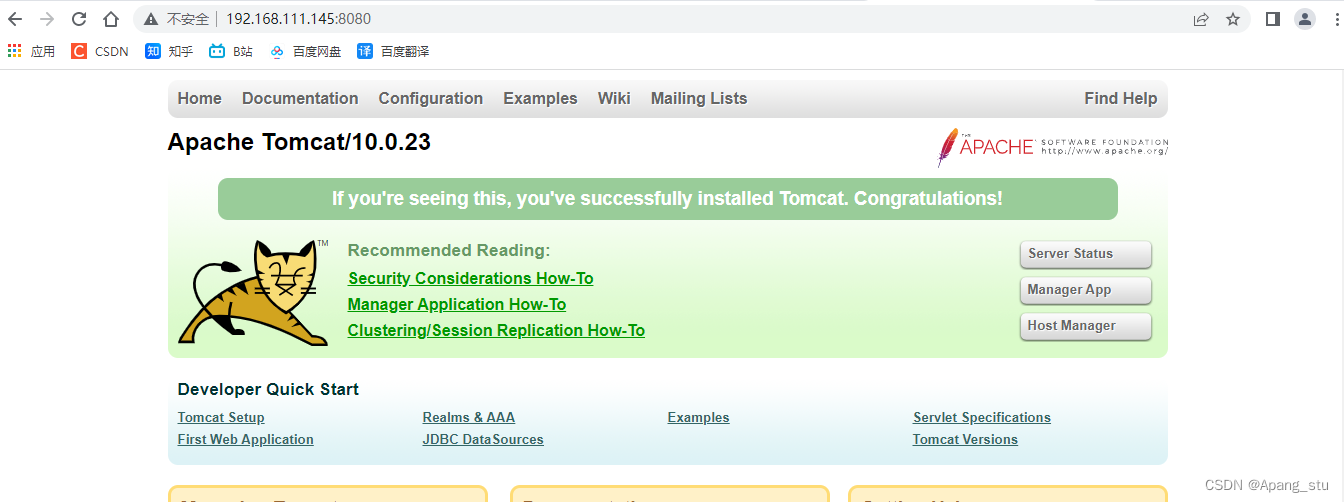
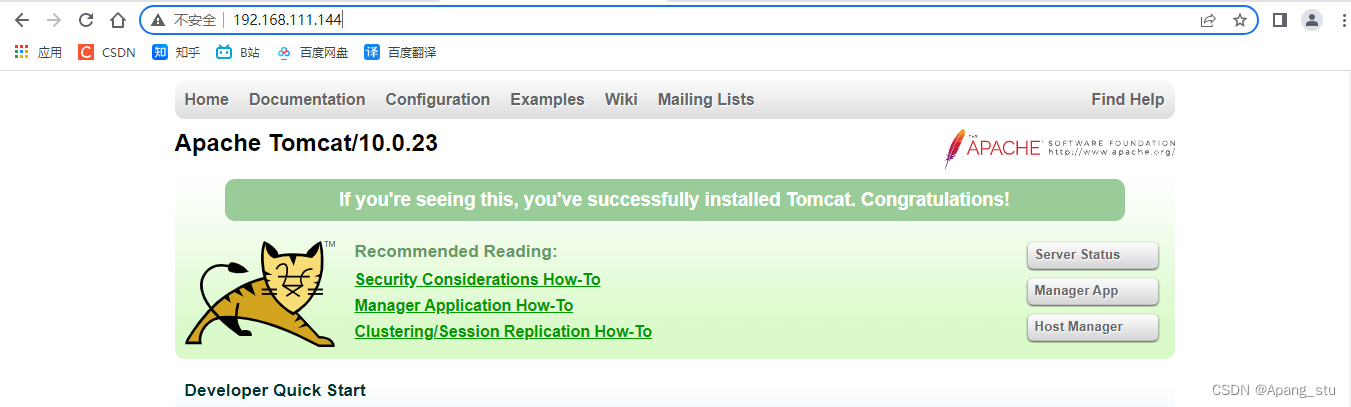
访问http://192.168.111.144跳转到tomcat
向192.168.111.145虚拟机中安装tomcat,去tomcat官网拉一个tomcat的包,然后解压,进入/bin目录,执行命令./startup.sh?就开启了tomcat
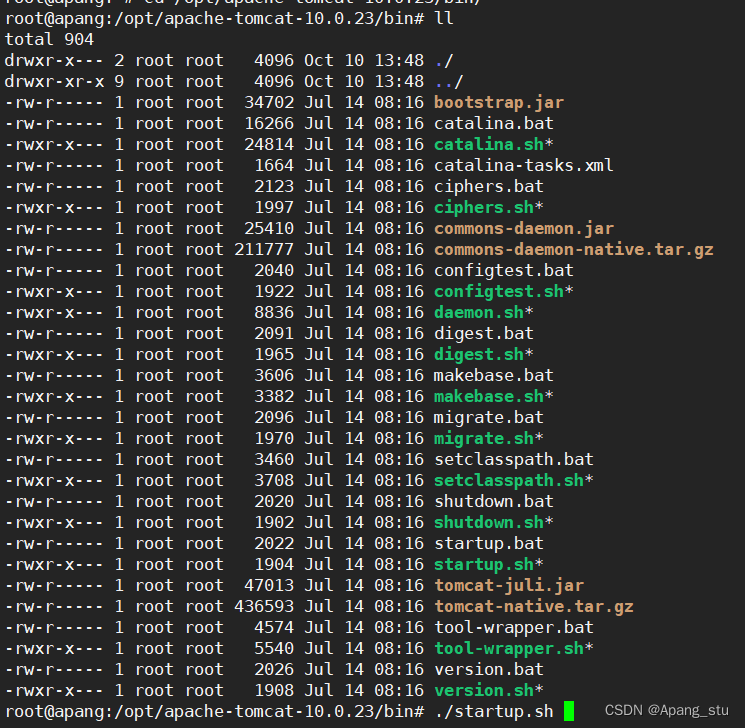
这样就ok了
 向192.168.111.144虚拟机中安装nginx,因为我的是ubuntu20.04系统,我直接下载就行
向192.168.111.144虚拟机中安装nginx,因为我的是ubuntu20.04系统,我直接下载就行
apt -y install nginx然后进入/etc/nginx/sites-available文件夹中配置default文件,配置如下。
root@apang:/etc/nginx/sites-available# cat default
##
# You should look at the following URL's in order to grasp a solid understanding
# of Nginx configuration files in order to fully unleash the power of Nginx.
# https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/
# https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/tutorials/config_pitfalls/
# https://wiki.debian.org/Nginx/DirectoryStructure
#
# In most cases, administrators will remove this file from sites-enabled/ and
# leave it as reference inside of sites-available where it will continue to be
# updated by the nginx packaging team.
#
# This file will automatically load configuration files provided by other
# applications, such as Drupal or Wordpress. These applications will be made
# available underneath a path with that package name, such as /drupal8.
#
# Please see /usr/share/doc/nginx-doc/examples/ for more detailed examples.
##
# Default server configuration
#
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
# SSL configuration
#
# listen 443 ssl default_server;
# listen [::]:443 ssl default_server;
#
# Note: You should disable gzip for SSL traffic.
# See: https://bugs.debian.org/773332
#
# Read up on ssl_ciphers to ensure a secure configuration.
# See: https://bugs.debian.org/765782
#
# Self signed certs generated by the ssl-cert package
# Don't use them in a production server!
#
# include snippets/snakeoil.conf;
#root /var/www/html;
# Add index.php to the list if you are using PHP
#index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html;
#server_name _;
location / {
# First attempt to serve request as file, then
# as directory, then fall back to displaying a 404.
#try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
proxy_pass http://192.168.111.145:8080;
}
#location /tomcat {
# proxy_pass http://192.168.111.145:8080;
# index index.html index.htm;
#}
# pass PHP scripts to FastCGI server
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
#
# # With php-fpm (or other unix sockets):
# fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
# # With php-cgi (or other tcp sockets):
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# Virtual Host configuration for example.com
#
# You can move that to a different file under sites-available/ and symlink that
# to sites-enabled/ to enable it.
#
#server {
# listen 80;
# listen [::]:80;
#
# server_name example.com;
#
# root /var/www/example.com;
# index index.html;
#
# location / {
# try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
# }
#}
?然后我们用我们的真机去访问192.168.111.144, 发现已经转发了
?顺便说一下正向代理和反向代理。
正向代理就像我们经常用的VPN技术一样。我们可以更换我们的代理点,从而访问到我们想要访问的资源。
反向代理就是我们访问一台服务器,而这台服务器只不过是一个代理点,会转发到我们真正想要访问的资源,如同上面操作一样。
简单来说,正向代理就是需要我们去更换代理点的,而反向代理你是根本就没察觉的。
负载均衡:
希望在操作之前将默认的要修改的配置文件都备份一下,养成好习惯。
环境:
| ubuntu04 | 192.168.111.144 | nginx |
| ubuntu05 | 192.168.111.145 | tomcat |
| rooky06 | 192.168.111.111 | tomcat |
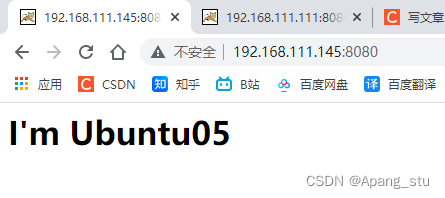
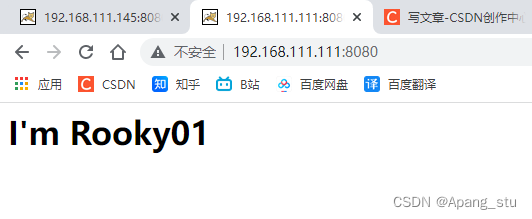
修改一下tomcat默认的页面进行辨别。
默认页面在这里
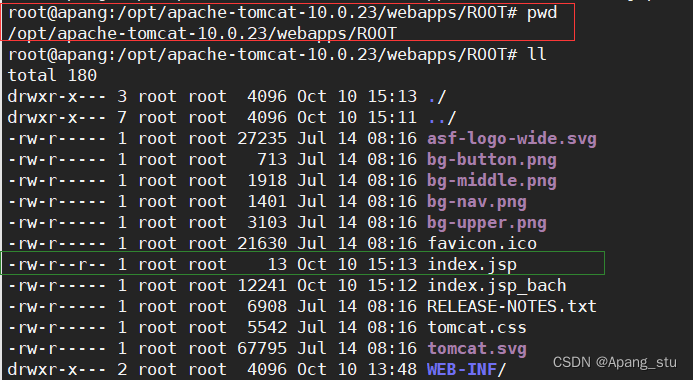
?修改为这样:
?配置ubuntu04上面的nginx的配置文件,我的是ubuntu系统,其他系统可能不一样,但是应该大差不差。
在/etc/nginx/conf.d下创建一个以 .conf 为后缀的文件。我这里创建的是tomcat.conf?
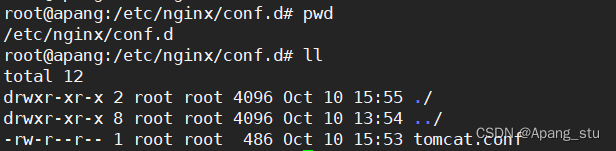
?配置如下:
upstream tomcat {
#负载均衡方法,可以自己选,默认为轮询方式
#服务器的访问方式,
server 192.168.111.145:8080 weight=1;
server 192.168.111.111:8080 weight=1;
}
server {
#负载均衡监视的端口
listen 81 default_server;
listen [::]:81 default_server;
#负载均衡服务器的名称,没有的话填_
server_name _;
location / {
#代理转发,注意这个tomcat要与上面的upstream后面的字符一样
proxy_pass http://tomcat;
}
}
后面的数值为权重,我是两台服务器,如果那个性能好的话,我们可以将权重相对来说调的大些。
重启nginx。
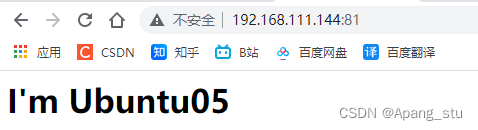
访问http://192.168.111.144:81
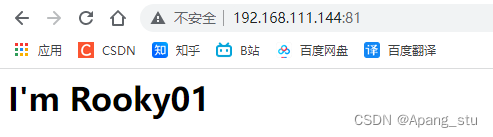
刷新一下,变为了ubuntu05,这就是轮询,轮着来。
?完事!!!
又是充足的一天。hhhh
?