网络扫描
通过一些工具对网络进行扫描,比如TCP端口扫描、ping等操作,以获取一些所需要的信息。目前知道此用处有这些:
- OS探测
- TCP程序探测
通过TCP端口可匹配到某些后台程序。
masscan TCP端口扫描
MASSCAN是TCP端口扫描程序,它异步传输SYN数据包,并产生类似于nmap的结果,nmap是最著名的端口扫描程序。在内部,它更像scanrand、unicornscan和ZMap,使用异步传输。它是一个灵活的实用程序,允许任意地址和端口范围。
异步SYN数据包
SYN数据包是TCP连接的第一个包,三次连接的第一个包,通过大量发送这样的数据包,但不做后面的数据包发送,就会构成一个半连接,消耗目标机器的进程资源,而使得他瘫痪。
异步进程的话,不进行阻塞,而发送发送大量这样的包,就可以快速的对一段IP主机进行扫描。
指令
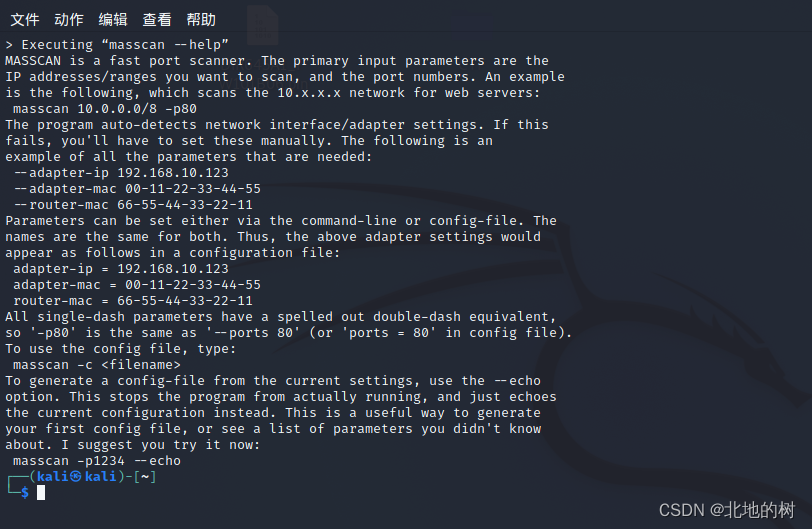
root@kali:~# masscan --help
MASSCAN is a fast port scanner. The primary input parameters are the
IP addresses/ranges you want to scan, and the port numbers. An example
is the following, which scans the 10.x.x.x network for web servers:
masscan 10.0.0.0/8 -p80
The program auto-detects network interface/adapter settings. If this
fails, you'll have to set these manually. The following is an
example of all the parameters that are needed:
--adapter-ip 192.168.10.123
--adapter-mac 00-11-22-33-44-55
--router-mac 66-55-44-33-22-11
Parameters can be set either via the command-line or config-file. The
names are the same for both. Thus, the above adapter settings would
appear as follows in a configuration file:
adapter-ip = 192.168.10.123
adapter-mac = 00-11-22-33-44-55
router-mac = 66-55-44-33-22-11
All single-dash parameters have a spelled out double-dash equivalent,
so '-p80' is the same as '--ports 80' (or 'ports = 80' in config file).
To use the config file, type:
masscan -c <filename>
To generate a config-file from the current settings, use the --echo
option. This stops the program from actually running, and just echoes
the current configuration instead. This is a useful way to generate
your first config file, or see a list of parameters you didn't know
about. I suggest you try it now:
masscan -p1234 --echo
nmap 多种扫描方式:端口、ping等。
nmap,俺认为其是最强大的一个扫描工具,扫描TCP端口那可真是一绝
Nmap是一个用于网络探索或安全审计的实用程序。它支持ping扫描(确定哪些主机在运行)、多种端口扫描技术、版本检测(确定服务协议和应用程序版本,在端口后侦听)和TCP/IP指纹识别(远程主机操作系统或设备标识)。Nmap还提供灵活的目标和端口规范、诱饵/隐形扫描、sunRPC扫描等。大多数Unix和Windows平台都支持GUI和命令行模式。还支持几种流行的手持设备,包括Sharp Zaurus和iPAQ。
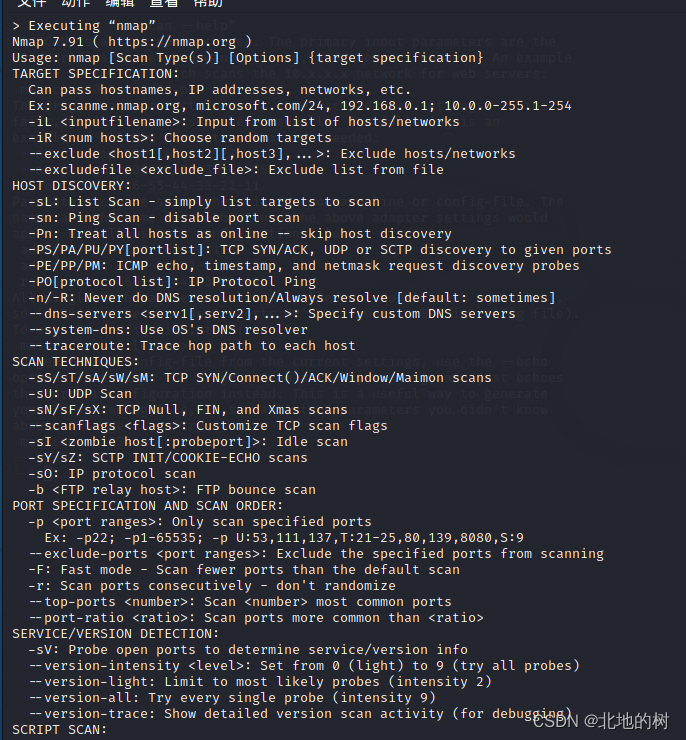
nmap和一些其他工具的一些指令
ncat
ncat是NMAP项目对Netcat的重新实现,提供了原始实现中的大部分功能,以及一些新功能,如IPv6和SSL支持。端口扫描支持已删除。
root@kali:~# ncat -h
Ncat 7.92 ( https://nmap.org/ncat )
Usage: ncat [options] [hostname] [port]
Options taking a time assume seconds. Append 'ms' for milliseconds,
's' for seconds, 'm' for minutes, or 'h' for hours (e.g. 500ms).
-4 Use IPv4 only
-6 Use IPv6 only
-U, --unixsock Use Unix domain sockets only
--vsock Use vsock sockets only
-C, --crlf Use CRLF for EOL sequence
-c, --sh-exec <command> Executes the given command via /bin/sh
-e, --exec <command> Executes the given command
--lua-exec <filename> Executes the given Lua script
-g hop1[,hop2,...] Loose source routing hop points (8 max)
-G <n> Loose source routing hop pointer (4, 8, 12, ...)
-m, --max-conns <n> Maximum <n> simultaneous connections
-h, --help Display this help screen
-d, --delay <time> Wait between read/writes
-o, --output <filename> Dump session data to a file
-x, --hex-dump <filename> Dump session data as hex to a file
-i, --idle-timeout <time> Idle read/write timeout
-p, --source-port port Specify source port to use
-s, --source addr Specify source address to use (doesn't affect -l)
-l, --listen Bind and listen for incoming connections
-k, --keep-open Accept multiple connections in listen mode
-n, --nodns Do not resolve hostnames via DNS
-t, --telnet Answer Telnet negotiations
-u, --udp Use UDP instead of default TCP
--sctp Use SCTP instead of default TCP
-v, --verbose Set verbosity level (can be used several times)
-w, --wait <time> Connect timeout
-z Zero-I/O mode, report connection status only
--append-output Append rather than clobber specified output files
--send-only Only send data, ignoring received; quit on EOF
--recv-only Only receive data, never send anything
--no-shutdown Continue half-duplex when receiving EOF on stdin
--allow Allow only given hosts to connect to Ncat
--allowfile A file of hosts allowed to connect to Ncat
--deny Deny given hosts from connecting to Ncat
--denyfile A file of hosts denied from connecting to Ncat
--broker Enable Ncat's connection brokering mode
--chat Start a simple Ncat chat server
--proxy <addr[:port]> Specify address of host to proxy through
--proxy-type <type> Specify proxy type ("http", "socks4", "socks5")
--proxy-auth <auth> Authenticate with HTTP or SOCKS proxy server
--proxy-dns <type> Specify where to resolve proxy destination
--ssl Connect or listen with SSL
--ssl-cert Specify SSL certificate file (PEM) for listening
--ssl-key Specify SSL private key (PEM) for listening
--ssl-verify Verify trust and domain name of certificates
--ssl-trustfile PEM file containing trusted SSL certificates
--ssl-ciphers Cipherlist containing SSL ciphers to use
--ssl-servername Request distinct server name (SNI)
--ssl-alpn ALPN protocol list to use
--version Display Ncat's version information and exit
See the ncat(1) manpage for full options, descriptions and usage examples
ndiff
Ndiff是帮助比较Nmap扫描的工具。它获取两个Nmap XML输出文件,并打印它们之间的差异:主机启动和关闭、端口打开或关闭等等。它可以生成人类可读的文本或机器可读的XML格式的输出。
root@kali:~# ndiff -h
Usage: /usr/bin/ndiff [option] FILE1 FILE2
Compare two Nmap XML files and display a list of their differences.
Differences include host state changes, port state changes, and changes to
service and OS detection.
-h, --help display this help
-v, --verbose also show hosts and ports that haven't changed.
--text display output in text format (default)
--xml display output in XML format
nmap
root@kali:~# ndiff -h
Usage: /usr/bin/ndiff [option] FILE1 FILE2
Compare two Nmap XML files and display a list of their differences.
Differences include host state changes, port state changes, and changes to
service and OS detection.
-h, --help display this help
-v, --verbose also show hosts and ports that haven't changed.
--text display output in text format (default)
--xml display output in XML format
nping
网络数据包生成工具/ping实用程序
root@kali:~# nping -h
Nping 0.7.92 ( https://nmap.org/nping )
Usage: nping [Probe mode] [Options] {target specification}
TARGET SPECIFICATION:
Targets may be specified as hostnames, IP addresses, networks, etc.
Ex: scanme.nmap.org, microsoft.com/24, 192.168.0.1; 10.0.*.1-24
PROBE MODES:
--tcp-connect : Unprivileged TCP connect probe mode.
--tcp : TCP probe mode.
--udp : UDP probe mode.
--icmp : ICMP probe mode.
--arp : ARP/RARP probe mode.
--tr, --traceroute : Traceroute mode (can only be used with
TCP/UDP/ICMP modes).
TCP CONNECT MODE:
-p, --dest-port <port spec> : Set destination port(s).
-g, --source-port <portnumber> : Try to use a custom source port.
TCP PROBE MODE:
-g, --source-port <portnumber> : Set source port.
-p, --dest-port <port spec> : Set destination port(s).
--seq <seqnumber> : Set sequence number.
--flags <flag list> : Set TCP flags (ACK,PSH,RST,SYN,FIN...)
--ack <acknumber> : Set ACK number.
--win <size> : Set window size.
--badsum : Use a random invalid checksum.
UDP PROBE MODE:
-g, --source-port <portnumber> : Set source port.
-p, --dest-port <port spec> : Set destination port(s).
--badsum : Use a random invalid checksum.
ICMP PROBE MODE:
--icmp-type <type> : ICMP type.
--icmp-code <code> : ICMP code.
--icmp-id <id> : Set identifier.
--icmp-seq <n> : Set sequence number.
--icmp-redirect-addr <addr> : Set redirect address.
--icmp-param-pointer <pnt> : Set parameter problem pointer.
--icmp-advert-lifetime <time> : Set router advertisement lifetime.
--icmp-advert-entry <IP,pref> : Add router advertisement entry.
--icmp-orig-time <timestamp> : Set originate timestamp.
--icmp-recv-time <timestamp> : Set receive timestamp.
--icmp-trans-time <timestamp> : Set transmit timestamp.
ARP/RARP PROBE MODE:
--arp-type <type> : Type: ARP, ARP-reply, RARP, RARP-reply.
--arp-sender-mac <mac> : Set sender MAC address.
--arp-sender-ip <addr> : Set sender IP address.
--arp-target-mac <mac> : Set target MAC address.
--arp-target-ip <addr> : Set target IP address.
IPv4 OPTIONS:
-S, --source-ip : Set source IP address.
--dest-ip <addr> : Set destination IP address (used as an
alternative to {target specification} ).
--tos <tos> : Set type of service field (8bits).
--id <id> : Set identification field (16 bits).
--df : Set Don't Fragment flag.
--mf : Set More Fragments flag.
--ttl <hops> : Set time to live [0-255].
--badsum-ip : Use a random invalid checksum.
--ip-options <S|R [route]|L [route]|T|U ...> : Set IP options
--ip-options <hex string> : Set IP options
--mtu <size> : Set MTU. Packets get fragmented if MTU is
small enough.
IPv6 OPTIONS:
-6, --IPv6 : Use IP version 6.
--dest-ip : Set destination IP address (used as an
alternative to {target specification}).
--hop-limit : Set hop limit (same as IPv4 TTL).
--traffic-class <class> : : Set traffic class.
--flow <label> : Set flow label.
ETHERNET OPTIONS:
--dest-mac <mac> : Set destination mac address. (Disables
ARP resolution)
--source-mac <mac> : Set source MAC address.
--ether-type <type> : Set EtherType value.
PAYLOAD OPTIONS:
--data <hex string> : Include a custom payload.
--data-string <text> : Include a custom ASCII text.
--data-length <len> : Include len random bytes as payload.
ECHO CLIENT/SERVER:
--echo-client <passphrase> : Run Nping in client mode.
--echo-server <passphrase> : Run Nping in server mode.
--echo-port <port> : Use custom <port> to listen or connect.
--no-crypto : Disable encryption and authentication.
--once : Stop the server after one connection.
--safe-payloads : Erase application data in echoed packets.
TIMING AND PERFORMANCE:
Options which take <time> are in seconds, or append 'ms' (milliseconds),
's' (seconds), 'm' (minutes), or 'h' (hours) to the value (e.g. 30m, 0.25h).
--delay <time> : Adjust delay between probes.
--rate <rate> : Send num packets per second.
MISC:
-h, --help : Display help information.
-V, --version : Display current version number.
-c, --count <n> : Stop after <n> rounds.
-e, --interface <name> : Use supplied network interface.
-H, --hide-sent : Do not display sent packets.
-N, --no-capture : Do not try to capture replies.
--privileged : Assume user is fully privileged.
--unprivileged : Assume user lacks raw socket privileges.
--send-eth : Send packets at the raw Ethernet layer.
--send-ip : Send packets using raw IP sockets.
--bpf-filter <filter spec> : Specify custom BPF filter.
OUTPUT:
-v : Increment verbosity level by one.
-v[level] : Set verbosity level. E.g: -v4
-d : Increment debugging level by one.
-d[level] : Set debugging level. E.g: -d3
-q : Decrease verbosity level by one.
-q[N] : Decrease verbosity level N times
--quiet : Set verbosity and debug level to minimum.
--debug : Set verbosity and debug to the max level.
EXAMPLES:
nping scanme.nmap.org
nping --tcp -p 80 --flags rst --ttl 2 192.168.1.1
nping --icmp --icmp-type time --delay 500ms 192.168.254.254
nping --echo-server "public" -e wlan0 -vvv
nping --echo-client "public" echo.nmap.org --tcp -p1-1024 --flags ack
SEE THE MAN PAGE FOR MANY MORE OPTIONS, DESCRIPTIONS, AND EXAMPLES
nmap-common
Nmap是一个用于网络探索或安全审计的实用程序。它支持ping扫描(确定哪些主机在运行)、多种端口扫描技术、版本检测(确定服务协议和应用程序版本,在端口后侦听)和TCP/IP指纹识别(远程主机操作系统或设备标识)。Nmap还提供灵活的目标和端口规范、诱饵/隐形扫描、sunRPC扫描等。大多数Unix和Windows平台都支持GUI和命令行模式。还支持几种流行的手持设备,包括Sharp Zaurus和iPAQ。
此包包含所有架构共享的nmap文件。
例子
- os探测
以详细模式(-v)扫描,启用操作系统检测、版本检测、脚本扫描和跟踪路由(-A),并针对目标IP(192.168.1.1)进行版本检测(-sV):
root@kali:~# nmap -v -A -sV 192.168.1.1
Starting Nmap 6.45 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2014-05-13 18:40 MDT
NSE: Loaded 118 scripts for scanning.
NSE: Script Pre-scanning.
Initiating ARP Ping Scan at 18:40
Scanning 192.168.1.1 [1 port]
Completed ARP Ping Scan at 18:40, 0.06s elapsed (1 total hosts)
Initiating Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 18:40
Completed Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 18:40, 0.00s elapsed
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan at 18:40
Scanning router.localdomain (192.168.1.1) [1000 ports]
Discovered open port 53/tcp on 192.168.1.1
Discovered open port 22/tcp on 192.168.1.1
Discovered open port 80/tcp on 192.168.1.1
Discovered open port 3001/tcp on 192.168.1.1
- nping使用
使用TCP模式(–TCP)在远程主机(192.168.1.1)上使用TTL为2(–TTL 2)的SYN标志(–flags SYN)探测端口22(-p 22):
root@kali:~# nping --tcp -p 22 --flags syn --ttl 2 192.168.1.1
Starting Nping 0.6.45 ( http://nmap.org/nping ) at 2014-05-13 18:43 MDT
SENT (0.0673s) TCP 192.168.1.15:60125 > 192.168.1.1:22 S ttl=2 id=54240 iplen=40 seq=1720523417 win=1480
RCVD (0.0677s) TCP 192.168.1.1:22 > 192.168.1.15:60125 SA ttl=64 id=0 iplen=44 seq=3377886789 win=5840 <mss 1460>
SENT (1.0678s) TCP 192.168.1.15:60125 > 192.168.1.1:22 S ttl=2 id=54240 iplen=40 seq=1720523417 win=1480
RCVD (1.0682s) TCP 192.168.1.1:22 > 192.168.1.15:60125 SA ttl=64 id=0 iplen=44 seq=3393519366 win=5840 <mss 1460>
SENT (2.0693s) TCP 192.168.1.15:60125 > 192.168.1.1:22 S ttl=2 id=54240 iplen=40 seq=1720523417 win=1480
RCVD (2.0696s) TCP 192.168.1.1:22 > 192.168.1.15:60125 SA ttl=64 id=0 iplen=44 seq=3409166569 win=5840 <mss 1460>
SENT (3.0707s) TCP 192.168.1.15:60125 > 192.168.1.1:22 S ttl=2 id=54240 iplen=40 seq=1720523417 win=1480
RCVD (3.0710s) TCP 192.168.1.1:22 > 192.168.1.15:60125 SA ttl=64 id=0 iplen=44 seq=3424813300 win=5840 <mss 1460>
SENT (4.0721s) TCP 192.168.1.15:60125 > 192.168.1.1:22 S ttl=2 id=54240 iplen=40 seq=1720523417 win=1480
RCVD (4.0724s) TCP 192.168.1.1:22 > 192.168.1.15:60125 SA ttl=64 id=0 iplen=44 seq=3440460772 win=5840 <mss 1460>
Max rtt: 0.337ms | Min rtt: 0.282ms | Avg rtt: 0.296ms
Raw packets sent: 5 (200B) | Rcvd: 5 (230B) | Lost: 0 (0.00%)
Nping done: 1 IP address pinged in 4.13 seconds
- ndiff 使用
将昨天的端口扫描(yesterday.xml)与今天的扫描(today.xml)进行比较
root@kali:~# ndiff yesterday.xml today.xml
-Nmap 6.45 scan initiated Tue May 13 18:46:43 2014 as: nmap -v -F -oX yesterday.xml 192.168.1.1
+Nmap 6.45 scan initiated Tue May 13 18:47:58 2014 as: nmap -v -F -oX today.xml 192.168.1.1
endian.localdomain (192.168.1.1, 00:01:6C:6F:DD:D1):
-Not shown: 96 filtered ports
+Not shown: 97 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
-22/tcp open ssh
- ncat使用
详细(-v),在连接时运行/bin/bash(–exec“/bin/bsh”),只允许1个IP地址(–allow 192.168.1.123),侦听TCP端口4444(-l 4444),并在断开连接时保持侦听器打开(–keep open):
root@kali:~# ncat -v --exec "/bin/bash" --allow 192.168.1.123 -l 4444 --keep-open
Ncat: Version 6.45 ( http://nmap.org/ncat )
Ncat: Listening on :::4444
Ncat: Listening on 0.0.0.0:4444
Ncat: Connection from 192.168.1.123.
Ncat: Connection from 192.168.1.123:39501.
Ncat: Connection from 192.168.1.15.
Ncat: Connection from 192.168.1.15:60393.
Ncat: New connection denied: not allowed
总
网络扫描按说应该属于信息收集中重要的一步吧,这里面的两个工具俺还是比较喜欢用nmap。